42 carbon monoxide molecular orbital diagram
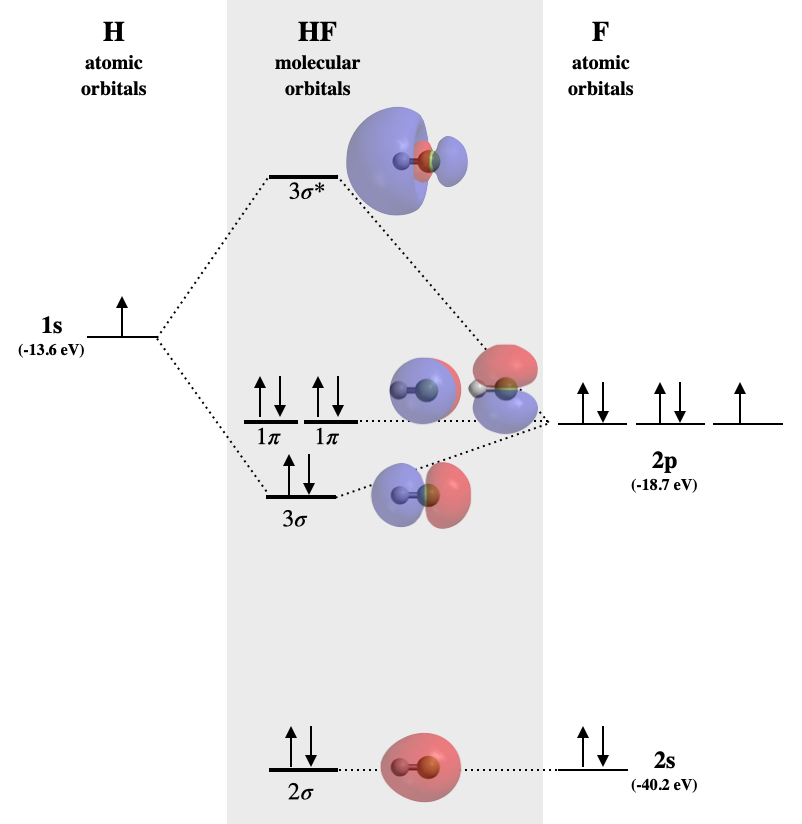
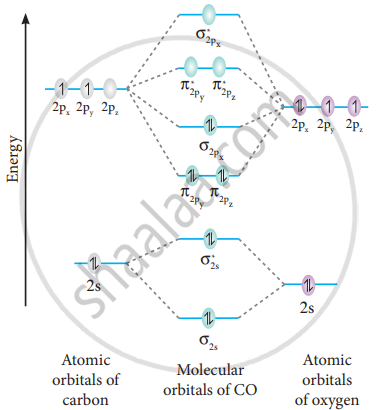
The ground state electronic configuration of CO molecule ... Hint: Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. Carbon monoxide is isoelectronic with nitrogen. Isoelectronic species are those species which have the same number of electrons. Complete step by step answer: Heteronuclear Molecules Energy Level Diagram of CO In H-F the 1s orbital of H is energetically well above the 1s and 2s orbitals of F. –> it interacts only with the 2pz orbital (all remaining electrons are in ...18 pages
Molecular Orbital diagram of Carbon monoxide(CO) #MOT # ... see more informative chemistry lectureshttps://youtu.be/iZhZRWNonVshttps://youtu.be/3bQ2YZVCRqUhttps://youtu.be/PEkZoDgbMdIhttps://youtu.be/FMsg4LDrjkohttps:...
