39 dicotyledonous leaf diagram
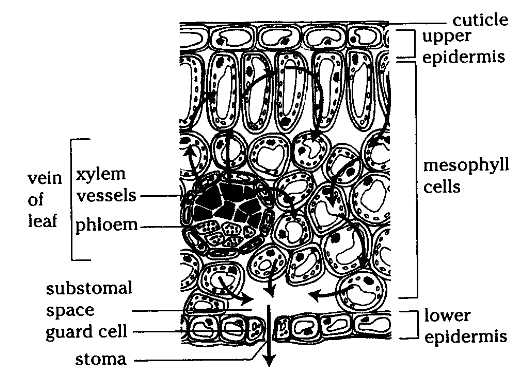
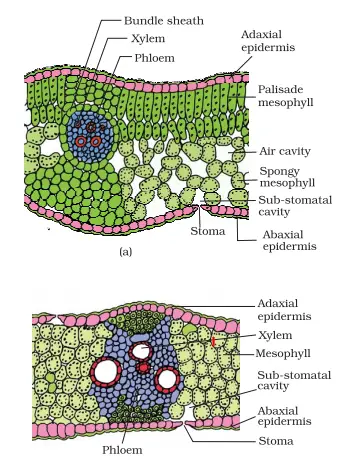
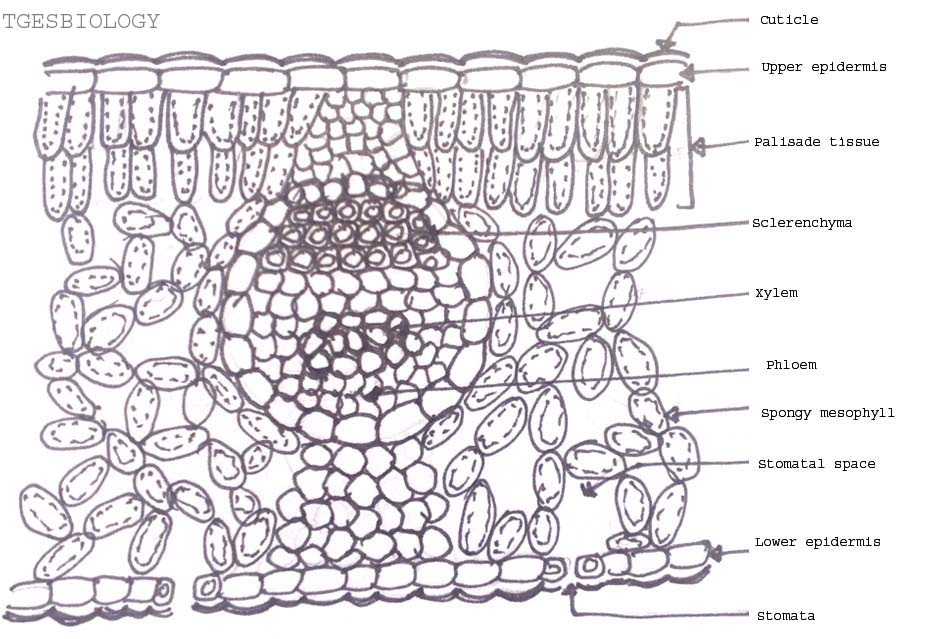
Plants | Free Full-Text | Comprehensive Genomic Survey ... 21/02/2022 · Schematic diagram of A. thaliana and soybean GIF gene organization and conserved motifs analysis. On the left side, the neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree is shown, followed by the exons–introns, which are shown as black boxes and grey lines, respectively. On the right side of the picture, the neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree is shown, followed by … Describe the internal structure of dicot leaf with the ... (i) Epidermis: A dicotyledonous leaf is generally dorsiventral. It has upper and lower epidermis. The epidermis is usually made up of a single layer of cells that are closely packed. The cuticle on the upper epidermis is thicker than that of lower epidermis. The minute openings found on the epidermis are called stomata.
