40 molecular orbital diagram f2
Jan 15, 2022 · A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory ... 29 Sept 2017 — Fluorine molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of two fluorine atoms, each having nine electrons, thus making 18 electrons.2 answers · 62 votes: O2 and F2 is an execption so their Z shell is down ... Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons . Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than ...
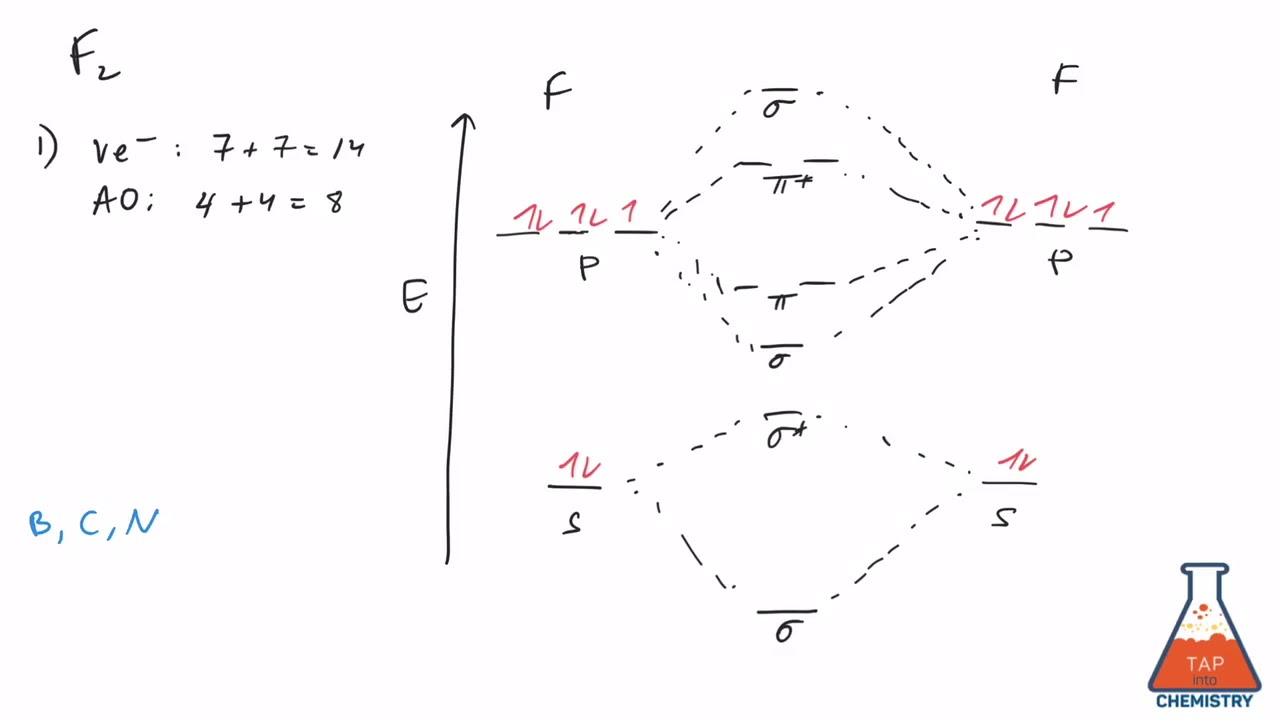
The molecular orbital diagrams for molecules and ions are drawn from the order of increasing energies shown in the molecular orbital configuration. Always remember that the number of molecular orbitals formed must be equal to the number of atomic orbitals that were combined in the molecule.