Carbon monoxide molecular orbital diagram
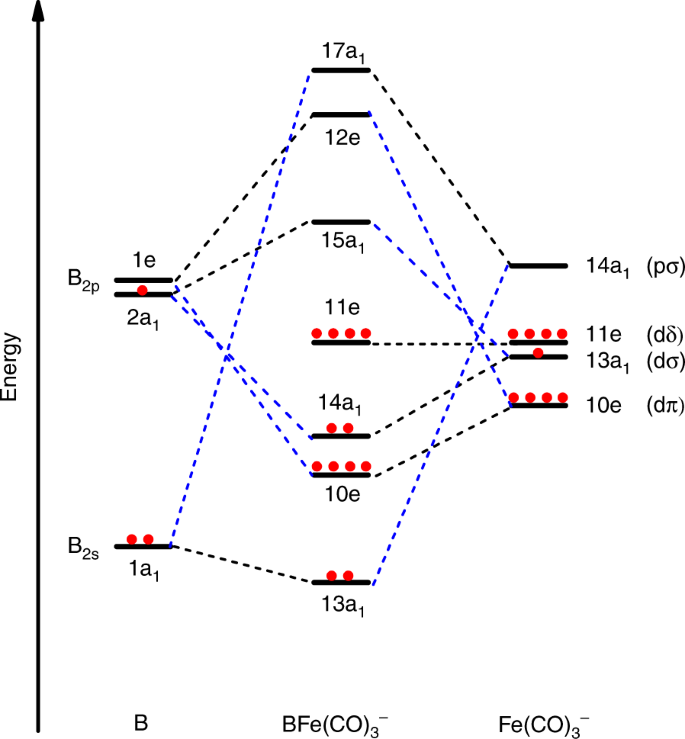
What is the molecular orbital diagram of co2? - idswater.com Carbon dioxide has a formal double bond between C-O. The Lewis structure of carbon monoxide shows that it is relatively electron-rich at carbon. Carbon dioxide is electron-poor at the central carbon and acts as an electrophile. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxideis very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbitals | A selection of CO ... The degenerate orbitals are perpendicular to each other. Order of MOs 3A to 10A (L-to-R). Total energy = -113.3505 a.u. CO bond length = 1.127 Å. CO bond order = 2.2. The LUMO+1 surfaces are different to the 6-311G(d) basis set (and other work). Jmol visualization (via NBO 5.9 molecular orbital file). PDF BONDING IN METALLIC CARBONYLS Carbon monoxide Carbon monoxide: In order to understand the bonding in metal carbonyls, let us first see the MO diagram of carbon monoxide. Figure: Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram of Carbon Monoxide . The order of energy of the molecular orbitals and the accommodation of ten electrons of the
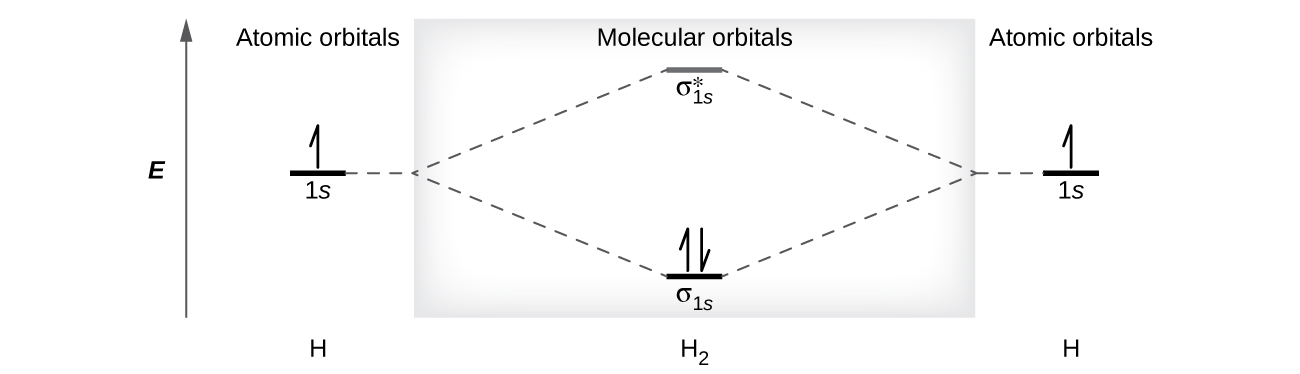
Carbon monoxide molecular orbital diagram. Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Carbon Monoxide - Facts, Bonding, Properties, Uses Molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide The chemical bonding in carbon monoxide is best represented by the molecular orbital diagram given below the picture, On the molecular orbital model of carbon monoxide, the two sp x hybrid orbitals of oxygen and carbon combine to give two molecular orbitals. How To Draw Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co - Drawing ... The mo diagram for co is: Mo diagram for hf the ao energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. Save as pdf page id 83511; The antibonding mo is the 2σ*, which gives 2 antibonding electrons. Molecule has no unpaired electron, hence it is diamagnetic.