Cycas: Distribution, Morphology and Reproduction| Cycadales Similar to root, the stem of Cycas also resembles internally with a dicotyledonous stem. It shows the following anatomical features: Epidermis is the outermost layer consisting of compactly arranged thick- walled cells. Presence of several persistent leaf bases makes the epidermis a discontinuous and ruptured layer. Cortex is large and consists of thin- walled, parenchymatous …

Dicotyledonous leaf diagram
dicot leaf.pdf - D SBA#: Title: Dicot leaf Aim: To draw ... Diagram: SBA# Dicot leaf Skilled Assessed: D (Drawing) Criteria Total Marks Marks Obtained No evidence of shading 1 Drawing is a good representation of specimen 1 Parts of drawings are proportional to parts of specimen (-1 for deviation) 1 Drawing is large enough to observe necessary details 1 Absence of double lines in drawing 1 Drawing of ... Plant Anatomy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The diagram indicates the essential parts of the mangrove tree from the standpoint of water relations, particularly the membranes of the endodermis and of the leaf cells. It is important to note that if leaf membranes should suddenly cease to be differentially permeable, salt and subsequently water would move from leaf cells into the pathway due to the high tension of … Preparation And Study Of T.S Of Dicot And Monocot Roots ... Diagram. T.S Of Dicot Stem. T.S Of Monocot Stem. Procedure Taking Sections. Hold the dissected plant material between your index finger and thumb, while keeping the edge of the razor perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the plant. Slice it into thin sections. Using the edge of the blade, shift these sections into a watch glass with the help of a brush. The watch glass must …
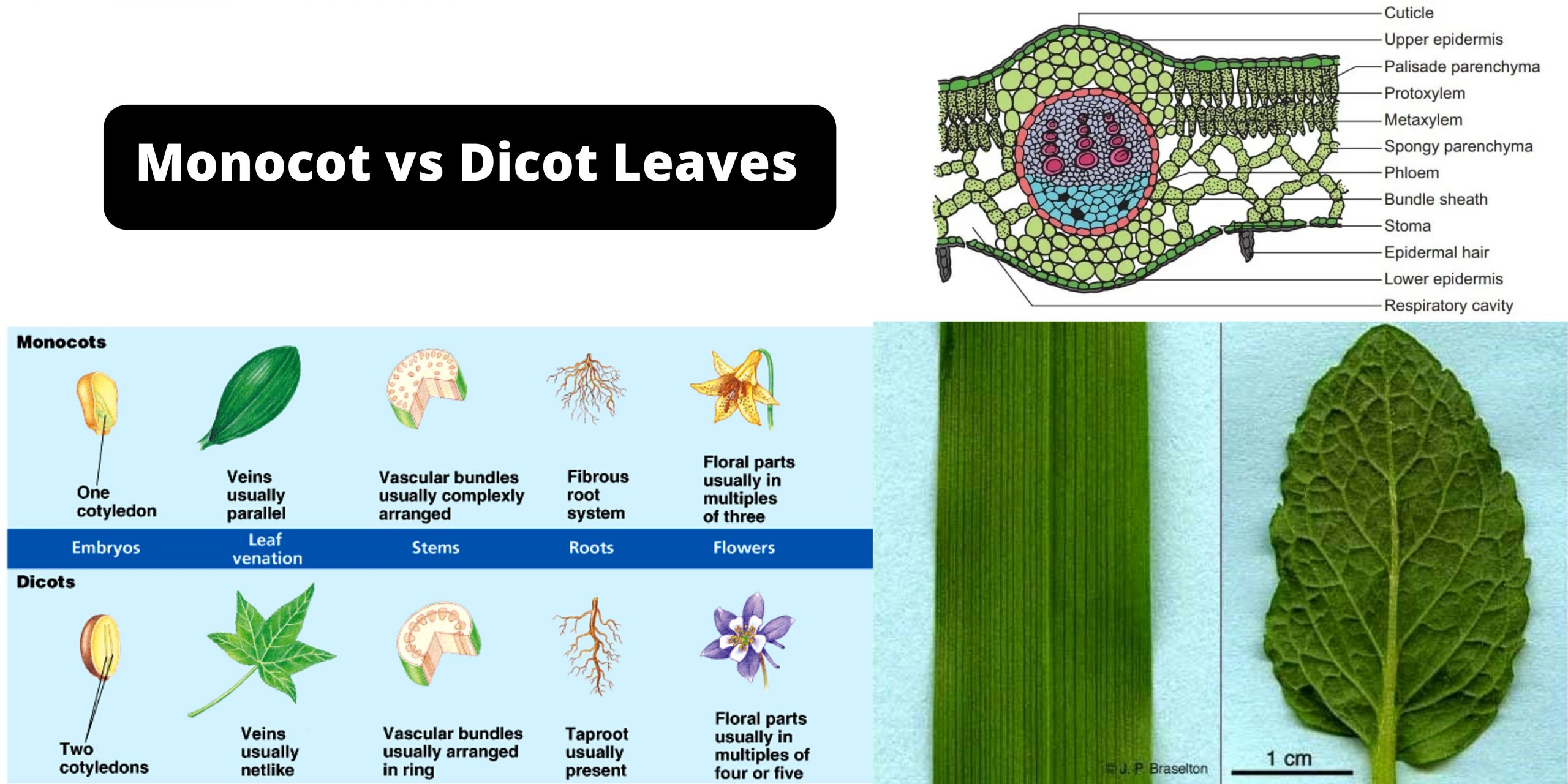
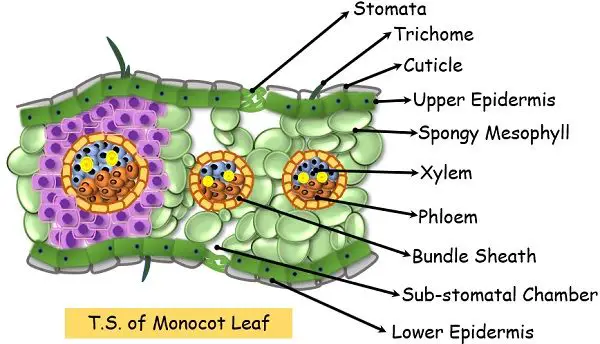
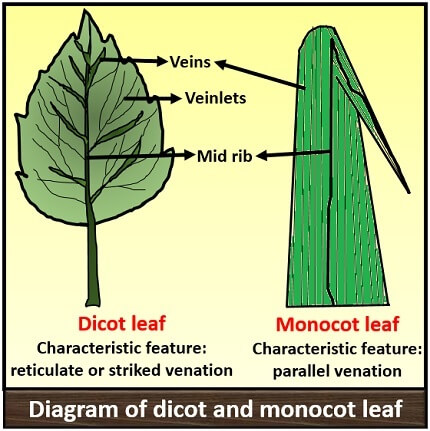
Dicotyledonous leaf diagram. Plant Development I: Tissue differentiation and function ... This diagram is showing the differences between monocotyledonous flowers or dicotyledonous flowers. Monocots have a single cotyledon and long and narrow leaves with parallel veins. Their vascular bundles are scattered. Their petals or flower parts are in multiples of three. Dicots have two cotyledons and broad leaves with network of veins. Monocot and Dicot Leafs (With Diagram) | Plants ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top two types of monocot and dicot leafs. The types are: 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf 2. Anatomy of Dicot Leaf. Monocot and Dicot Leaf: Type # 1. Anatomy of Monocot