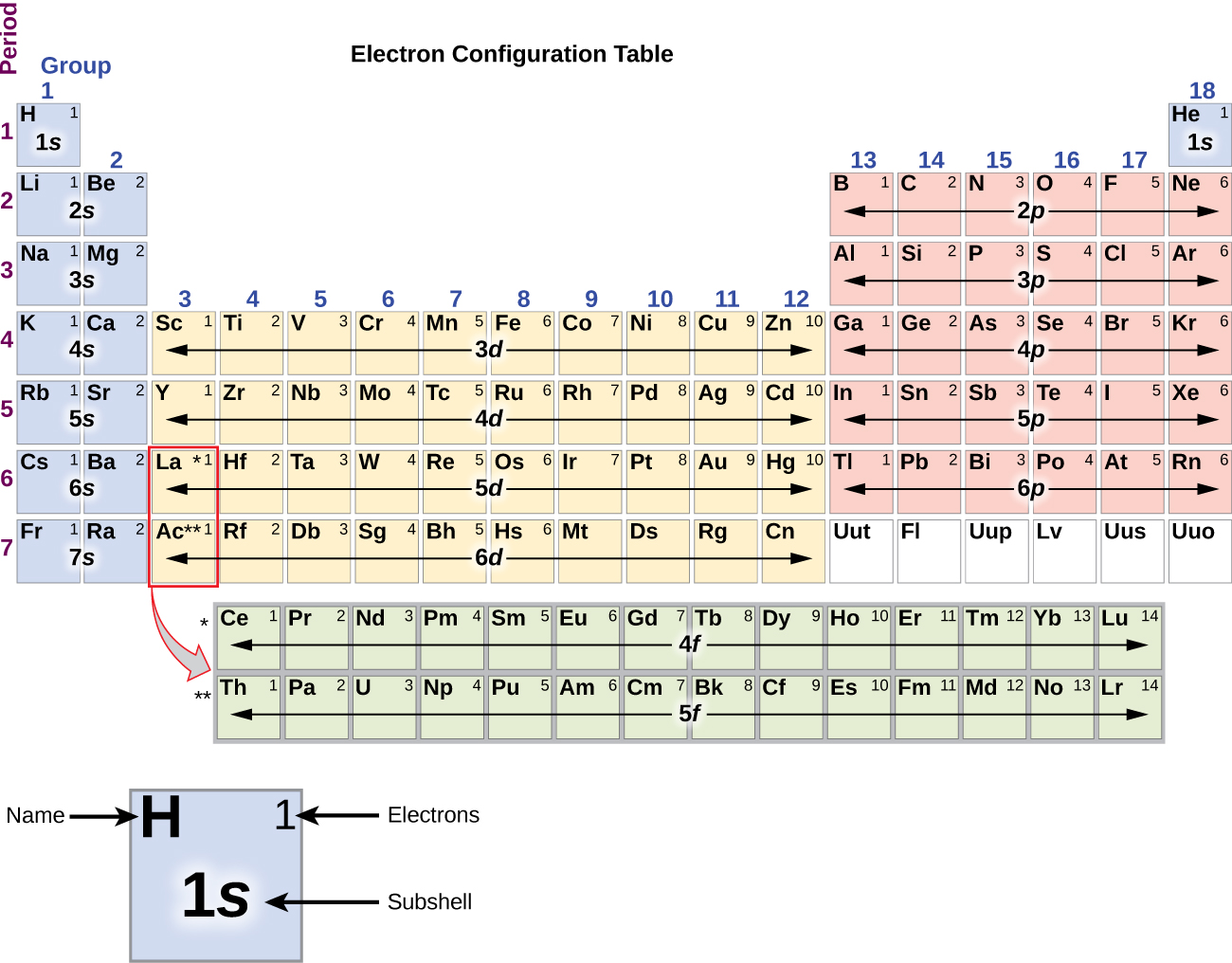
38 rubidium orbital diagram
(2 pts) Write the full e- configuration for the rubidium ion, Rb : 3. (2 pts) Draw the full orbital diagram for the aluminum atom, AI: 4. (2 pts) Draw the condensed orbital diagram for arsenic, As: 5. The electron configuration of lithium shows that lithium has an electron in the last orbital. Therefore, the valency of lithium is 1. Li – e – → Li + The electron configuration of lithium ions shows that lithium ions have only one shell and that shell has two electrons. 3 electrons. 3 protons. 4 neutrons
Lithium (Li) electron configuration with full orbital diagram. Lithium is the 3rd element in the periodic table and the 2nd element in group-1. The atomic number of lithium is 3 and its symbol is 'Li'. The standard atomic mass of lithium is 6.938.

