40 diagram of a carbon atom
Nov 05, 2021 · Diagram 4 shows an example of this carbon bond type. Even more complex than type two and type one, two double bonds are available for the bonding of an atom to carbon. CH2F2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity. CH2F2 or difluoromethane or difluoromethylene is an organic compound of the haloalkane family. Haloalkanes or alkyl halides are organic compounds, which contain at least one halogen atom bonded to the carbon atom. It is a colorless gas at standard temperature and pressure.
Now, there is 1 carbon atom, 1 oxygen atom, and 4 hydrogen atoms in one CH3OH molecule. Therefore the total valence electrons are: (1*4) + (1*6) + (1*4) = 14 valence shell electrons. 2) Sketching a rough diagram. For drawing a rough sketch, it is required to select the central atom of the molecule.

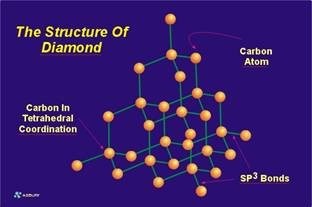
Diagram of a carbon atom
B Carbon has a 2s 2 2p 2 valence electron configuration. By hybridizing its 2s and 2p orbitals, it can form four sp 3 hybridized orbitals that are equal in energy. Eight electrons around the central atom (four from C, one from H, and one from each of the three Cl atoms) fill three sp 3 hybrid For example, a carbon atom can stay in sedimentary rocks for millions of years before moving to a different carbon reservoir. This would be an example of a "very long and slow time scale." If the information is available, indicate a time scale for movement of carbon from one reservoir to the next reservoir. Bonds to other carbon atoms are ignored. This count should be conducted for each carbon atom undergoing any change during a reaction. If the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to a carbon increases, and/or if the number of bonds to more electronegative atoms decreases, the carbon in question has been reduced (i.e. it is in a lower oxidation state).
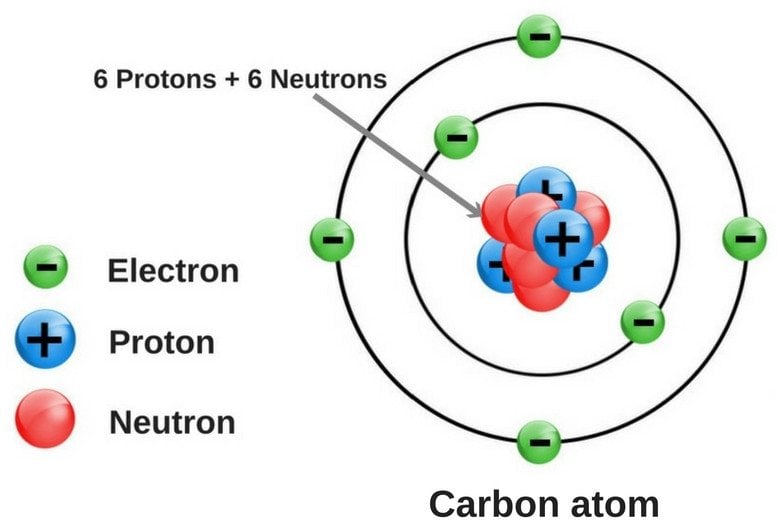
Diagram of a carbon atom. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. Unlike O 3, though, the actual structure of CO 32− is an average of three resonance structures. 1. Because carbon is the least electronegative element, we place it in the central position: 2. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, each oxygen has 6 valence electrons, and there are 2 more for the −2 charge. Aug 27, 2017 · The atomic number of carbon is 6, which is also the number of positively charged protons its atomic nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of negatively charged electrons. Its electron configuration is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^2". The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is 2, each with ... In graphite, each carbon atom uses only 3 of its 4 outer energy level electrons in covalently bonding to three other carbon atoms in a plane. Each carbon atom contributes one electron to a delocalized system of electrons that is also a part of the chemical bonding. The delocalized electrons are free to move throughout the plane.