Leaf: Triticum-Leaf: ADVERTISEMENTS: T.S. shows prominent ridges and grooves and reveals the following tissues: Epidermis: 1. Two epidermal […] Internal Structure of Leaf: Parts, Function, Diagram - Embibe The leaf base is the part where a leaf attaches to the stem; it has two small leaf-like structures called stipules. The petiole is the long, thin stalk that connects the leaf blade to the stem. Lamina, also known as leaf blade, is the green, flat surface of the leaf that consists of midrib, veins and veinlets. Cotyledons, Monocotyledons and Dicotyledonous - An Overview Dicotyledonous. It comprises two cotyledons emerging from the seeds after seed germination. Almonds, cashews, tomato, peas are the best examples of dicotyledonous. Dicotyledons are also known as dicots. There are around 200,000 species of dicotyledons. Explore more: Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Seeds.
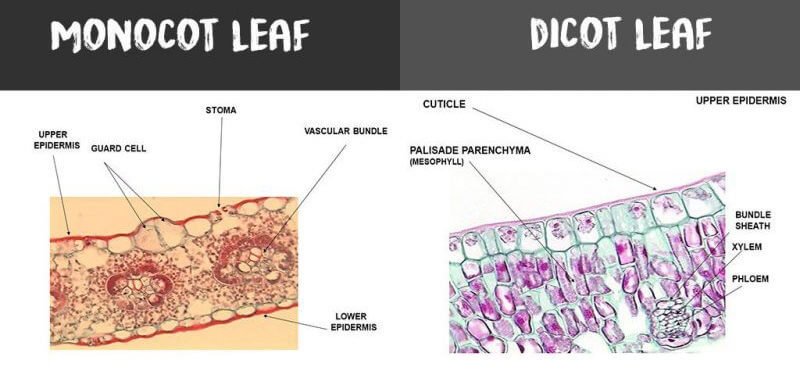
Leaf Anatomy (Transverse Section of Leaf) | EcoBioHub In this tutorial, we have discussed the leaf anatomy (Transverse Section of Leaf) of dicot and monocot plants. Transverse Section of Leaf: Dorsiventral/ Dicotyledonous Leaf The leaves of dicotyledonous plants are arranged in a horizontal position, i.e., at a right angle to the rays of the sun so that they receive more light on the upper surface than the lower surface. The leaves with such an ... Chapter 5 The Shoot System I: The Stem vascular cylinder and the number of leaf traces differ by species and are dependent on the number and arrangement of leaves. Figure 5.3. Shoot apex of Coleus blumei, a common houseplant. X114 Figure 5.4. The pattern of vascular development in a dicot stem. (a) Longitudinal view showing vascular bundles and leaf connections. (b) Cross WRKY transcription factors: evolution, binding, and action ... Apr 16, 2019 · The WRKY transcription factor (TF) gene family expanded greatly in the evolutionary process from green algae to flowering plants through whole genome, segmental, and tandem duplications. Genomic sequences from diverse plant species provide valuable information about the origin and evolution of WRKY domain-containing proteins. Accumulating data indicate that WRKY TFs bind W-box and/or other cis ... IB Biology Notes - 9.1 Plant structure and growth 9.1.1 Draw and label plan diagrams to show the distribution of tissues in the stem and leaf of a dicotyledonous plant. Figure 9.1.1 - Transverse section of a stem. Figure 9.1.2 - Leaf Structure. 9.1.2 Outline three differences between the structures of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants.