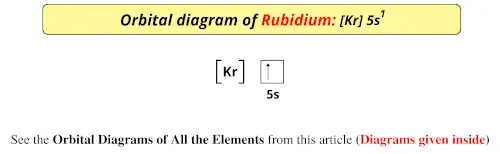
Rubidium orbital diagram
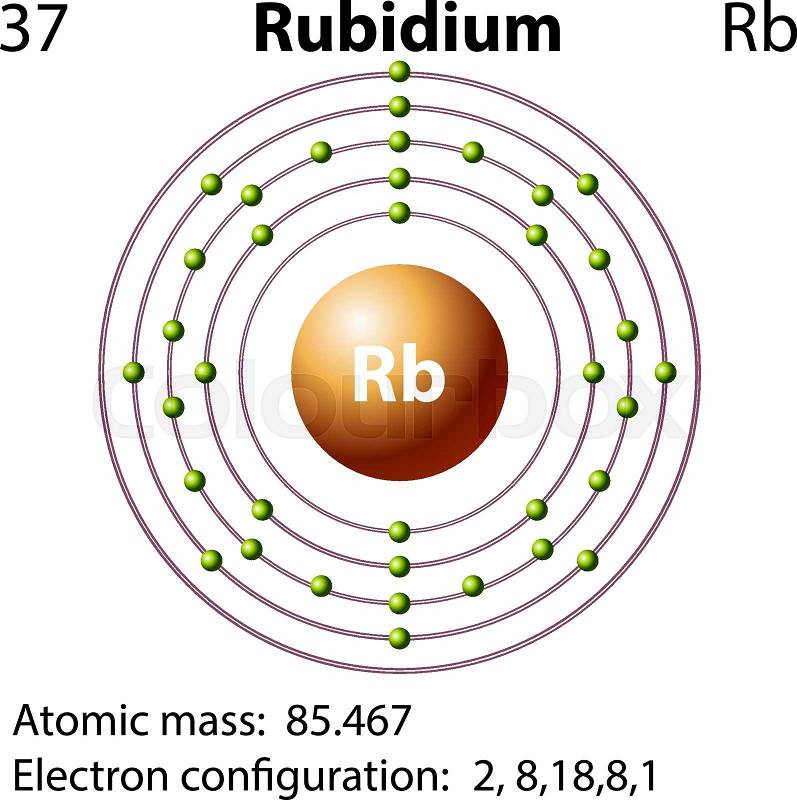
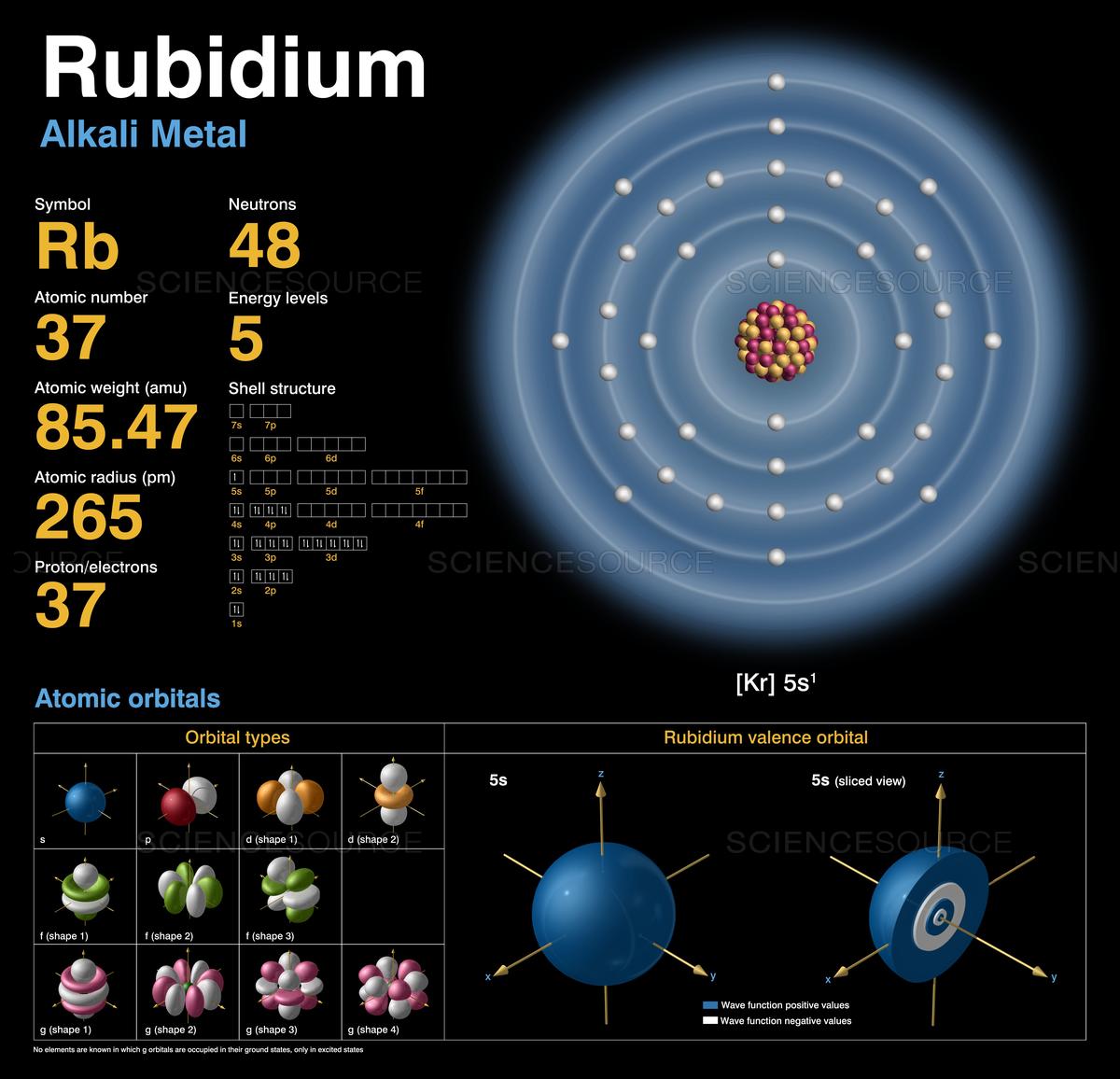
Rubidium Atomic and Orbital Properties Rubidium atoms have 37 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 18, 8, 1] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 2S1/2. What is the order of orbital diagram? In the case of Rubidium the abbreviated electron configuration is [Kr] 5s1. Nevertheless, check the complete configuration and other interesting facts about Rubidium that most people don't know. Rubidium Overview Rubidium Complete Electron Configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4 s2 3 d10 4 p6 5 s1 Abbreviated Electron Configuration [Kr] 5s1 Sources 9) The full electronic configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state is 37Rb85.46 : 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s1 The last subshell of Rb is 5s and thu …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 9. Give the full electron configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state. Provide the orbital diagram of the last subshell ...