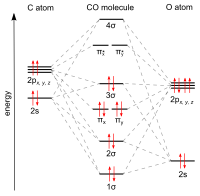
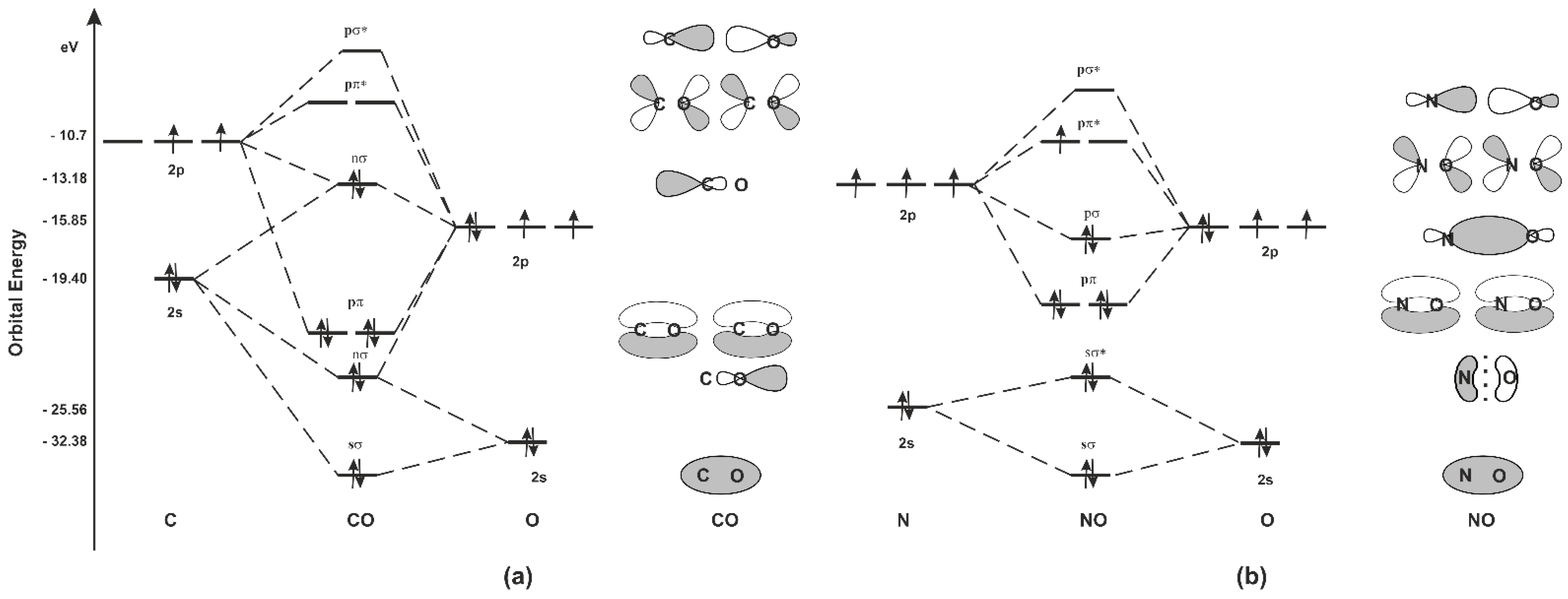
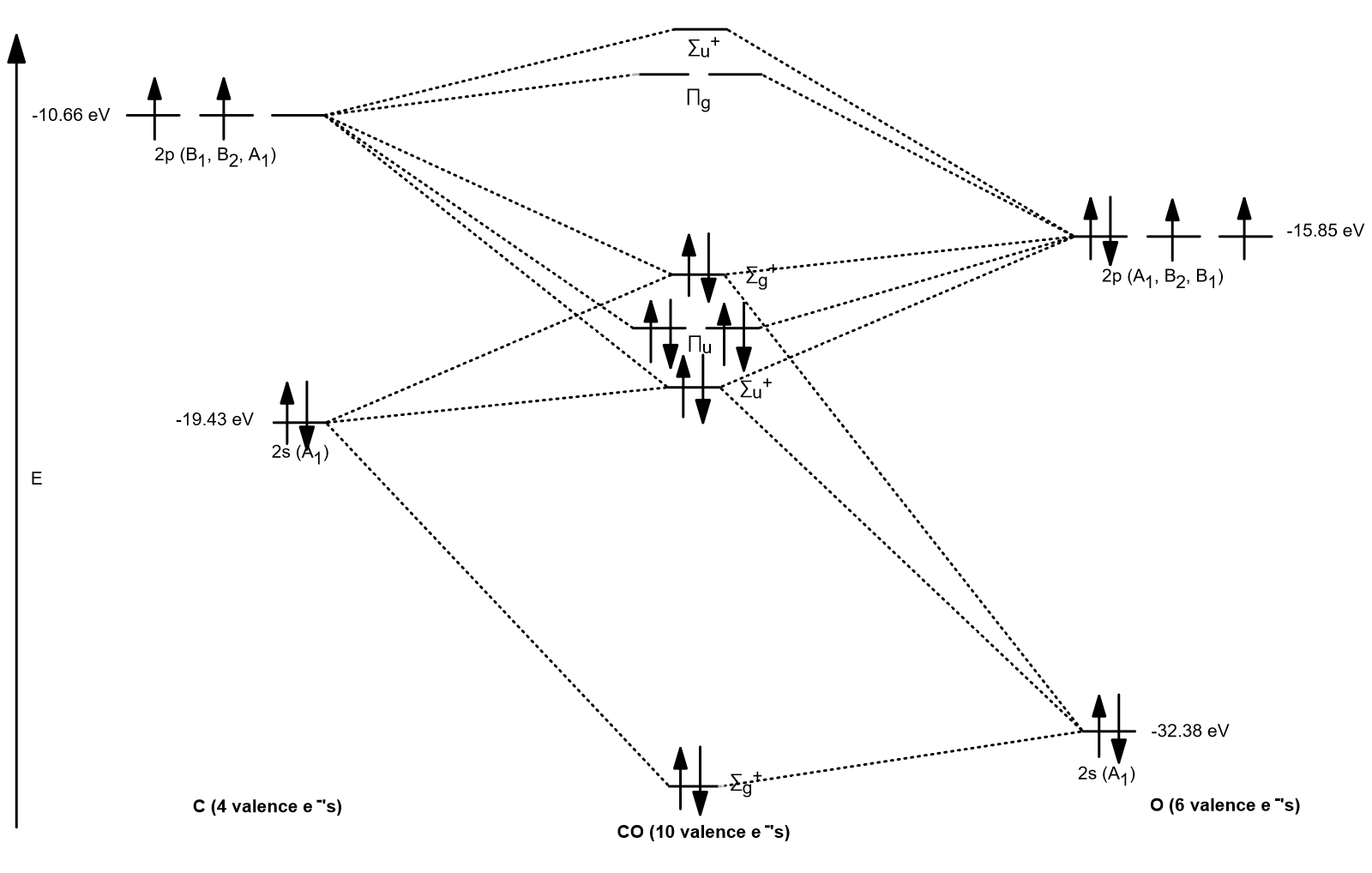
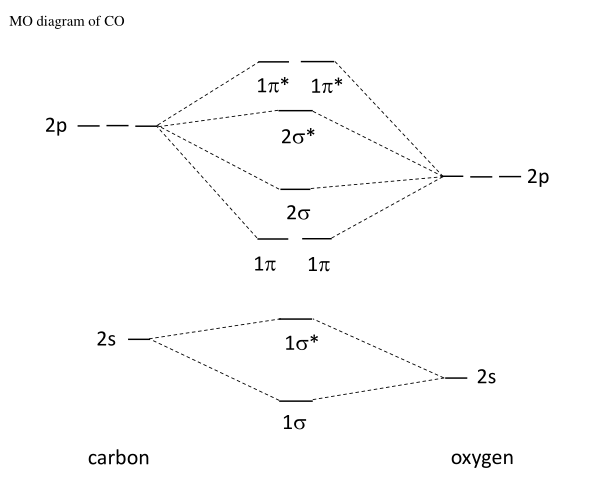
Molecular orbitals of carbon monoxide determined by LCAO Carbon monoxide has 14 electrons. Four electrons occupy the two molecular orbitals that are mainly comprised of the 1s atomic orbitals but were neglected in this calculation. The other 10 electrons occupy 5 molecular with the lowest energies that were calculated here. Molecular Nitrogen and Related Diatomic Molecules The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. On the left you can see all of the orbitals. On the right, the total valence electrons (4 from C, 6 from O) have been added to the orbitals. BackCompassTablesIndexIntroductionNext Professor Patricia Shapley, University of Illinois, 2012 What is molecular orbital diagram of CO? - handlebar ... The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. Which overlap is strongest? During the axial overlap of p-p orbitals, the electron density increases around the axis, so the bond formed is the strongest. Therefore, the strongest bond formed is when p-p orbital overlap occurs. Molecular Orbital Diagram || Carbonyl M.o.t || Back ... in this video i have discussed about the molecular orbital diagram of co which is the most important ligand in organometalics and coordination chemistry.con...