Oxford Cambridge and RSA AS Level Biology A 2 OCR 2017 Answer all the questions. 1 Fig. 1.1 shows a student’s diagrams of two plant cells. Each cell was observed using a different type of microscope. The cells are not drawn to scale. (a) Cell A Cell B Fig. 1.1 (i) Cell B in Fig. 1.1 was observed using an electron microscope. Give one piece of evidence from Fig. 1.1 that supports this. Cross Section Of A Dicotyledonous Leaf Anatomy of dicot leaf. How to draw the diagram of cross section of a leaf class x. Short distance for carbon dioxide to diffuse into leaf. Diagram of transverse section dicot leaf. If a plant has 2 seed leaves we call it a dicotyledon or dicot for short. A dicotyledonous leaf is generally dorsiventral. Role Of Rhizobium Bacteria In Nitrogen Fixation - BYJUS 08/09/2020 · Infectious hairy root disease in dicotyledonous plants is caused by ... Digestive System Diagram: Manure Meaning : Lysosome Function: Fungi Examples: Leaf Structure: What Is A Ligament: 3 Comments. Gunjan Raj April 8, 2020 at 10:27 am. It is awesome answer. Reply. Shruti pakhale September 8, 2020 at 7:48 am. So easy answer. Reply. rohit September 12, … Structure Of Dicotyledonous Leaf Photosynthesis ... 3 Dorsiventral Cross Section Of A Dicot Leaf With The Adaxial Surface Scientific Diagram Schematic Transverse Section Through A Dicotyledon Leaf Indicating The Scientific Diagram Leaf Anatomy The Two Parts Of Monocot And Dicot Leaves Ruzivo Digital Learning Anatomy Of Dorsiventral Dicotyledonous Leaf Sciencetopia ...
Plant Structure and Growth - IB Biology HELP 9.1.1: Plan diagrams in the stem and leaf of a dicotyledonous plant. Plan diagrams are used to show the distribution of tissues (for example, xylem and phloem) and do not show individual cells. They are sometimes called "low-power" diagrams. You can place the mouse pointer on to the plan diagram of the leaf to see the tissues labeled in an ...
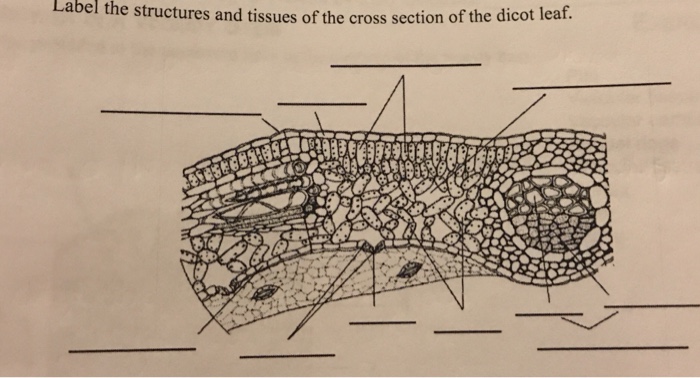
Diagram Of Transverse Section A Dicot Leaf | Leafandtrees.org Schematic Transverse Section Through A Dicotyledon Leaf Indicating The Scientific Diagram. Describe The Anatomical Structure Of A Dicot Leaf Qs Study. Label The Structures And Tissues Of Cross Section Chegg Com. Anatomy Of Dorsiventral Dicotyledonous Leaf Sciencetopia. Q 14 In The Diagrams Below Identify Cross Chegg Com.
Sep 23, 2021 · The cells in the leaf of a plant that control the opening and closing of stomata are guard cells. These cells are in bean shape and surround the stoma. These are the epidermal cells and help in the exchange of gases by opening and closing of stomata. These also play a major role in transpiration and minimal loss of water.
