39 net force free body diagram
The existence of an unbalanced force for a given situation can be quickly realized by looking at the free-body diagram for that situation. Free-body diagrams for three situations are shown below. Note that the actual magnitudes of the individual forces are indicated on the diagram. In each of the above situations, there is an unbalanced force. Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Understanding free body diagrams is crucial to understanding the concept of Net Force. Watch this video to know more! To learn more about Force, enrol in our...

Net force free body diagram
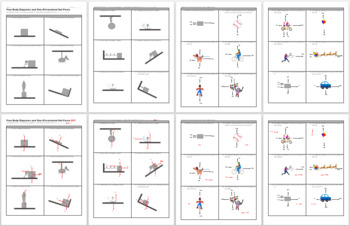
View Aleksei Avila - Kami - Finding the Net Force.pdf from BIO 101 at Lemon Bay High School. Using Free-Body Diagrams to find Net Force A. Provide (draw and label) the force(s) to achieve equilibrium Free Body Diagrams and Net Force Directions: For each of the following diagrams, determine if forces are balanced (same) or unbalanced (not the same), and determine the direction of the net force. 1. 2 3.. Free Body Diagrams Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. These diagrams will be used throughout this entire forces unit.
Net force free body diagram. Net Force: combination of all the forces acting on an object 5N 5N 5N 5N 5N 10 N Net Force = 10N East ... Free-body diagrams Free-body diagrams are used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. This diagram shows four forces acting Play this game to review Science. What is the net force for the following scenario. 100 N going left and 25 N going right. Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Quiz. Net Force and Free Body Diagrams. DRAFT. 8th grade . Played 0 times. 0% average accuracy. Science. 30 minutes ago by. janelle_wagner_97436. 0. Save. Share. Edit. Edit. Net Force and Free ... The diagram I have shows the force F point left, a force of 4N point right and a force of 8N pointing straight up. I found that Fnet would be 20 (F = ma - 5*4 = 20). Which leads me to my question... A free body diagram is a diagram of a chosen system in which we represent all the forces acting on it and thus calculate the net force. These diagrams are used to show the direction and magnitude of all the forces acting upon an object. The length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the force and arrows are labelled to indicate the type of ...
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams… Drawing Free-Body Diagrams . Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free -body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams; these diagrams will be used throughout your study of physics. Borna Haghighat Net Force and Free Body Diagrams Lab Directions: Go to the Phet Link: When the APP opens select "Net Force" Choose the "Sum Forces" and "Sound" on Net Force Section 1. Think back to the discussion for solving for Fnet. How do you solve for a Net Force? The sum of all the forces on a object or Fnet=ma To draw a free body diagram, start by sketching a simple representation of the body you want to make the diagram of, like a square to represent a box. Next, draw arrows on the shape that show the forces acting on the object. For example, draw a downward arrow to signify the weight of the object, since gravity pulls the object down. Quiz Flashcard. To calculate net force: add vectors in the same direction; subtract vectors in the opposite direction. To calculate acceleration: acceleration = net force / mass Use the following abbreviations for units: newtons = N meters per second squared = m/ss Use the following for directions: right, left, up, down. Questions and Answers. 1.
The net force obtained from all the forces acting on a body do not preserve its motion unless applied at the same point, and with the appropriate torque associated with the new point of application determined. The net force on a body applied at a single point with the appropriate torque is known as the resultant force and torque. Play this game to review Science. What is the net force for the following scenario. 100 N going left and 25 N going right. Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Quiz. Net Force and Free Body Diagrams. DRAFT. 8th grade . Played 19 times. 53% average accuracy. Science. 4 hours ago by. lemmea_62981. 0. Save. Edit. Edit. Net Force and Free Body Diagrams ... This is a complete free-body diagram. • It contains ALL forces that act on the object. • Every force is identified with a label and direction. • It does not have too much detail—a rough sketch is all that is needed. F F N F N Free-body diagrams Free-body diagrams for four situations are shown below. The net force is known for each situation. However, the magnitudes of a few of the individual forces are not known. Analyze each situation individually and determine the magnitude of the unknown forces. For each of the situations below, draw a system diagram and a free-body diagram.