Molecular orbital diagram f2
Answer (1 of 5): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th... molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Open in App. Solution. Verified by Toppr. Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:-Patterns of problems >
Molecular orbital diagram f2. Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a.F22+b. Ne22+c. F22-d. O22+e. F2 Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Describe the sigma molecular orbital. 3. Sketch the resultant molecular orbital when two 2p y orbitals overlap. 4. Consider the Ne 2 molecule. a. Construct labelled molecular orbital diagram for the molecule. b. Write the electronic configuration of the molecule. c. Calculate the bond order. State whether the molecule is exist or not. 5. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
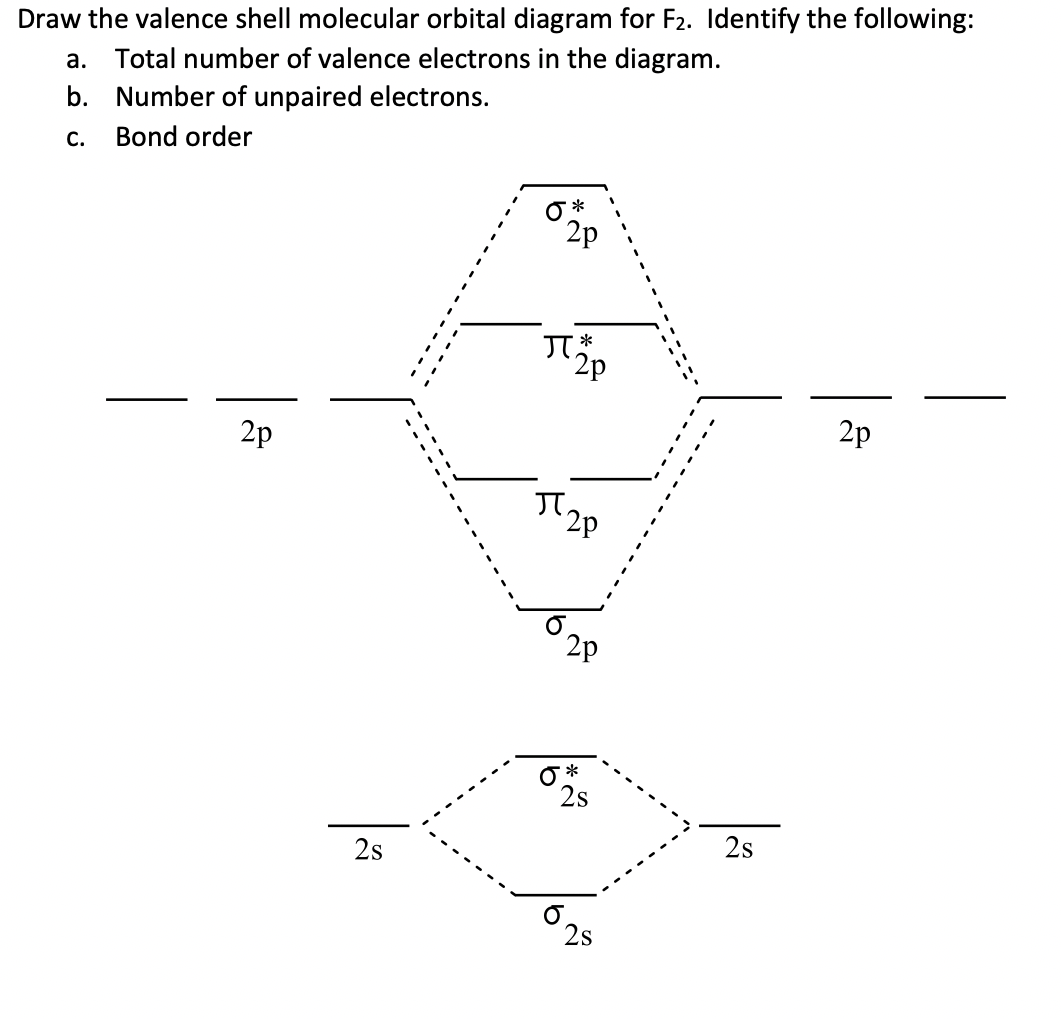
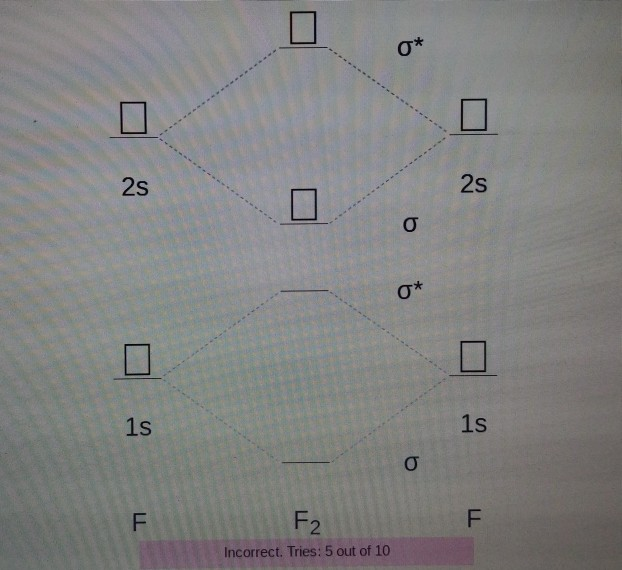
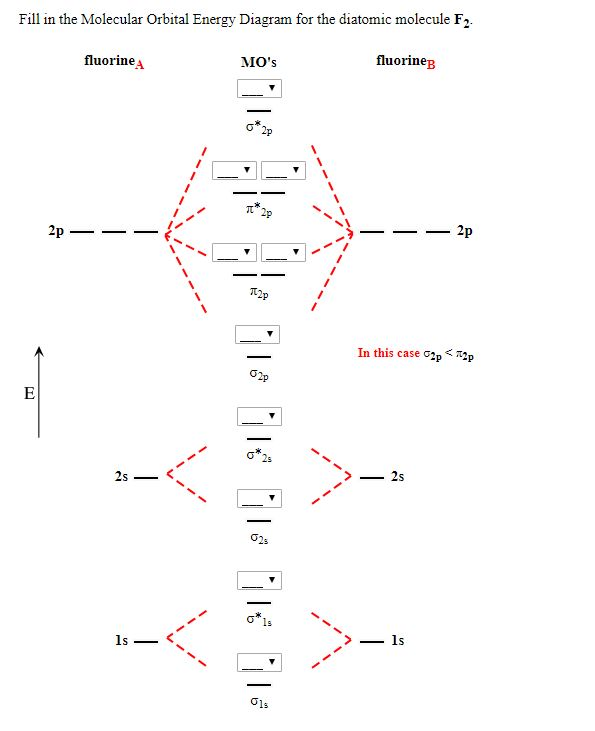
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ... The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————... Which of the species F2, F2+, or. Question: Question 11 a. Complete the molecular orbital diagram for F2. Do not include the