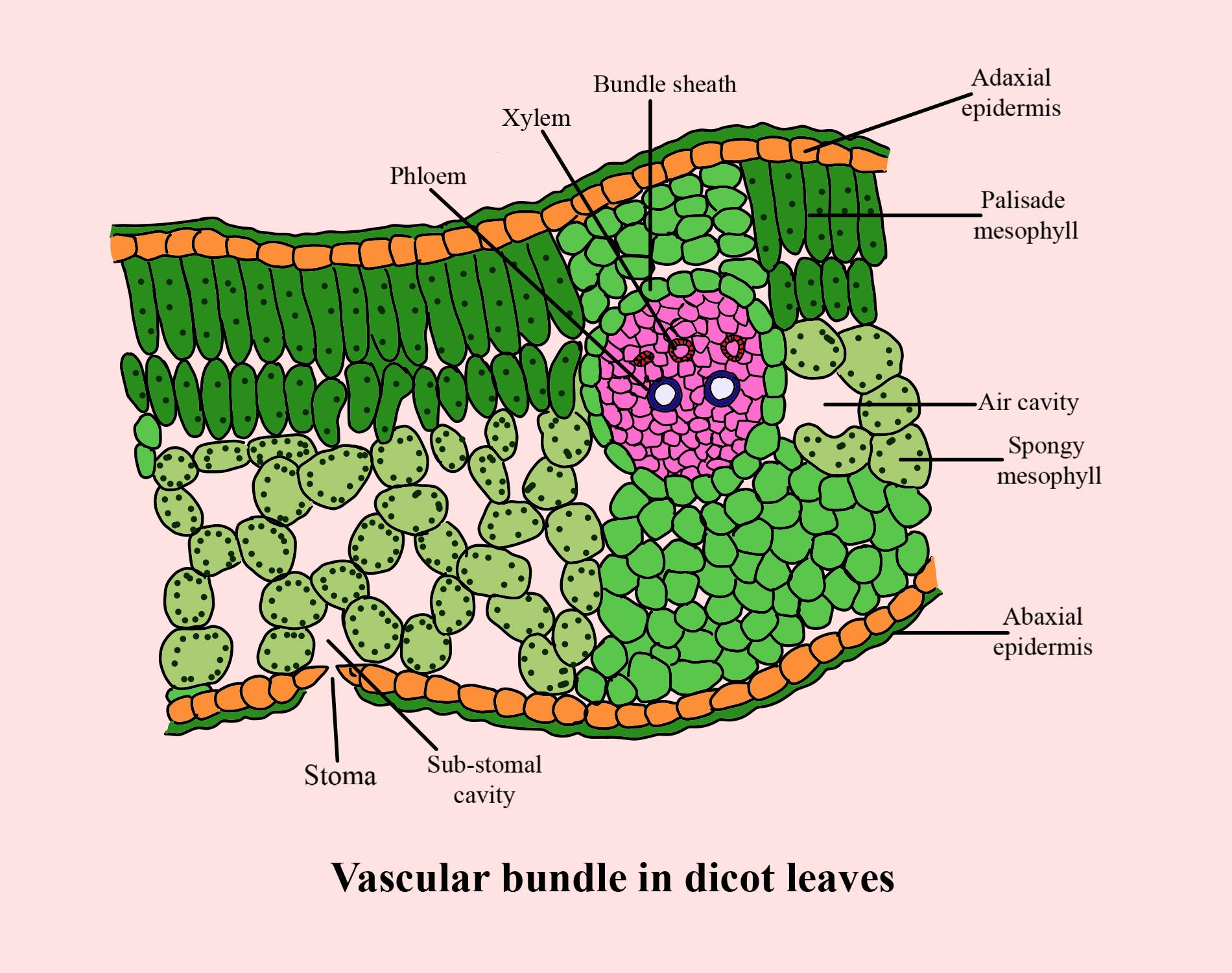
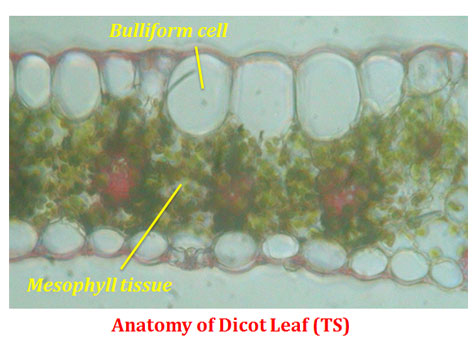
Internal Leaf Structure Internal Structure of the Leaf of a Typical Dicotyledonous Plant. Internal Leaf Structure a) Cuticle: Waxy layer water proofing upper leaves. b) Upper epidermis: Upper layer of cells.No chloroplasts. Protection. c) Palisade Mesophyll: Tightly packed upper layer of chloroplast containing cells. d) Spongy Mesophyll: Lower layer of chloroplast containing cells.