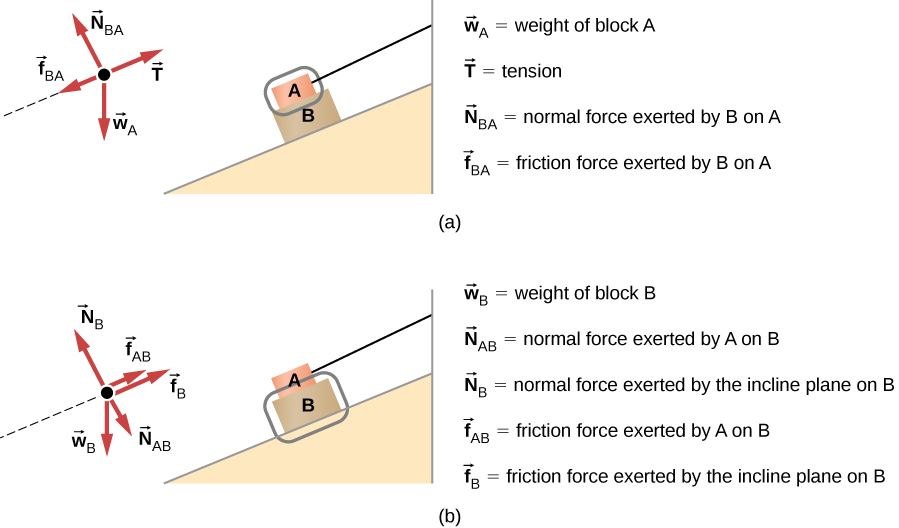
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...

BUILDING ASTRAL BRIDGES...Spaceship Earth is a Holographic Being... It will be like gazing at a hologram in a painting. The picture looks a certain way in one moment, and it changes completely in the next.
Lesson Worksheet: Free-Body Diagrams. In this worksheet, we will practice analyzing free-body diagrams and use them to determine the net force and unknown forces acting on objects. In which of the following diagrams do the directions of all the vectors shown correctly represent the vectors in a free-body diagram of the forces acting on Earth ...
NET FORCE Video Series - This video shows an example of how to solve a Net Force problem in physics. The net force results from an unbalanced force, which th...
Free-body diagrams for three situations are shown below. Note that the actual magnitudes of the individual forces are indicated on the diagram. In each of the above situations, there is an unbalanced force. It is commonly said that in each situation there is a net force acting upon the object. The net force is the vector sum of all the forces ...
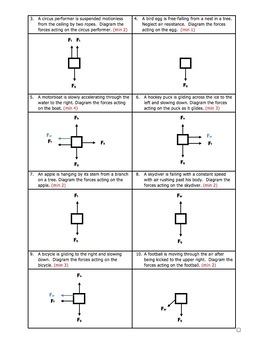
1. Free-body diagrams for four situations are shown below. For each situation, determine the net force acting upon the object. 2. Free-body diagrams for four situations are shown below. The net force is known for each situation. However, the magnitudes of a few of the individual forces are not known.
Remember that a free-body diagram must only include the external forces acting on the body of interest. ... Do not include the net force on the object.Net external force: →Fnet=∑→F=→F1+→F2+...Newton’s second law, vector form: →Fnet=∑...Definition of weight, vector form: →w=m→gw...Definition of weight, scalar form: w=mgw=mg
This processes is illustrated by free body diagrams for a skydiver with 90 kg mass in the following image: Free body diagrams of a person with 90 kg mass during a skydive. The initial speed is zero, so drag force is zero. As speed increases, the drag force grows, eventually cancelling out the person's weight.