STRUCTURE OF CARBON MONOXIDE - Ohio State University The low dipole moment and the formation of complexes of CO are explained as due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the remote side of the carbon atom. The CO molecule is shown to have a triple-bond structure (two Π and one σ bonding orbitals). Description: ∗ Formerly of the Theoretical Chemistry Department, Cambridge University ... Bonding in Metal Carbonyls: Explaination, Type, Property ... Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. To understand the bonding in metal carbonyls, we need to first learn the Molecular Orbital \(\left( {{\rm{MO}}} \right)\) diagram of carbon monoxide. There are ten electrons in the carbon monoxide ligand. Carbon(C) electron configuration and orbital diagram Carbon(C) is the 6th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'C'. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of carbon and the orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of carbon, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science Molecular Orbital Diagram. As we've established (link to last lesson), bonding and antibonding interactions are the key to molecular orbital theory. In fact, the idea of molecular orbitals, the distribution of electrons across a molecule, arises from how electrons distribute themselves energetically. ... This is the case in carbon monoxide ...
Solved Draw the molecular orbital diagram for carbon ... Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide. Label all molecular orbitals. Take into account that the high energy 2s orbital for carbon will mix with the low energy 2px orbital for oxygen. This problem has been solved!
Solved Below is shown the molecular orbital diagram for ... Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Below is shown the molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide (CO). Click on the pair of electrons that is most consistent with a lone pair of electrons localized on the carbon atom.
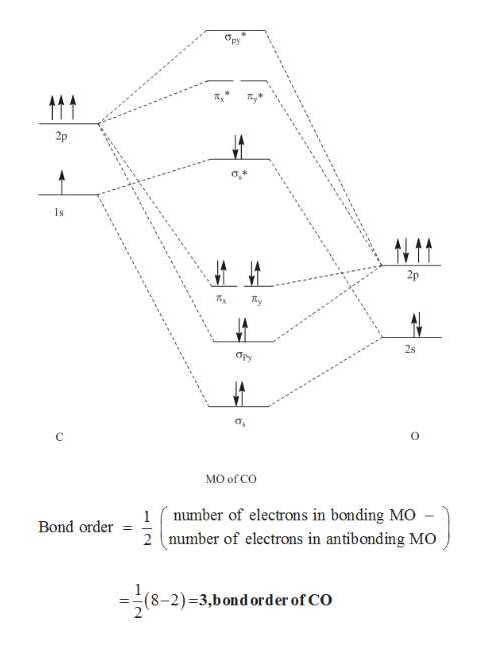
bond - How can the dipole moment of carbon monoxide be ... The MO diagram shows that the C O molecule forms three filled MO's with σ symmetry and two MO's with π symmetry. Of the five filled MO's (10 electrons) formed for C O, only four of them can be half-filled from carbon electrons (4 valence electrons). So one of the filled MO's must have two electrons that originally came from the oxygen atom. Share
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above.
Carbon Oxides - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Carbon dioxide is electron-poor at the central carbon and acts as an electrophile. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxideis very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen.