EUR-Lex - 32013R0283 - EN - EUR-Lex - Europa (1) In accordance with Article 8(4) of Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009, Commission Regulation (EU) No 544/2011 of 10 June 2011 implementing Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the data requirements for active substances (2) was adopted. It contains the requirements for the dossiers to be submitted for the approval of active …
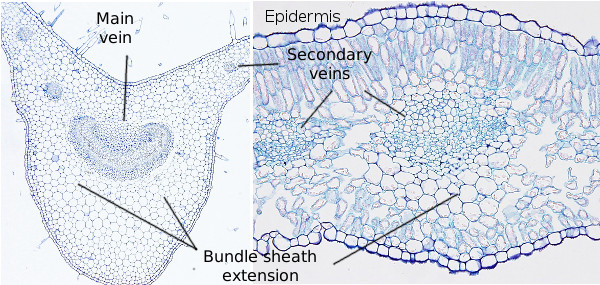
Cellular and tissue structure of a dicotyledonous leaf ... The dicot leaves have two side the upper side and the lower side.The upper side is directed above and the lower side is directed below so these leaves are known as bifacial leaf or dorsiventral leaves.The leaves obtain more sunlight on the upper side than on the lower side so there is difference in the anatomical structure and the tissue orientation on either side.
Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Leaves Dicot Leaf. Dicotyledonous leaf shows reticulate venation. Lamina consists of epidermis, mesophyll and vascular system. The epidermis is covered by cuticle and stomata; abaxial epidermis (lower surface) possesses more stomata than adaxial epidermis (upper surface). Sometimes adaxial epidermis lack stomata.
Monocot Diagram - schematron.org Angiosperms are divided into two subgroups, dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants, mainly on the basis of number of embryonic leaves or cotyledons. Anatomy of Monocot Root (Monocot Root Cross Section Under Microscope with Diagram) Ø The anatomical features of a monocot root can be studied through a cross section (CS) through the root..
CHAPTER - 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS - Kar Dicotyledonous plants, Monocotyledonous plants, Banyan tree (Prop roots) e.g., gram, pea, mango. e.g., wheat, paddy, grasses. Maize (Stilt roots) Rhizophora (Respiratory roots) Root Cap: The root is covered at the apex by the thumble-like structure which protects the tender apical part. Regions of the root: 1. Region of meristematic activity: Cells of this region have the capability to …
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 - High School Biology ... Biology Questions and Answers Form 3; Biology notes, outlines, diagrams, study guides, vocabulary, practice exams and more! Free online downloads and pdf. General biology study guide. Biology revision. Biology syllabus. Biology questions and answers. Biology tests. Biology.
AS Level Biology (9700) P3 Guide - Diagrams - Stude Mate Dicotyledonous Mesophyte Plant - TS Leaf, TS Stem & TS Root: Pretty much all that you have to do with the slides of this sort is to draw the diagram correctly and label it as fully as you can.; For TS Leaf, the most common questions ask you to draw a plan diagram or a diagram of a certain section of the leaf clearly showing a specific number of cells.
[email protected] - wunderino-236.de 11/03/2022 · State of California. email protected]
Parts of a Seed, Their Structure, and Functions with Diagram 06/10/2020 · Parts of a Seed Diagram A typical seed consists of three main parts: 1) seed coat, 2) endosperm, and 3) embryo.
Of The Best Diagram Of A Leaf - Glaucoma Template The Internal Structure of a Leaf Diagram below is a cross section of a dicotyledonous leaf that shows all the different tissues that make up the leaf. The External Structure Of The Leaf Image Credit Passmyexams Co Uk Leaves Leaf Structure Biology For Kids . They can be in many different forms ie. Diagram of a leaf. Diagram Of a Leaf.
Body Plan of a Dicotyledonous Plants (With Diagram) ADVERTISEMENTS: The below mentioned article provides a practical exercise to observe the Body Plan of a Dicotyledonous Plant. Exercise 1: To study the body plan of a dicotyledonous plant. ADVERTISEMENTS: Requirements: A complete, small-sized herbaceous plant (e.g., Brassica campestris or Solanum nigrum, etc.) and a chart showing basic anatomical details of the plant. Observations and […]
PDF DICOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS 07 MAY 2014 Lesson Description Summary DICOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS 07 MAY 2014 Lesson Description In this lesson we: ... o Transport of water and mineral salts from the root to the leaf o Transport organic substances from the leaf to the rest of the plant The Internal structure of a dicot stem Line diagram of a cross section through a dicotyledonous stem: Test Yourself
Dicot - Definition, Examples and Quiz of Dicotyledon ... Dicotyledon Definition. Dicotyledon, or dicot for short, refers to one of two main groups into which flowering plants (angiosperms) are categorized. Most flowering plants are traditionally divided into two different categories: monocots and dicots. Members of each group tend to share similar features.