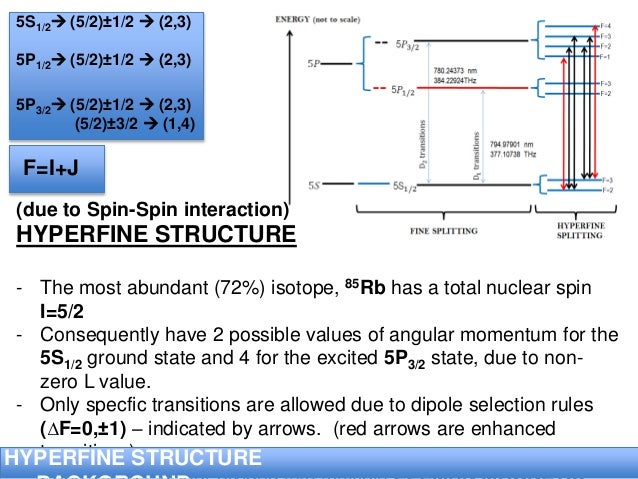
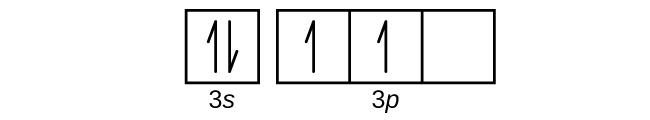
Rubidium orbital diagram. transition. To understand the energy levels of rubidium, we need to consider the interaction between the electron and the nucleus and between both and an external magnetic field. The angular momentum of the valence electron is given by J = L+S (1:) where L is the orbital angular momentum and S is the spin angular momentum. To get the total angular Orbital diagram of Rubidium (Rb) 38: Orbital diagram of Strontium (Sr) 39: Orbital diagram of Yttrium (Y) 40: Orbital diagram of Zirconium (Zr) 41: Orbital diagram of Niobium (Nb) 42: Orbital diagram of Molybdenum (Mo) 43: Orbital diagram of Technetium (Tc) 44: Orbital diagram of Ruthenium (Ru) 45: Aluminum (Al) atom electron configuration (Bohr model) K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, N is the name of the fourth orbit. The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n 2. For example, n = 1 for K orbit. The electron holding capacity of K orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 1 2 = 2 electrons. Alkali metals (IA group) have small ionization energies, especially when compared to halogens or VII A group (see diagram 1). In addition to the radius (distance between nucleus and the electrons in outermost orbital), the number of electrons between the nucleus and the electron(s) you're looking at in the outermost shell have an effect on the ...
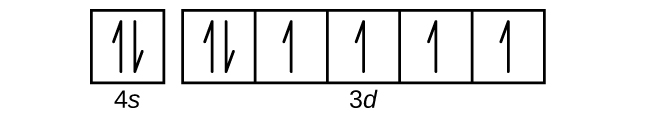
This is called quantum jump. Ground state electron configuration of silicon is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2. The valency of the element is determined by electron configuration in the excited state. The p-orbital has three sub-orbitals. The sub-orbitals are p x, p y and p z. Each sub-orbital can have a maximum of two electrons. The electronegativity of an atom changes depending on the hybridization of the orbital employed in bonding. Electrons in s orbitals are held more tightly than electrons in p orbitals. Hence, a bond to an atom that employs an sp x hybrid orbital for bonding will be more heavily polarized to that atom when the hybrid orbital has more s character. 1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of .. Rb+, Se2−. The first orbital (an s orbital) can contain only two electrons. . Rubidium. This diagram of a rubidium atom shows the electron shell.
Rubidium (Rb) orbital diagram 1s is the closest and lowest energy orbital to the nucleus. Therefore, the electron will first enter the 1s orbital. According to Hund's principle, the first electron will enter in the clockwise direction and the next electron will enter the 1s orbital in the anti-clockwise direction. Problem Details. 9. Give the full electron configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state. Provide the orbital diagram of the last subshell with electrons. Provide the quantum numbers for the last electron. Learn this topic by watching The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers Concept Videos. Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital . Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of rubidium-85 (atomic number: 37), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 37 protons (red) and 48 neutrons (orange). 37 electrons (white) include a relatively unstable electron in the outer shell (ring).
Diagram atom helium, menunjukkan kepadatan probabilitas elektron warna abu-abu. Jari-jari atom adalah jarak dari inti atom ke orbital elektron terluar yang stabil dalam suatu atom dalam keadaan setimbang .
