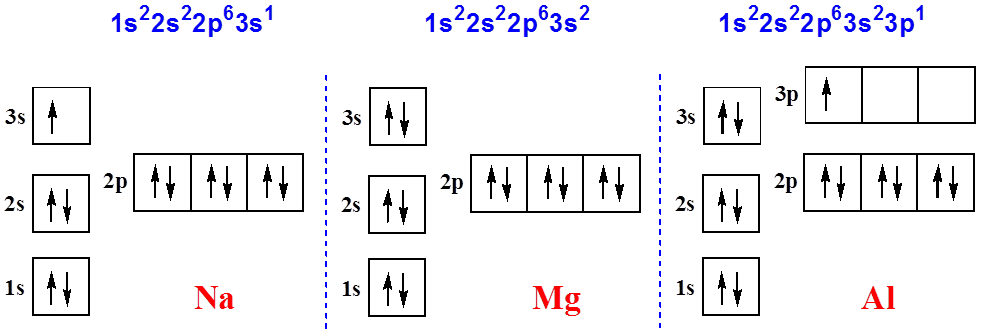
38 atomic orbital diagram for arsenic
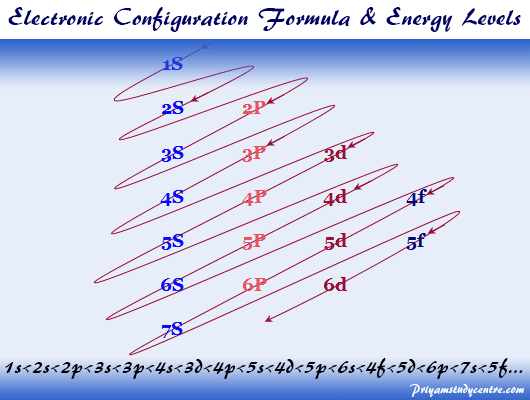
electrons. The number of electrons = number of protons = Z, the atomic number. 1. The Pauli principle: No more than two electrons can occupy a given orbital. If there are two electrons in an orbital, their spins must be paired (one must have m s = 1 2 and the other, m s = − 1 2). 2. BOHR DIAGRAM FOR ARSENIC INFO: Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. You can find metric conversion tables for SI units, as well as English units, currency, and other data.
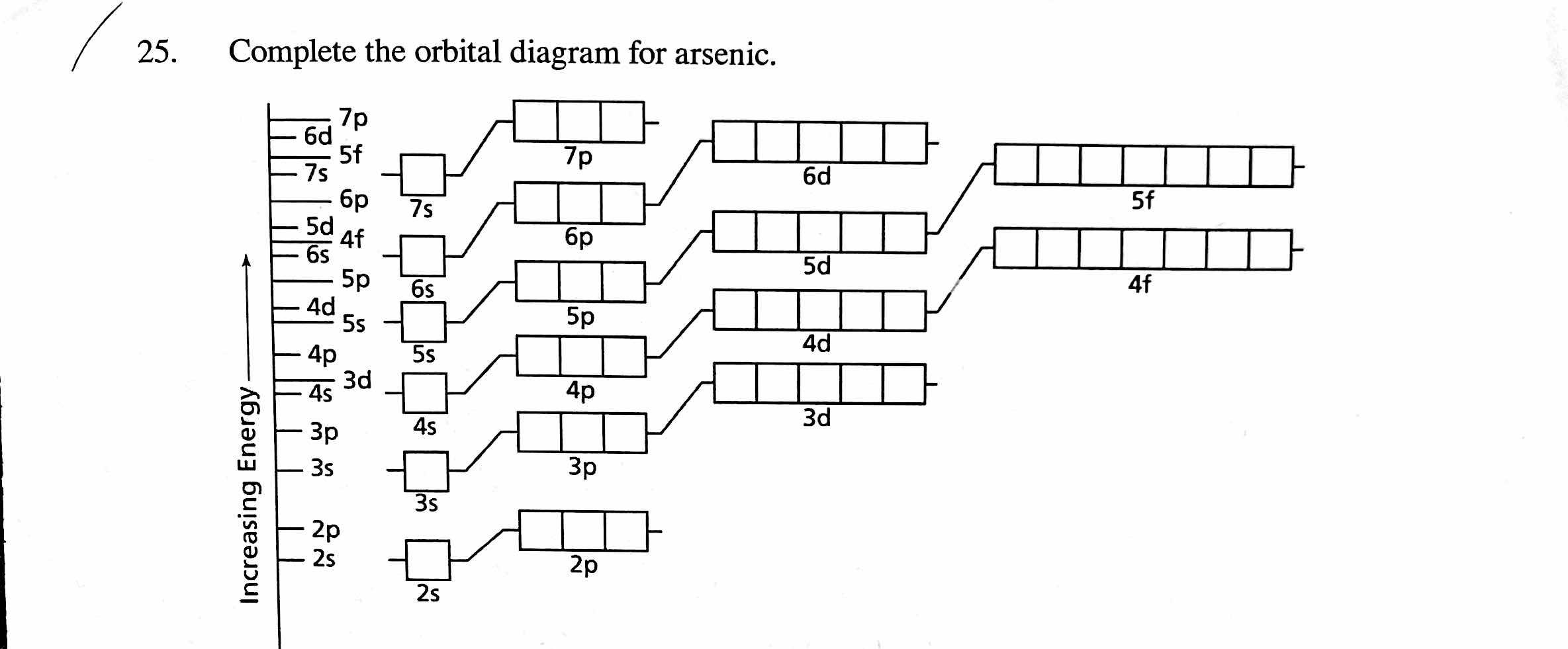
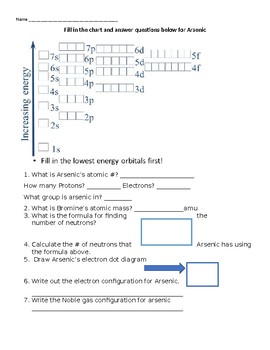
(a) (3 pts) Draw and label the full orbital energy level diagram for a ground-state arsenic atom. Note: On the left side you will have an arrow indicating energy, to the right of this, you will feature each orbital as a box) (b) (1 pt) Write the condensed electron-configuration of the arsenic atom.
Atomic orbital diagram for arsenic
I’ve been tasked with drawing rhe MO diagram for Sulfure Oxide and I’m not sure about the energies of the relatove orbitals. Since Oxygen is more electronegative I expect the 2s and 2p orbitals to have much lower energy than the 3s and 3p orbitals sulfur has. But the energy difference would be really high then. So I’m not sure what 2 orbitals combine to form the sigma 3s or sigma* 3s orbital. The difference in energy kevels confuses me as every example I’ve done has the same orbitals (2s,2p’s) c... Scientist Niels Bohr was the first to give an idea of the atom’s orbit. He provided a model of the atom in 1913. The complete idea of the orbit is given there. The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. These circular paths are called orbit(shell). These orbits are expressed by n. [n = 1,2,3,4 . . . The serial number of the orbit] K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, N is the name of the fourth orbit. The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n2. For example, 1. n = 1 for K orbit. The electron holding capacity of K orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 12= 2 electrons. 