inner shell electrons. b. Count the number of valence electrons in F2. c. What is the bond order in F2? d.
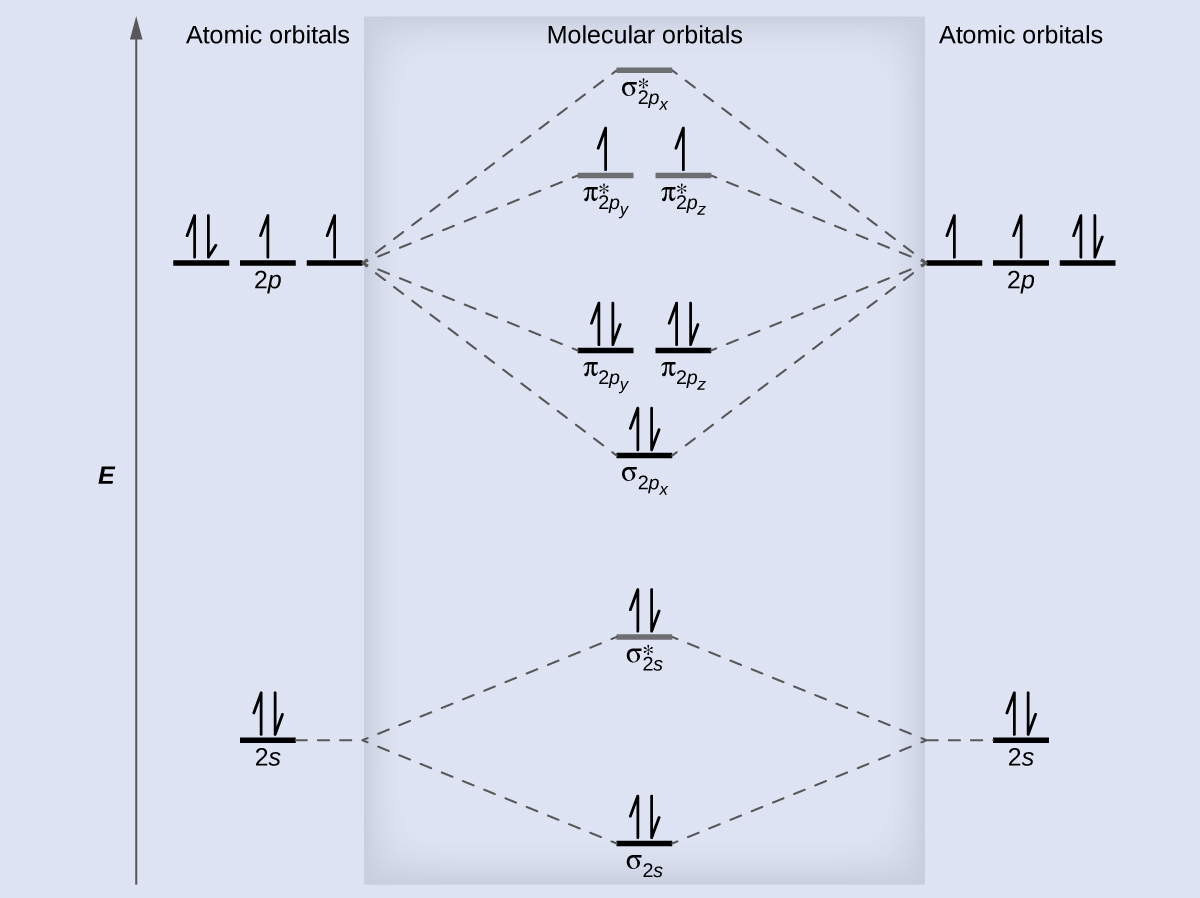
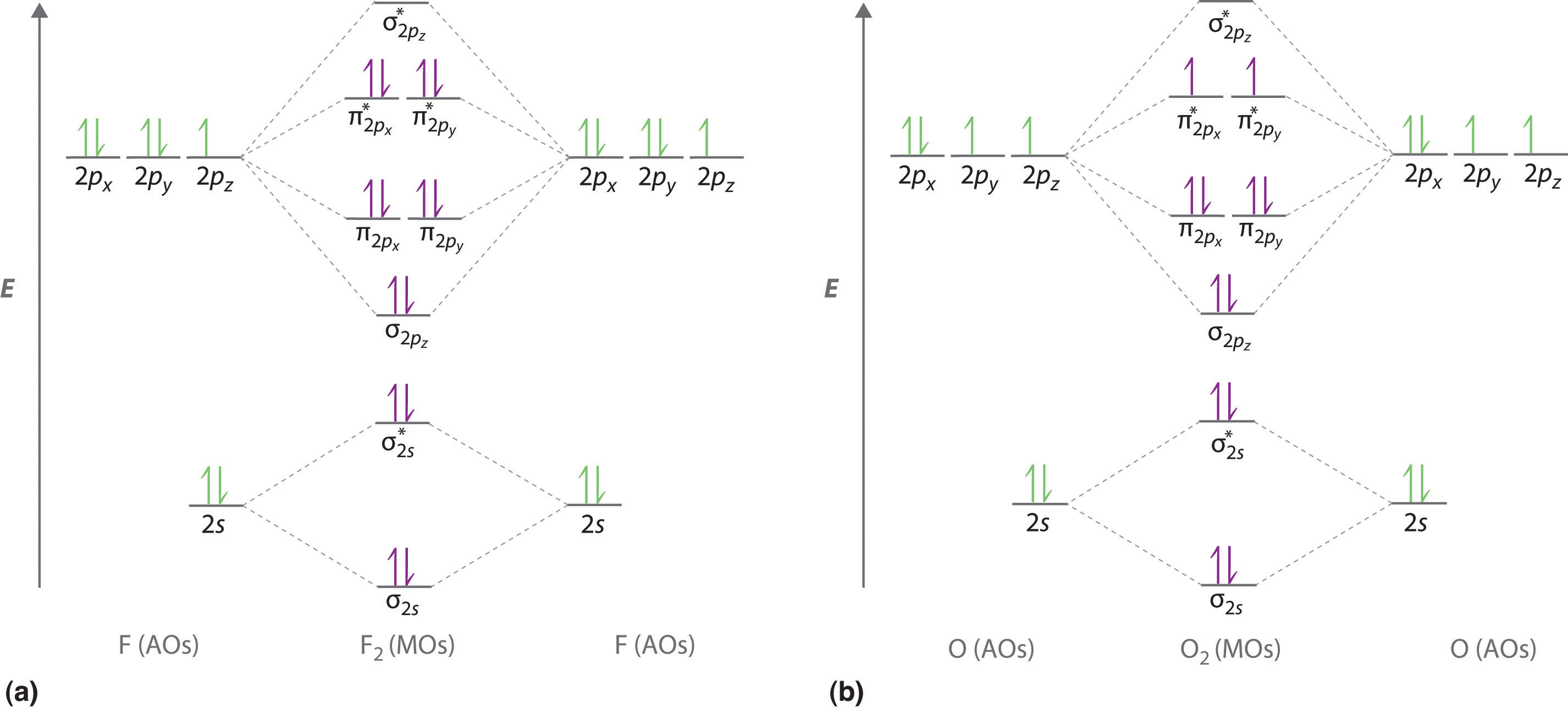
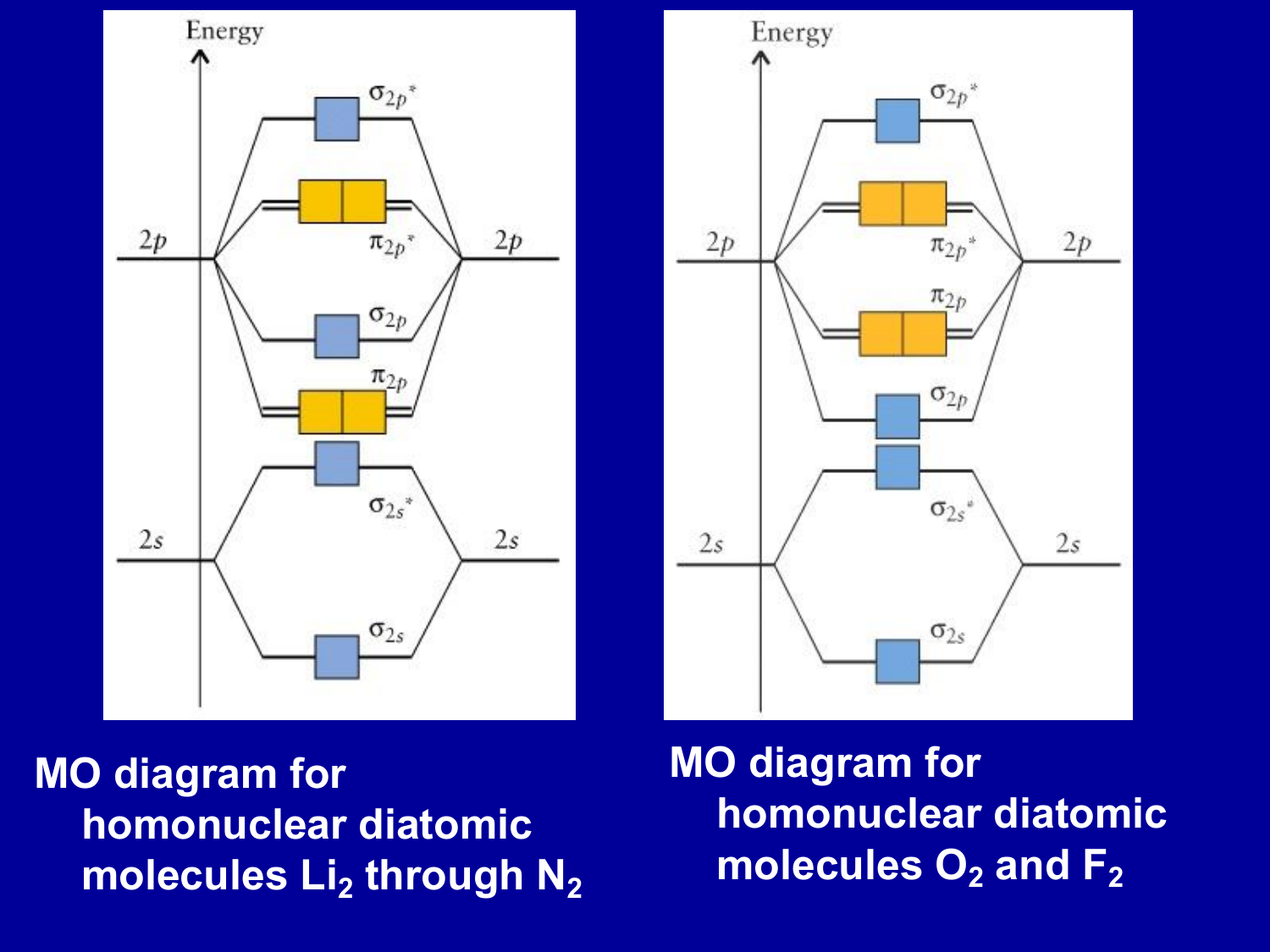
Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-. What type of orbital contains the highest energy electron (s) in F2? pi, antibonding sigma, bonding sigma, antibonding pi, bonding Which atom is larger in size (radius), Cr or Cr3+? Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-. This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2 Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Molecular orbitals: Orbitals that span two or more atoms. These are constructed by overlapping atomic orbitals (AOs) which match in symmetry and size. In principle, To construct MO diagram of a any Molecule, first, set up Schrödinger wave equation for that molecule and then, solve it!!!
Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Page 1. MO Diagrams for Elements Li2 through Ne2. (Don't memorize.) Li2 through N2. O2 through Ne2.
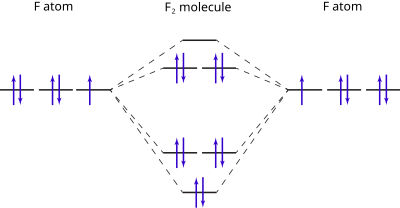
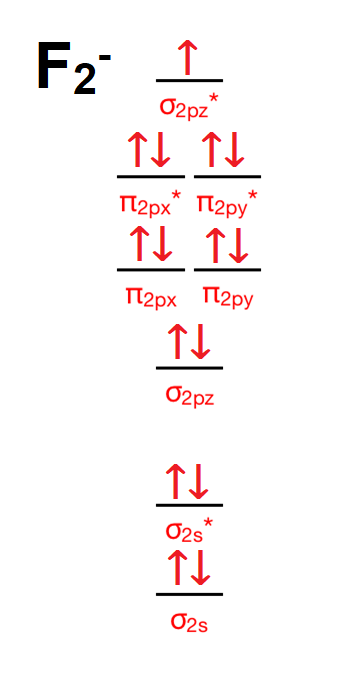
Molecular orbital diagram and bond order of fluorine molecule . Fluorine molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of two fluorine atoms, each having nine electrons, thus making 18 electrons.; These 18 electrons are filled in various molecular orbitals, in the increasing order of their energies (aufbau principle) and on the basis of Hund's rule and Pauli's exclusion principle as ...
A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. These MOs are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Thus, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbital diagram f2. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for ...