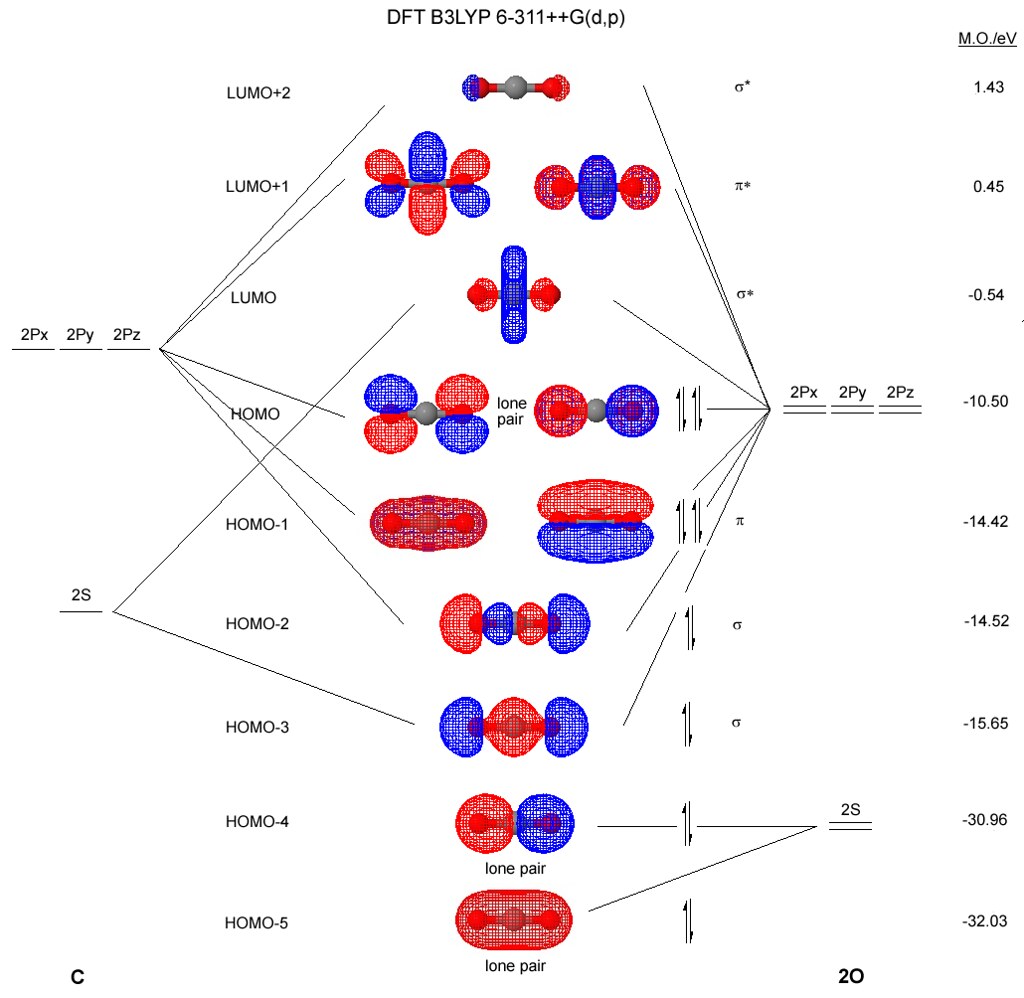
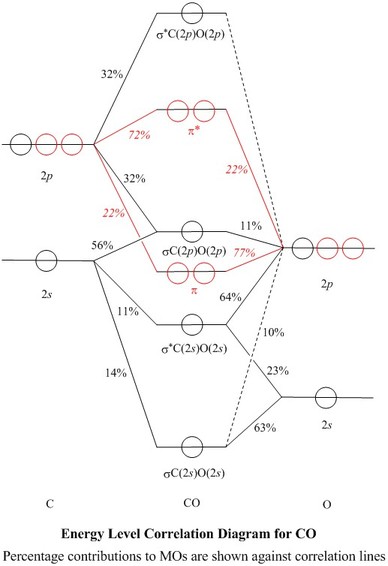
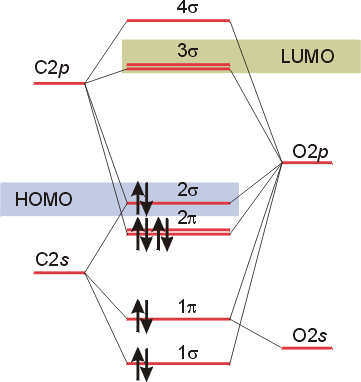
Molecular Orbitals for Carbon Monoxide - Newcastle University The HOMO of carbon monoxide is σC(2p)O(2p) because the antibonding contribution from sp mixing pushes it above the π-bonding orbitals in energy Its main components are C 2 s and C 2 p z , so it is strongly polarised towards carbon, and will bond to σ -acceptor species through carbon, providing that the CO ligand is also acting as a π ...
Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide - ChemTube3D Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
Molecular Orbital Theory | Chemistry [Master] Carbon monoxide, CO, has a total of 10 valence electrons. To satisfy the octet rule for the carbon, the two atoms form a triple bond with six shared electrons in three bonding molecular orbitals. Since four of the shared electrons come from the oxygen atom and only two from carbon, one of the bonding orbitals is occupied by two electrons from ...
What is the molecular orbital energy diagram of CO? - Quora The geometry of this molecule about the C atom is trigonal planar, with 120 degrees separating each of the 3 sigma bonds. The carbon atom therefore hybridises ...
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals.