Carbon (from Latin: carbo "coal") is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds.It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, 12 C and 13 C being stable, while 14 C is a radionuclide ... The structure is drawn using dots which determine the number of valence electrons in an atom and lines between the atoms, determining the number of bonds forming. The maximum number of valence electrons that can be written around an atom is eight. Lewis structure of single carbon and oxygen atom separately is as shown below. Finally, two double bonds might share a carbon atom, as in 1,2-hexadiene. The central carbon atom in such a system is sp-hybridized, and we call such double bonds cumulated. These three isomers are shown in the following diagram, and three other similar isomers will be displayed on clicking the Change Examples button. In cases where ... Carbon plays an essential role in biology because of its ability to form many bonds—up to four per atom—in a seemingly endless variety of complex organic molecules. Many organic molecules contain carbon atoms that have formed strong bonds to other carbon atoms, combining into long chains and rings.
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth.Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many minerals such as limestone.Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle, the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to make ... The below-mentioned diagram is showing the existence of a single bond between the oxygen and carbon atoms. This structure is stabilizing the hydrogen atoms and oxygen atom only where, there is the dearth of two electrons on the carbon atom. The octet of carbon can only be filled with the help of a double bond formed by the carbon and oxygen atoms. C is further to the left than O, so C is the central atom. 2. Arrange the outer atoms around the central atom: H C H O carbon is the central atom 3. Count up the valence electrons: C (4) + O (6) + 2H (2x1) = 12 electrons 4. Draw a bond between each outer atom … Hence, Lewis Structure is also commonly called Electron Dot Structure. Let us proceed to draw the most appropriate LS diagram of CO32- ion. Step 1: Count the Total Number of Valence Electrons. In CO32- ion, we have one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms along with two negatively charged electrons carrying the charge.