#sigma# molecular orbitals are singly-degenerate, and #pi# molecular orbitals are doubly-degenerate. #sigma# molecular orbitals, in principle, get more stabilized upon overlap than #pi# molecular orbitals do. For example, an #ns//ns# overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this:
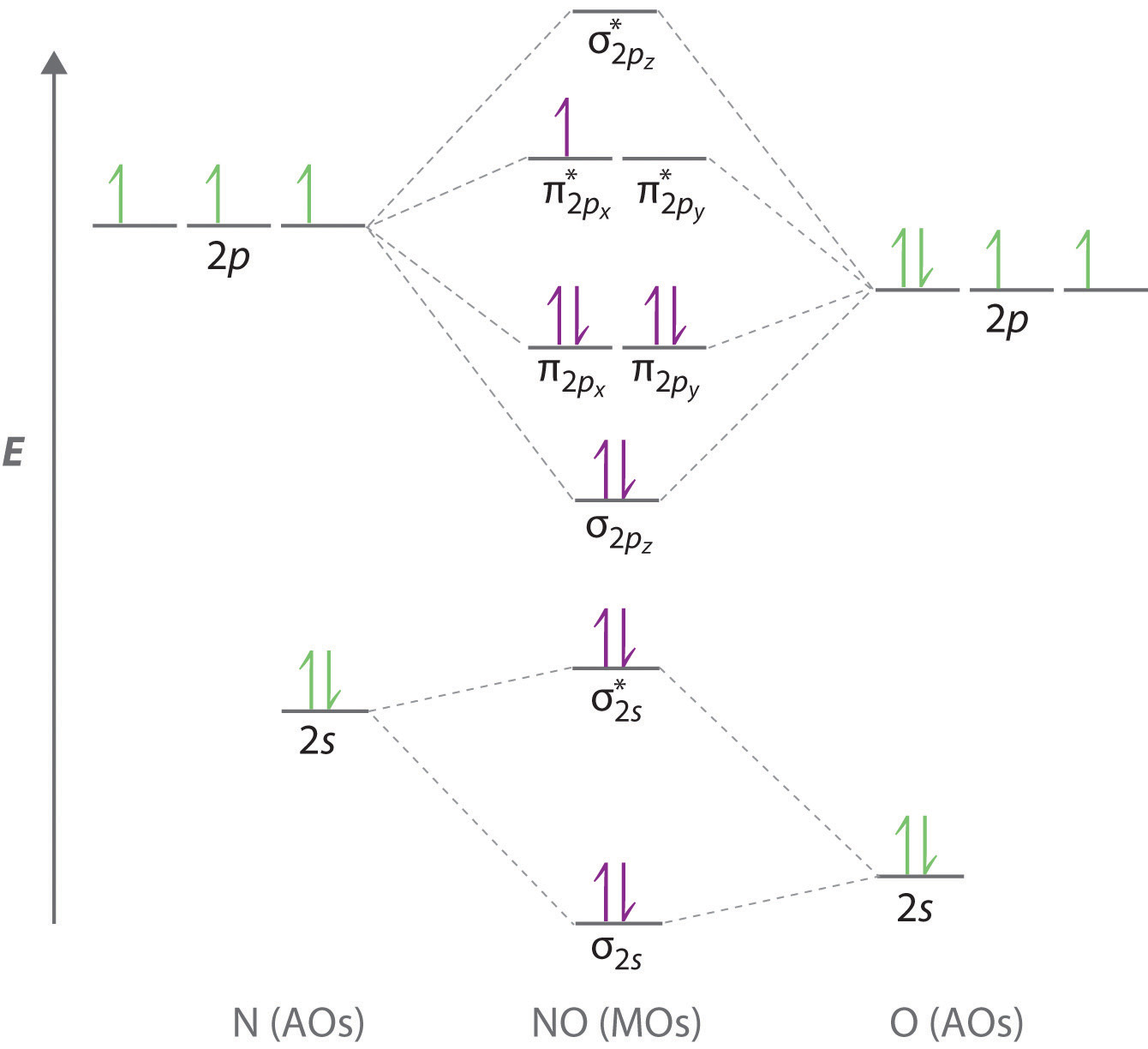
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ or ${O_2}$ with magnetic behavior and bond order. Verified. 82.1k+ views. Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to ...
Nov 01, 2021 · When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Open in App. Solution. Verified by Toppr. Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:-Patterns of problems >
molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the
Answer (1 of 5): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...



















Comments
Post a Comment