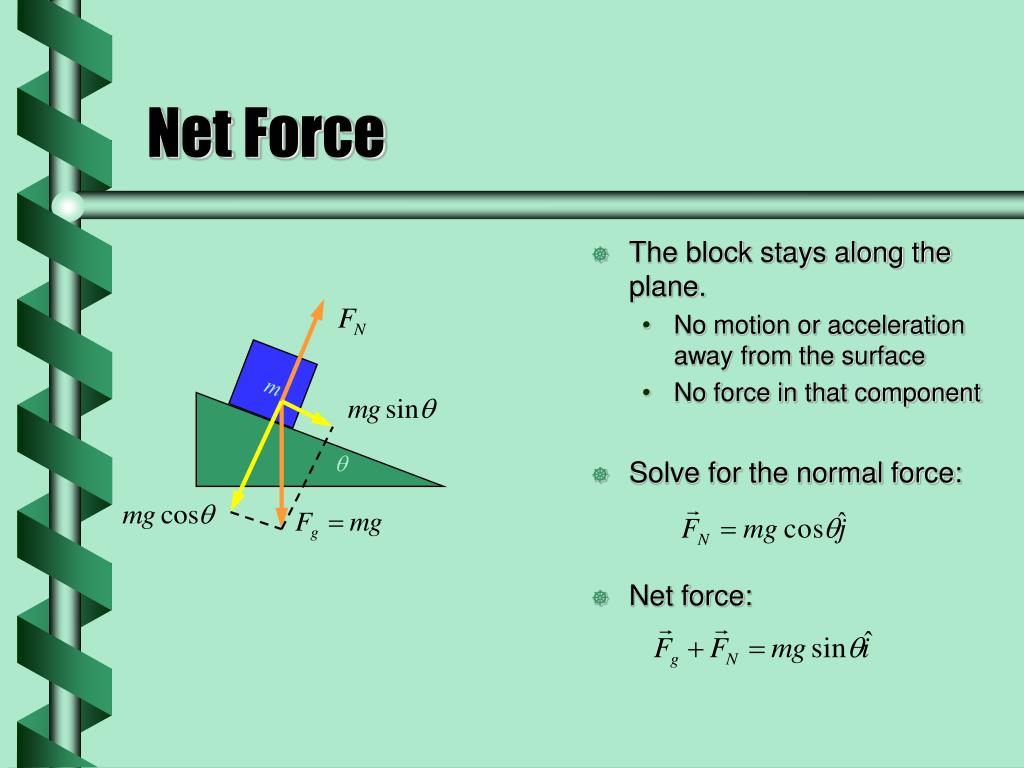
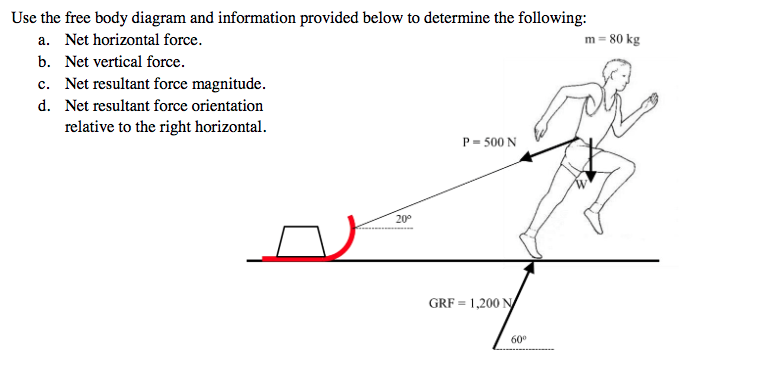
Draw a free-body diagram of the object; Draw coordinate axes on the free-body diagram; Decompose the forces acting on the object into x and y components; Calculate the x and y components of the resultant force by adding the x and y components of all forces; Finally, find the magnitude and direction of the resultant force by using its x and y ...
A free-body force diagram is used to show all the forces acting upon an object to predict the net force and ultimately the path of the object. Each force is drawn as vector arrow. Let's look at some force body force diagrams. These are basically diagrams that show the force or forces that are acting on an object and they help us illustrate how ...
And to be clear, this five newtons, this is equal to the weight, the magnitude of the weight of the object. So that was pretty straightforward, the free body diagram for just the block. And it's really important to see that, because notice, in the free body diagram, all you see is the block. But now let's draw the free body diagram for the shelf.