The valence electron for carbon (1s22s22p2) and hydrogen (1s1) is 4 and 1, respectively. In ethane, we have two carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms and hence, the total number of valence electron are (2 X 4) + (1 X 6) = 14. Step 2: Drawing the Lewis structure: A carbon atom has 4 valance electrons and it needs 4 more electrons to complete its octet.
After step \(4\), it was found that the octet configuration of the oxygen atom is satisfied but for the carbon atom, it is not satisfied. The oxygen atom possessing \(3\) lone pair of electrons shares two lone pairs with the neighbouring carbon atom. This leads to a triple bond between the carbon atom and oxygen atom, which is shown below.
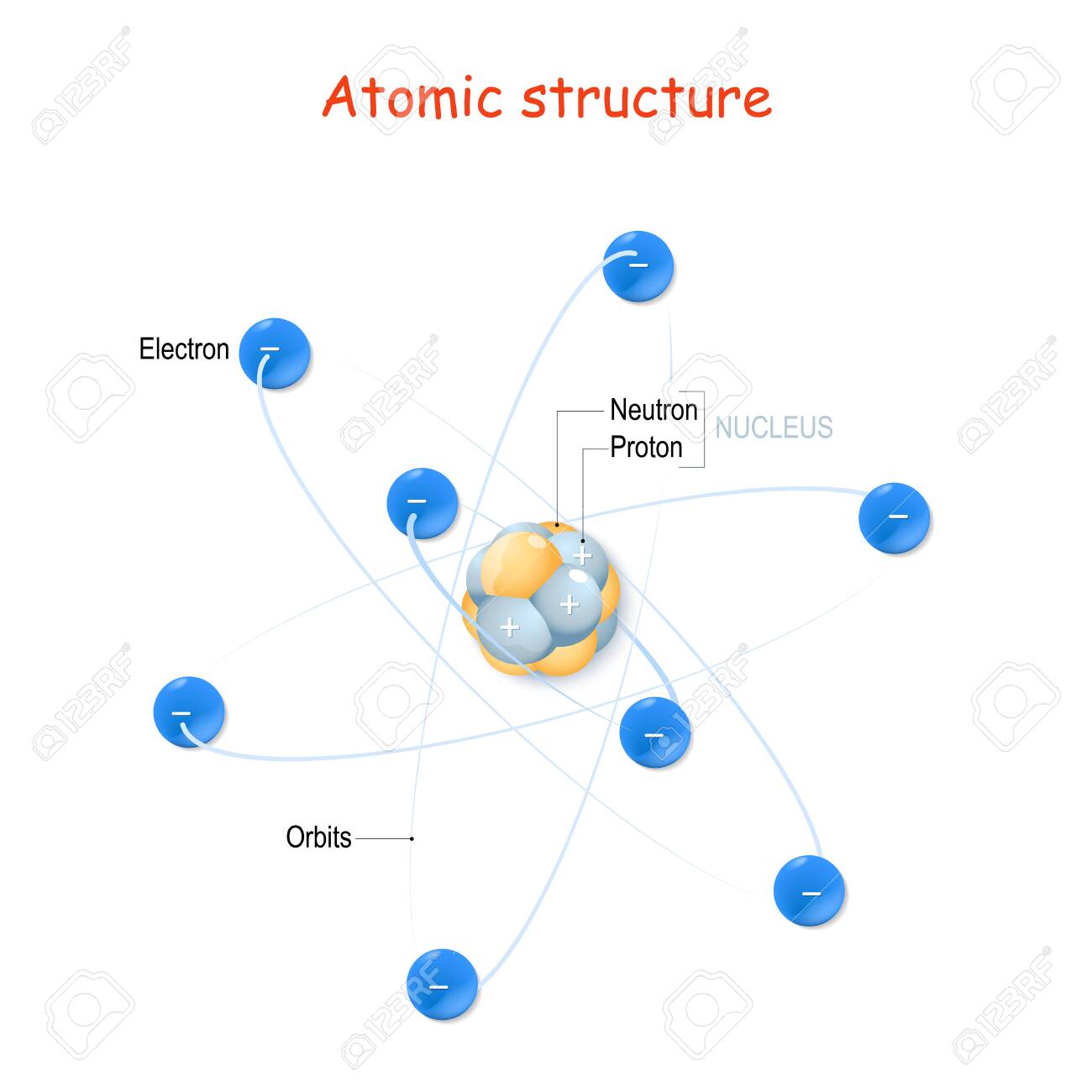
Atomic Structure For Example Carbon Atom Nucleus With Protons And Neutrons Orbits Of Electrons Vector Illustration For Educational And Science Use Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image 155951886
Use Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) to determine the molecular geometry around each carbon atom and then deduce the structure of the molecule as a whole. Solution: Because the carbon atom on the left is bonded to four other atoms, we know that it is approximately tetrahedral. The next two carbon atoms share a triple bond, and each has an additional ...
The structure is the product of a carboxylic acid (the R -portion) and an alcohol (the R' -portion). The general formula for an ester is RCOOR' or RC O 2 R', which is shown below. The R group can either be a hydrogen atom or a carbon chain. The R' group must be a carbon chain since a hydrogen atom would make the molecule a carboxylic acid.
Structure of single-walled tubes . The structure of an ideal (infinitely long) single-walled carbon nanotube is that of a regular hexagonal lattice drawn on an infinite cylindrical surface, whose vertices are the positions of the carbon atoms. Since the length of the carbon-carbon bonds is fairly fixed, there are constraints on the diameter of the cylinder and the arrangement of the atoms on it.
H2CO Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram. It is an organic compound with the molecular formula of H2CO and is classified as an aldehyde. Aldehydes are chemicals having the functional group -HCO- in their molecules and formaldehyde is the lowest member of this group with a single carbon atom.
A carbon reservoir is a place in the Earth System where carbon atoms are stored. Carbon reservoirs can be large like an ocean, microscopic like bacteria and somewhere in-between. Carbon Cycle Process. causes carbon to move from one reservoir to another; examples are photosynthesis, respiration, and combustion.