2. For L orbit, n = 2. The electron holding capacity of the L orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 22= 8 electrons. 3. n=3 for M orbit. The maximum electron holding capacity in M orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 32 = 18 electrons. 4. n=4 for N orbit. The maximum electron holding capacity in N orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 42= 32 electrons. Therefore, the maximum electron holding capacity in the first shell... What is the orbital notation of arsenic? The orbital notation of arsenic (As) is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3See the Related Questions for the electron configuration of all the elements. What...
Atomic orbital diagram for arsenic. By using the Aufbau diagram (shown below) we can determine the full electron configuration for a neutral arsenic atom. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p3 The shorthand electron configuration, which uses the symbol for the noble gas in the previous period, in this case argon. [Ar]3d104s24p3 Aufbau Diagram Answer link To write the orbital diagram for the Arsenic atom (As) first we need to write the electron configuration for just As. To do that we need to find the number o... Hey every one! Any one know how I can program some good modes for an orbit? I want modes that obviously utilize the motion changing. I’m struggling to program some good modes that work with the speed of an orbit. Please help :( Arsenic is found in the fourth period of the table of elements. It is a member of the phosphorus family with other elements including phosphorus (duh), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi). All of the members of this family have five electrons in their outer orbital. We keep mentioning that arsenic is a poison.