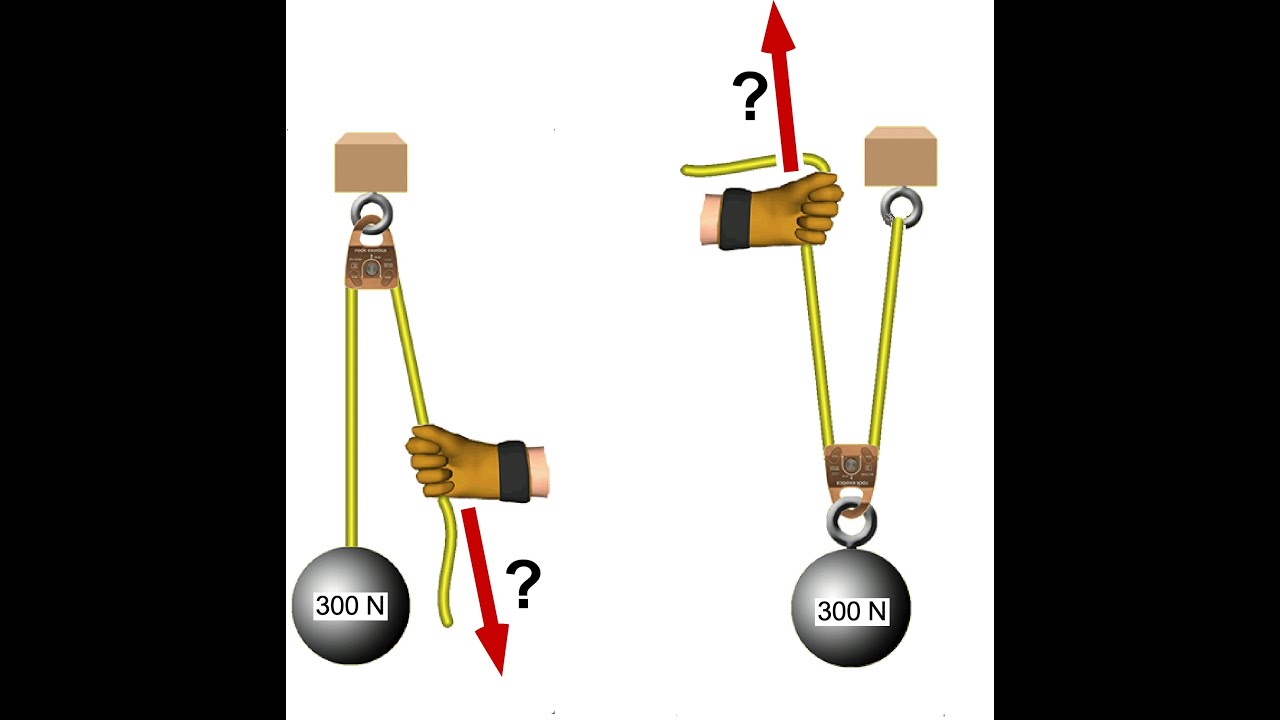
problem (because if we find the net force, we've found the acceleration - via ΣF = ma .). 1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object. We can ignore the pulley (it's not mentioned that we should take it into account, and we know nothing about it, so we can ignore it). Note that the tension FT is the same for both objects,
The Free Body Diagram Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot spot in the top-left corner. Clicking/tapping the hot spot opens the Interactive in full-screen mode. Use the Escape key on a keyboard (or comparable method) to exit from full-screen mode. There is a second hot-spot in the lower-right corner of the iFrame.
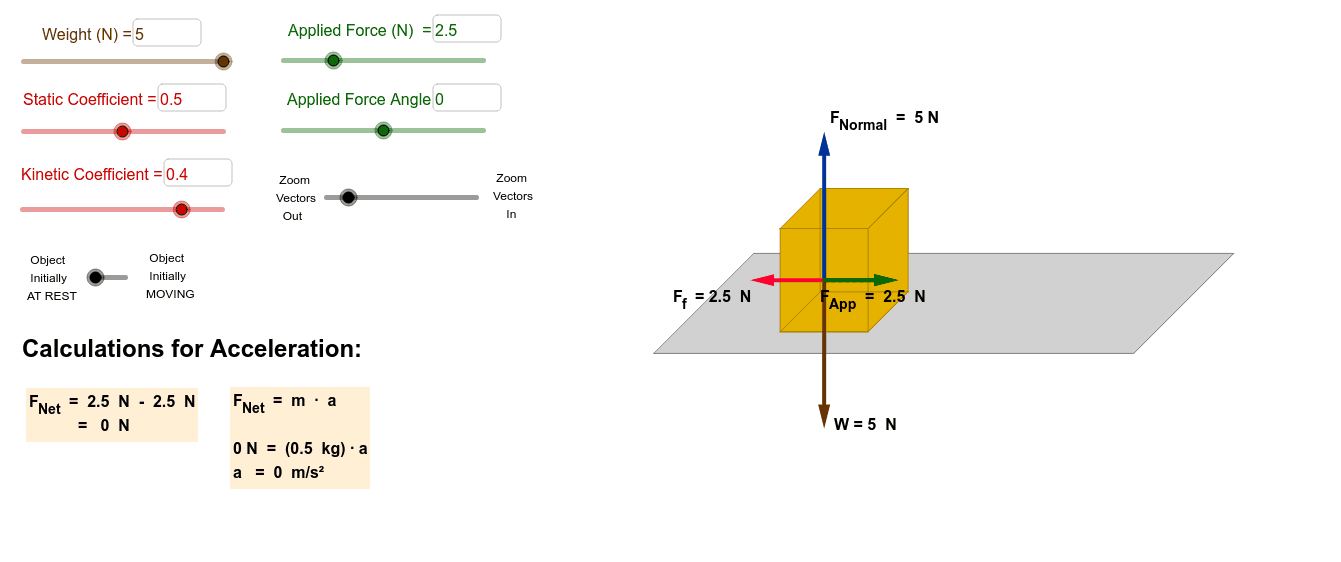
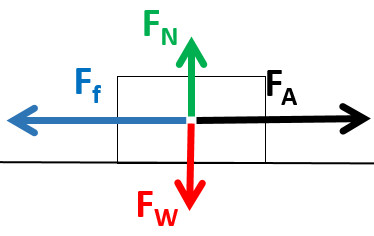
F a = applied force . F N = normal force . F NET = net force . F f = force due to friction . To keep track of how all these forces are affecting a single object, it is a good idea to draw a free body diagram. A free body diagram is just a simple sketch of the object showing all the forces that are acting on it. Draw a quick sketch of the object.