Rubidium has an atomic number of 37, making it an alkali metal. This means that its last shell is an s with only one electron. The full notation is [Kr] 5s1.
Hydrogen electron configuration is 1s 1.Hydrogen is a s-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of hydrogen, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of hydrogen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.. The first element of the periodic table is hydrogen and its position at the beginning of the periodic table.
The hydrogen molecule provides a simple example of MO formation. In the following diagram, two 1s atomic orbitals combine to give a sigma (σ) bonding (low energy) molecular orbital and a second higher energy MO referred to as an antibonding orbital. The bonding MO is occupied by two electrons of opposite spin, the result being a covalent bond.
Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Write the electron configuration and give the orbital diagram of a rubidium (Rb) atom $(Z=37)$..
Rb Rubidium Element information, facts. Rubidium properties, uses and trends | Periodic Table of the Elements - complete information about the rubidium element - Facts, atomic mass, melting point, How to Locate on Periodic Table, History, Abundance, Physical Properties, Thermal Properties, Crystal Structure, Atomic & Orbital Properties, electron configuration, Chemical Properties rubidium ...
Rubidium 87 D Line Data Daniel A. Steck Theoretical Division (T-8), MS B285 Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 25 September 2001 (revision 1.6, 14 October 2003) 1 Introduction In this reference we present many of the physical and optical properties of 87Rb that are relevant to various quantum optics experiments.
7.2 Orbital Energies in Single‐ and Multielectron Species The relationship between the principal quantum number, n, and orbital energy is shown in an orbital energy diagram (Figure 7.2.1). Figure 7.2.1 Identify Orbital Energies in Single-Electron Species Orbital energies (n = 1 to n = 4) in a single‐electron species
Rubidium Electronic configuration. Electronic configuration: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 5s 1 >> Back to key information about the elementBack to key information about the element
Rubidium is no exception to this rule, being silvery-white and melting at 39 ºC. The element has two naturally occurring isotopes. Rubidium-85 is the dominant form, accounting for 72 per cent of the total, while most of the remainder is the radioactive rubidium-87, which has a half-life of 50 billion years.
Rubidium (Rb) has an atomic mass of 37. Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more.
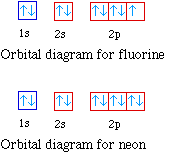
The orbital diagram for sulfur has seven boxes with two arrows pointing in opposite directions and two boxes with one arrow pointing up in each. The arrows. Energy levels: 2, 8, 6 Orbitals: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 If you need to fill in the little boxes, here's one for you. Each arrow represents one electron.
Rubidium (Rb) has an atomic mass of Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more. The orbital diagram has nine boxes with two arrows in the first seven and single arrows in the last two Write the electron configuration and draw the orbital notation for atoms of oxygen and sulfur.
Sep 23, 2021 · The s orbital is spherical and can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons. Elements in column 1 have one electron in the s orbital, and elements in column 2 (plus helium) have two electrons in ...
For each electron shell atom diagram, the element symbol is listed in the nucleus. The electron shells are shown, moving outward from the nucleus. The final ring or shell of electrons contains the typical number of valence electrons for an atom of that element. The element atomic number and name are listed in the upper left.
9) The full electronic configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state is 37Rb85.46 : 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s1 The last subshell of Rb is 5s and thu …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 9. Give the full electron configuration of a rubidium atom in the ground state. Provide the orbital diagram of the last subshell ...
In the case of Rubidium the abbreviated electron configuration is [Kr] 5s1. Nevertheless, check the complete configuration and other interesting facts about Rubidium that most people don't know. Rubidium Overview Rubidium Complete Electron Configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4 s2 3 d10 4 p6 5 s1 Abbreviated Electron Configuration [Kr] 5s1 Sources
Rubidium Atomic and Orbital Properties Rubidium atoms have 37 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 18, 8, 1] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 2S1/2. What is the order of orbital diagram?


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Rubidium-58b601ee3df78cdcd83d20d6.jpg)









Comments
Post a Comment