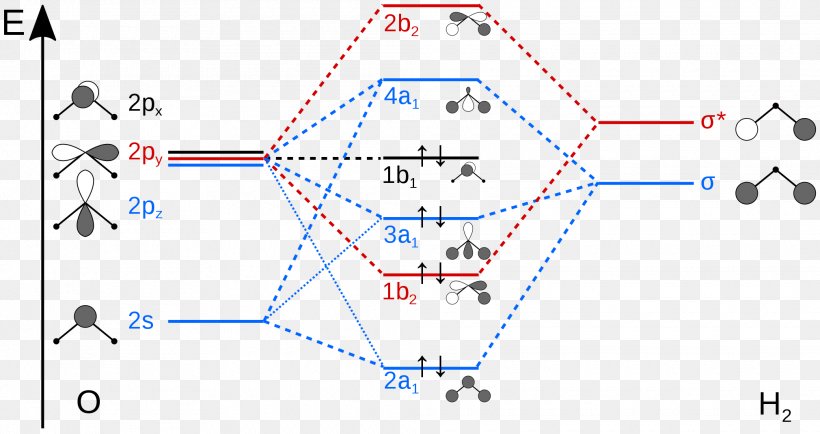
Organic Chemistry at Penn State: Carbon Monoxide Carbon monoxide is a simple diatomic molecule that illustrates how two different atoms interact to form molecular orbitals (MO). The oxygen atom and the carbon atom have an sand three porbitals each. For clarity, we draw the atomic orbitals of oxygen in red, and those on carbon in black
How to rationalise with MO theory that CO is a two-electron ... 16 May 2016 — In the above MO diagram, the 5σ is the HOMO. But it is closest in energy to oxygen's 2p orbitals, so why is it centered on carbon? molecular- ...
PDF BONDING IN METALLIC CARBONYLS Carbon monoxide Carbon monoxide: In order to understand the bonding in metal carbonyls, let us first see the MO diagram of carbon monoxide. Figure: Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram of Carbon Monoxide . The order of energy of the molecular orbitals and the accommodation of ten electrons of the