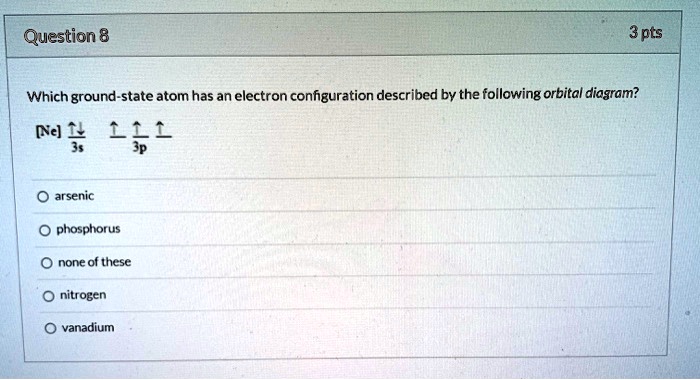
I am interested in finding out if there is a document with the time it takes for each atom to go from an excited state to a low-energy one. For example: when hydrogen passes from 1s to 2s it remains in this state for x seconds, etc. I'm a bit confused about this thing, thanks in advance! 6. Draw the orbital diagram for Arsenic As = 33 7 10 3 15 25 35 45² 4D 4 10 Vk VL VI VUVUNA V1y/Urve v VI. WAV 15 23 35 us LID 4B 4P -2 7. Write the electron configuration for Arsenic Z z 2 2 o 3 15 25 35 45 4D LIP - 2 8. Write the noble gas electron configuration for Arsenic - 2 9. Write the noble gas electron configuration for Magnesium -2 ... Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org! Jan 24, 2022 · Arsenic Electron Configuration - 9 images - rubidium electron configuration rb with orbital diagram, arsenic properties and occurrence assignment point,
I’m a little confused on the connection between a molecules molecular orbital diagram and it’s individual atomic hybridization. Can anyone help me? Thank you Arsenic is a chemical element with atomic number 33 which means there are 33 protons and 33 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Arsenic is As. The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Is this the correct atomic orbital diagram for a neutral atom of arsenic? Please indicate "true" or "false" accordingly on your Google quiz form. The p-orbital can have a maximum of six electrons. So, the next six electrons enter the 2p orbital and the remaining two electrons enter the 3s-orbital. Therefore, the magnesium (Mg) electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2. Magnesium (Mg) Electron Configuration. Magnesium orbital diagram.
The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org! Arsenic atomic orbital and chemical bonding information. There are also tutorials on the first thirty-six elements of the periodic table.
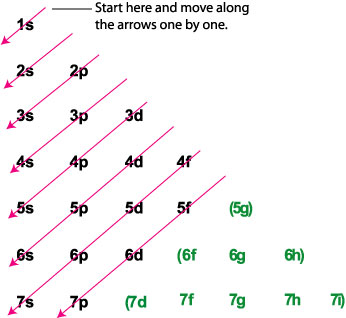
Hi I am new to reddit and I'm Edwin. We have s / p / d / f / g / h / i / k orbitals, but can someone explain why the alphabetical order is this, pls? a&b -> s&p and no C / E / J , and what comes after s-p-d-f-g-h-i-k-l-m-n-o? p again if it exists?
First, we need to determine the electron configuration for As (arsenic). The electron configuration depends on the number of electrons an atom or ion has. Since As is neutral (uncharged), we can say that Z (atomic number) = number of protons = number of electrons. Arsenic has an atomic number of 33, so it has 33 electrons. 90% (339 ratings)
The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. There are also tutorials on the first thirty-six elements of the periodic table. Arsenic 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 … What four features of bacteria that enable them to survive in a wide variety of habitats? Why don't libraries smell like bookstores?
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 90% (29 ratings) Transcribed image text: Construct the orbital diagram for arsenic. Answer Bank Energy.
The four chemically important types of atomic orbital correspond to values of l = 0, 1, 2, and 3. Orbitals with l = 0 are s orbitals and are spherically symmetrical, with the greatest probability of finding the electron occurring at the nucleus. All orbitals with values of n > 1 and l = 0 contain one or more nodes.
What is the orbital diagram of arsenic? The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in its outermost shell. What is the...
Arsenic Atomic Structure. Here are a number of highest rated Arsenic Atomic Structure pictures on internet. We identified it from obedient source. Its submitted by paperwork in the best field. We say yes this kind of Arsenic Atomic Structure graphic could possibly be the most trending topic in the same way as we ration it in google pro or facebook.
An atomic orbital is characterized by three quantum numbers. The principal quantum number, n, can be any positive integer. The general region for value of energy of the orbital and the average distance of an electron from the nucleus are related to n. Orbitals having the same value of n are said to be in the same shell.
Atomic no. Orbital Diagram of All Elements Diagrams; 1: Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram ...