Draw a labelled diagram of transverse section of a ... Time Transcript; 00:00 - 00:59: students question is draw a labelled diagram of transverse section of a dorsiventral leaf differentiate between the internal structures of dicotyledonous and monocot seeds so basically this is the structure of transverse section of a dorsiventral leaf physically it is the internal structure of the mango leaf transverse section show dorsiventral leaves are found ...
PDF DICOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS 01 MAY 2013 Key Concepts The External Structure of a Dicotyledonous Stem The internal structure of the dicot stem can be divided into three regions o The epidermis o The cortex o Central stele/cylinder Line diagram of a cross section through a dicotyledonous stem A cross section through a dicotyledonous stem showing the various tissues
Schematic transverse section through a dicotyledon leaf ... Download scientific diagram | Schematic transverse section through a dicotyledon leaf indicating the arrangement of tissues. Chloroplasts are drawn in one cell only of both palisade and spongy ...
bio practical diagrams.docx - Dicotyledonous Mesophyte ... Dicotyledonous Mesophyte Plant - TS Leaf, TS Stem & TS Root: Pretty much all that you have to do with the slides of this sort is to draw the diagram correctly and label it as fully as you can. For TS Leaf, the most common questions ask you to draw a plan diagram or a diagram of a certain section of the leaf clearly showing a specific number of cells.
Anatomy of a dicot leaf - Sunflower leaf - BrainKart A dicotyledonous leaf is generally dorsiventral. It has upper and lower epidermis. The epidermis is usually made up of a single layer of cells that are closely packed. The cuticle on the upper epidermis is thicker than that of lower epidermis. The minute openings found on the epidermis are called stomata.
Anatomy of Stem: Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous | Botany In this article we will discuss about the monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous stem with the help of suitable diagrams. The stem is the part of the axis, bearing leaves and reproductive bodies and is aerial in nature. The close association of stem and leaf as is indicated by the usage of the word 'shoot' combinedly for […]
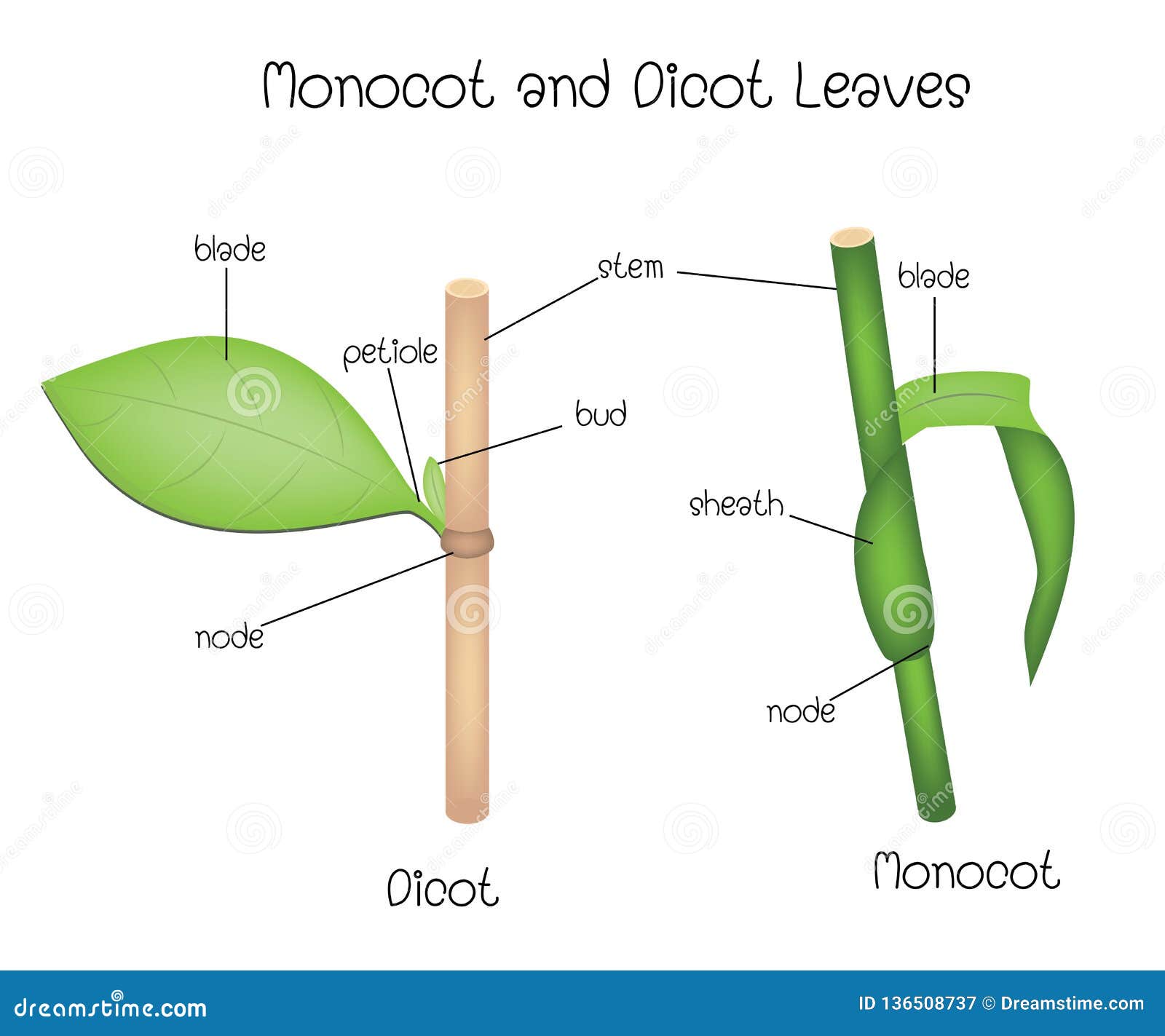
BIOLOGY FORM ONE NOTES FREE - Educationnewshub.co.ke Sep 08, 2021 · Leaf Apex: This is the tip of the leaf and usually it is pointed. Petiole: It attaches the leaf to the stem or branch. In some monocotyledonous plants the leaves are attached to the stem by the leaf sheath. Practical Activity 1: To examine the External Features of a Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous leaf. Study Question 1. Internal Structure ...