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbitals | A selection of CO ... The degenerate orbitals are perpendicular to each other. Order of MOs 3A to 10A (L-to-R). Total energy = -113.3505 a.u. CO bond length = 1.127 Å. CO bond order = 2.2. The LUMO+1 surfaces are different to the 6-311G(d) basis set (and other work). Jmol visualization (via NBO 5.9 molecular orbital file).
What is the molecular orbital diagram of co2? - idswater.com Carbon dioxide has a formal double bond between C-O. The Lewis structure of carbon monoxide shows that it is relatively electron-rich at carbon. Carbon dioxide is electron-poor at the central carbon and acts as an electrophile. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxideis very similar to that of molecular nitrogen.
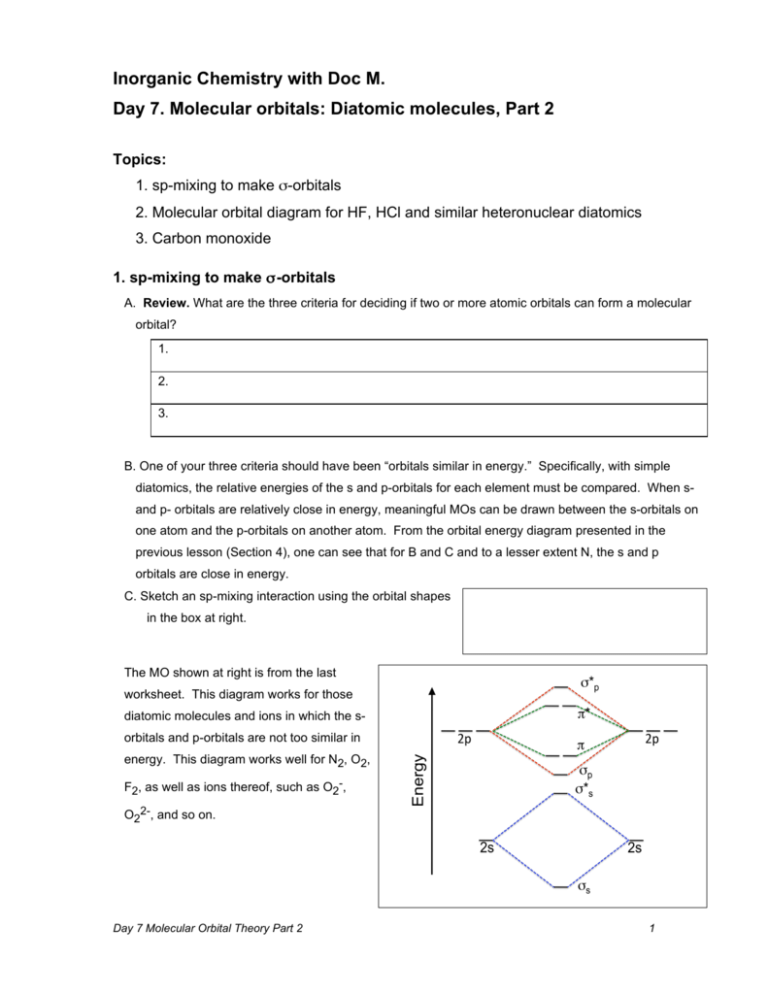
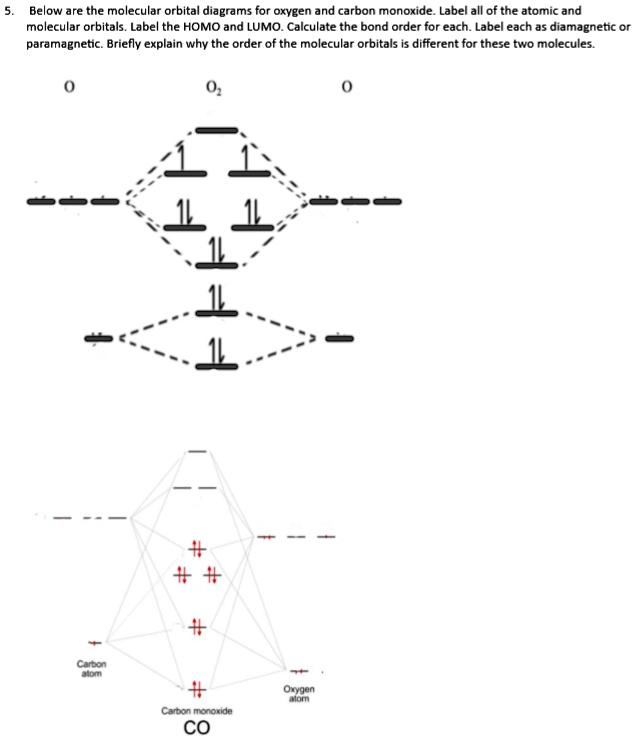

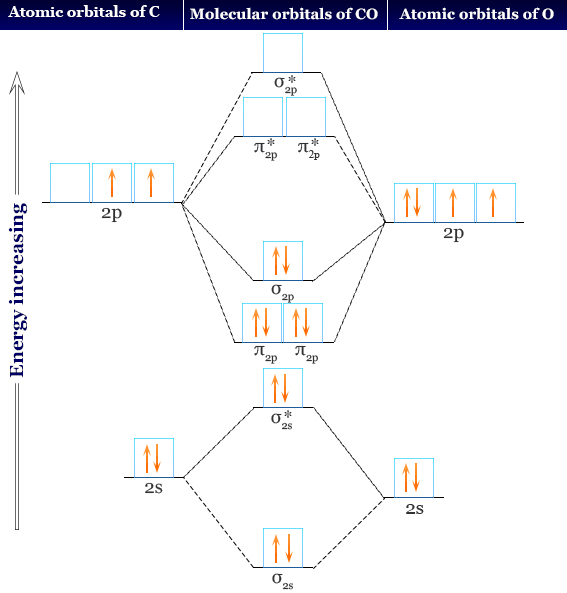
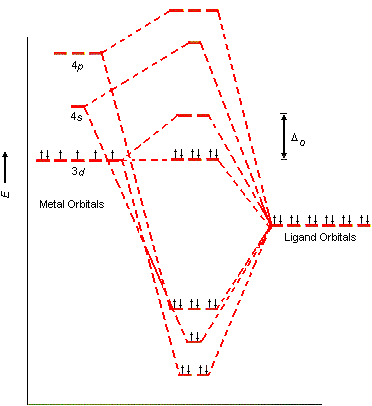





![Molecular orbitals diagrams of [Co(NH3)6]3+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularorbitalsdiagramsofconh3631-211121141527/95/molecular-orbitals-diagrams-of-conh363-2-638.jpg?cb=1637504464)




Comments
Post a Comment