Arsenic as 33 protons and 42 neutrons in its nucleus giving it an Atomic Number of 33 and an atomic mass of 75. Why does arsenic have 5 valence electrons? The configuration of outermost shell of Arsenic is 4s24p3 so its outermost shell has 5 electrons, thus making 5 valence electrons . How many valence electrons does arsenic have?
If they're how so? Is it that they jump from one place to another within that path or do they rotate within that boundary or something? If they aren't why not?
Arsenic (As) Atomic Data for Arsenic (As) Atomic Number = 33 Atomic Weight = 74.9216 Reference E95 As I Ground State 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p34S°3/2 Ionization energy 78950 cm-1(9.7886 eV) Ref. BJ71 As II Ground State 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p23P0 Ionization energy 149932 cm-1(18.5892 eV) Ref. LA71
Orbital diagram for arsenic Flickr user Jonathan Quintana loves to customize desktops, and this Ubuntu setup is his first linux desktop. It looks sharp, offers some useful information, and still has plenty of room to work and do things.
I know it has something to do with n + l (I think?), but I can't seem to wrap my head around it. My teacher has explained many times but he's always very rushed. Also, if I were to draw the electronic configuration of Br, would it be: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p⁵ or, like: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p⁵ (Assuming that I drew the squares instead of letters) Sorry, I am not a native English speaker so I don't really know all the technical terms or if the ones I used are correc...
Orbital Diagram and Symbol # e- Longhand Electron Configuration 1. 4. Mg 35 2 ... E xcited state electron configuration shows an electron becoming excited and jumping into a higher orbital. 10. ... Complete the orbital diagram for arsenic.. AsF5 Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles (Arsenic . Nov 05, 2020 · sp ...
For each electron shell atom diagram, the element symbol is listed in the nucleus. The electron shells are shown, moving outward from the nucleus. The final ring or shell of electrons contains the typical number of valence electrons for an atom of that element. The element atomic number and name are listed in the upper left.
What is the orbital notation of arsenic? The orbital notation of arsenic (As) is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p3See the Related Questions for the electron configuration of all the elements. What...
Scientist Niels Bohr was the first to give an idea of the atom’s orbit. He provided a model of the atom in 1913. The complete idea of the orbit is given there. The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. These circular paths are called orbit(shell). These orbits are expressed by n. [n = 1,2,3,4 . . . The serial number of the orbit] K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, N is the name of the fourth orbit. The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n2. For example, 1. n = 1 for K orbit. The electron holding capacity of K orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 12= 2 electrons. 2. For L orbit, n = 2. The electron holding capacity of the L orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 22= 8 electrons. 3. n=3 for M orbit. The maximum electron holding capacity in M orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 32 = 18 electrons. 4. n=4 for N orbit. The maximum electron holding capacity in N orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 42= 32 electrons. Therefore, the maximum electron holding capacity in the first shell...
I’ve been tasked with drawing rhe MO diagram for Sulfure Oxide and I’m not sure about the energies of the relatove orbitals. Since Oxygen is more electronegative I expect the 2s and 2p orbitals to have much lower energy than the 3s and 3p orbitals sulfur has. But the energy difference would be really high then. So I’m not sure what 2 orbitals combine to form the sigma 3s or sigma* 3s orbital. The difference in energy kevels confuses me as every example I’ve done has the same orbitals (2s,2p’s) c...
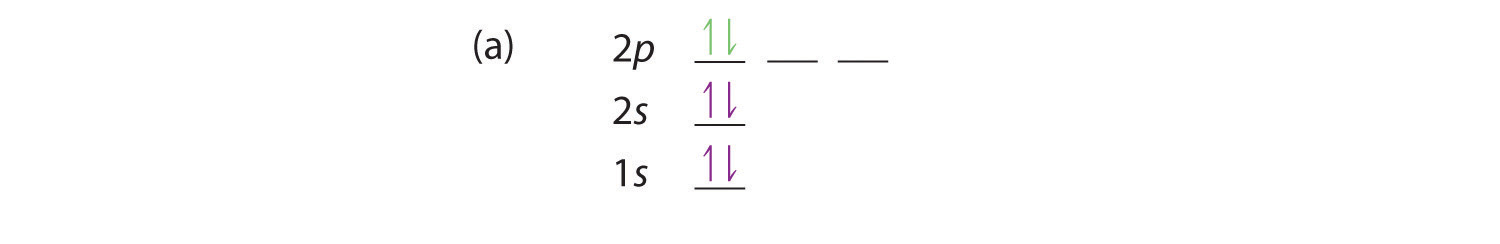





















Comments
Post a Comment