Monocot Dicot Plants Anatomy: Root, Stem, & Leaf The leaf has an auricle, which can be an ear-like projection or a hairy edge near the base of the leaf blade. Dicot Leaves. Mustard leaves; Mustard is a dicot plant that is mainly utilized in dicotyledonous plant research. Green leaves with reticulate venation are green and broad.
5.2 Anatomy of dicotyledonous plants | Support and ... Figure 5.9: Stem showing internode and nodes plus leaf petioles. Figure 5.10: Photo of a redwood. The trunk of the tree is its stem. The internal structure of the dicotyledonous stem. Figure 5.11 shows a schematic arrangement of tissues in a dicotyledonous stem. Details of each tissue type are described in this section.
Chapter 8 Section 2 Biology Quizlet - r-und-k-hausundgarten.de Details: Ap Biology Transcription Diagram Quizlet Transcription And Translation Steps Diagram Google Search Dna Chapter 15 Transcription Translation Addgene. ii) State the similarities and differences between a dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous root. Learn vocabulary terms and more with.
PDF Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level 6 The diagram shows a cross-section of a dicotyledonous leaf. 1 2 3 5 4 6 Which labelled parts of the leaf carry out photosynthesis? A 1, 2 and 3 B 1, 3 and 4 C 2, 5 and 6 D 4, 5 and 6 . 4 ... 18 The diagram shows changes in the volume of a person's lungs over a period of two minutes. XY 4 3 2 1 0 volume of air in lungs / litres 01
Preparation And Study Of T.S Of Dicot And Monocot Roots ... Diagram. T.S Of Dicot Stem. T.S Of Monocot Stem. Procedure Taking Sections. Hold the dissected plant material between your index finger and thumb, while keeping the edge of the razor perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the plant. Slice it into thin sections. Using the edge of the blade, shift these sections into a watch glass with the help of a brush. The watch glass must …
Plant Anatomy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The diagram indicates the essential parts of the mangrove tree from the standpoint of water relations, particularly the membranes of the endodermis and of the leaf cells. It is important to note that if leaf membranes should suddenly cease to be differentially permeable, salt and subsequently water would move from leaf cells into the pathway due to the high tension of …
dicot leaf.pdf - D SBA#: Title: Dicot leaf Aim: To draw ... Diagram: SBA# Dicot leaf Skilled Assessed: D (Drawing) Criteria Total Marks Marks Obtained No evidence of shading 1 Drawing is a good representation of specimen 1 Parts of drawings are proportional to parts of specimen (-1 for deviation) 1 Drawing is large enough to observe necessary details 1 Absence of double lines in drawing 1 Drawing of ...




















Comments
Post a Comment