Free-body diagrams for four situations are shown below. The net force is known for each situation. However, the magnitudes of a few of the individual forces are not known. Analyze each situation individually and determine the magnitude of the unknown forces. A book is at rest on a table-top. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this:
Draw a free body diagram. A free body diagram is a quick sketch of an object that illustrates all of the forces acting on it and the direction these forces are acting. Read through the problem and draw a simple sketch of the object in question and the arrows representing every force acting on that object.
The net force on the object must be zero if it is to be a situation of fluid statics such that Archimedes principle is applicable, and is thus the sum of the buoyancy force and the object's weight F net = 0 = m g − ρ f V disp g {\displaystyle F_{\text{net}}=0=mg-\rho _{f}V_{\text{disp}}g\,}
Forces are vectors and add like other vectors, so the total force on the third skater is in the direction shown. In part (b), we see a free-body diagram representing the forces acting on the third skater. Figure 4.3(b) is our first example of afree-body diagram, which is a technique used to illustrate all theexternal forcesacting on a body. The ...
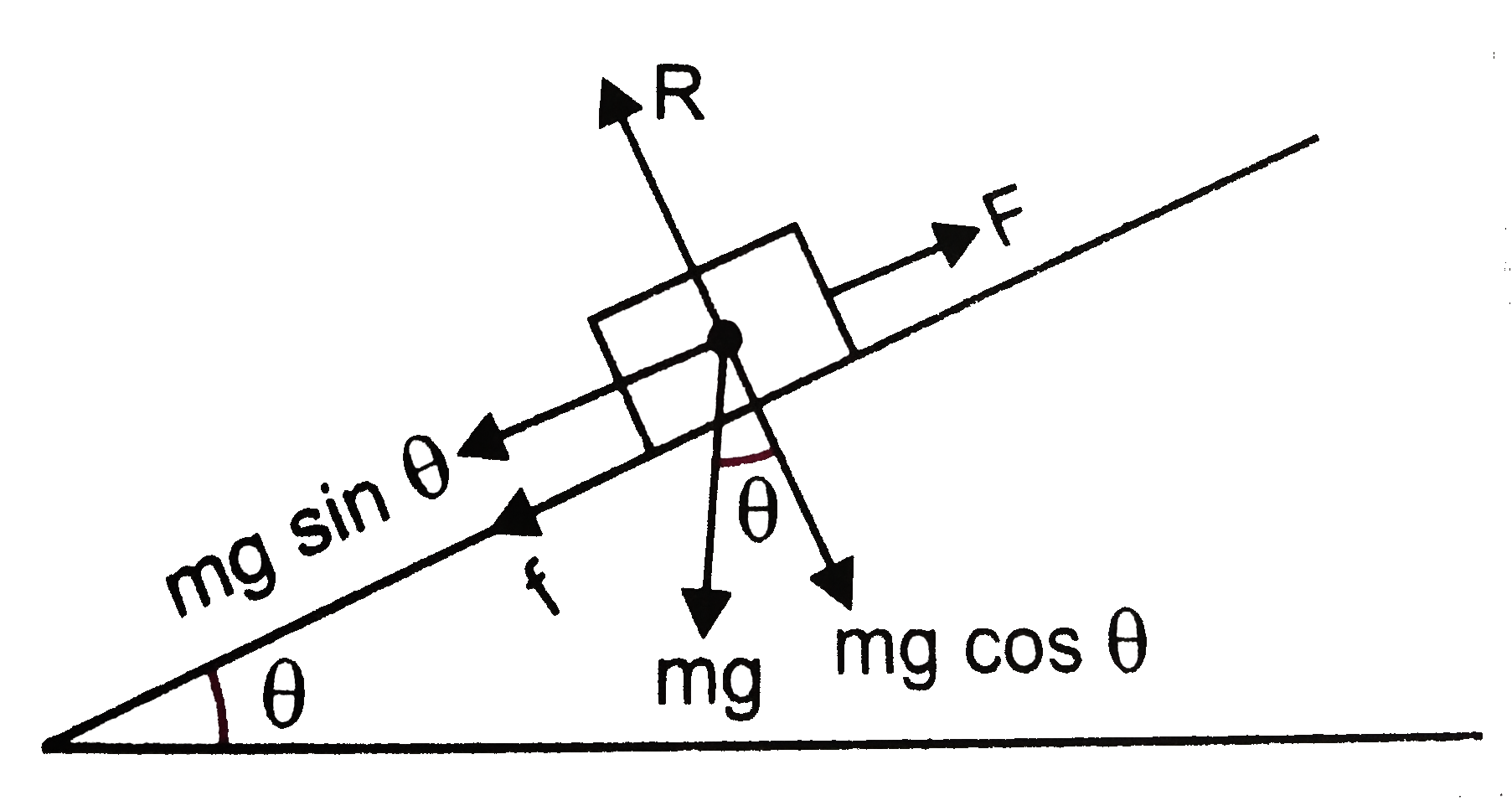
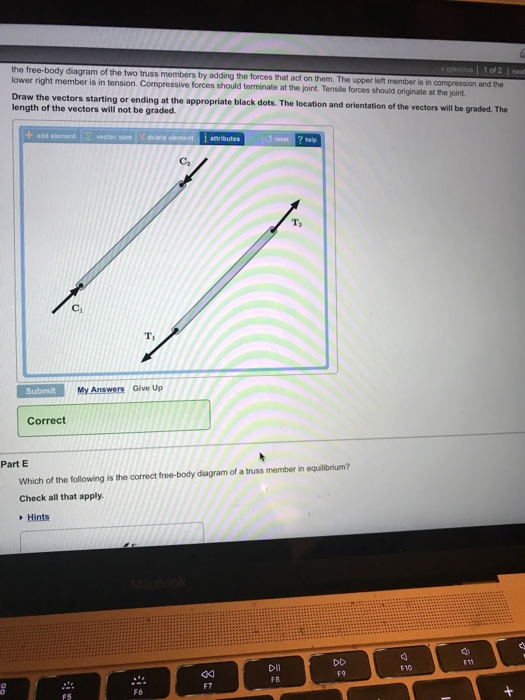
Net Force equations from Free Body Diagrams F n F a F g F k T o 6 F F F ma x a x k x, n 6 F F F F y n a y g, 0 o 6 F F F ma x a k x cosTsin 0 n 6 F F F F y n a g T Pulled up at an angle with friction Pushed down at an angle with friction F a cosT F a sinT F F ma a k x cosT
Free Body Diagrams Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. These diagrams will be used throughout this entire forces unit.
Free Body Diagrams and Net Force Directions: For each of the following diagrams, determine if forces are balanced (same) or unbalanced (not the same), and determine the direction of the net force. 1. 2 3..
View Aleksei Avila - Kami - Finding the Net Force.pdf from BIO 101 at Lemon Bay High School. Using Free-Body Diagrams to find Net Force A. Provide (draw and label) the force(s) to achieve equilibrium


















Comments
Post a Comment