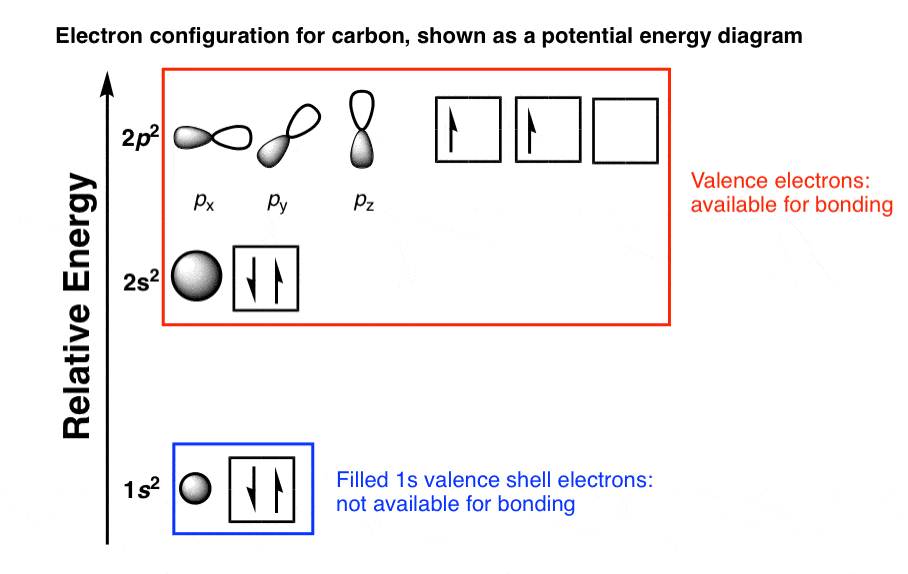
By Hund's rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c. Experimentally, it is found that the ground state of a neutral carbon atom does indeed contain two unpaired electrons.

A Model Of The Carbon Monoxide Co Molecule As An Example Of The Dynamics Of Molecules Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry Ap Chemistry
The steric number can be calculated by adding lone pairs of electrons on the central atom and the number of atoms directly bonded to the central atom. By looking at the structure you can easily see that the number of lone pairs on Carbon is 0. And the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon atoms is 4. Therefore, the Steric Number is =0+4 =4.
Feb 18, 2019 · Step 4 of creating a Lewis dot structure is choosing a central atom for the other atoms to branch off from in the diagram. The central atom of a molecule is typically the atom with the highest electron valence of the atom with the lowest level of electronegativity.
Aug 02, 2020 · DNA Replication Steps/Stages Initiation. This is the stage where DNA replication is initiated. DNA synthesis is initiated within the template strand at a specific coding region site known as origins.; The origin sites are targeted by the initiator proteins, which recruit additional proteins that help in the replication process to form a replication complex around the DNA origin.
STEM Interactives. Molecular models are the heart of Next-Generation Molecular Workbench. We've created many models that dynamically illustrate scientific concepts and allow you to interact with molecules or macroscopic phenomena like pendulums (at right) and their environment in various ways.
Jun 27, 2019 · 2) For reaction 3, it’s the same process (as reaction 1) by which another phosphate group is added to fructose-6-phosphate, but this time on its 1st carbon atom, phosphate goes in and removes the H of the OH on the CH2OH on carbon 1 of fructose, attaches itself to carbon 1, thus release another H atom.
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO 2) is an acidic colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas.The current concentration is about 0.04% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm.
Jul 24, 2015 · In the above diagram, the vertex and the ends of the lines represent the carbon atoms. The two end #"C"# atoms each have one bond to middle #"C"# atom, so the number of hydrogen atoms on them is #4-n = 4-3 = 3#. The middle #"C"# atom has two bonds going to the other carbons, so it has #4-n = 4-2 = 2# hydrogen atoms.
Bonds to other carbon atoms are ignored. This count should be conducted for each carbon atom undergoing any change during a reaction. If the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to a carbon increases, and/or if the number of bonds to more electronegative atoms decreases, the carbon in question has been reduced (i.e. it is in a lower oxidation state).
For example, a carbon atom can stay in sedimentary rocks for millions of years before moving to a different carbon reservoir. This would be an example of a "very long and slow time scale." If the information is available, indicate a time scale for movement of carbon from one reservoir to the next reservoir.
B Carbon has a 2s 2 2p 2 valence electron configuration. By hybridizing its 2s and 2p orbitals, it can form four sp 3 hybridized orbitals that are equal in energy. Eight electrons around the central atom (four from C, one from H, and one from each of the three Cl atoms) fill three sp 3 hybrid

Draw The Orbital Diagram For Carbon In Co 2 Showing How Many Carbon Atom Electrons Are In Each Orbital Study Com








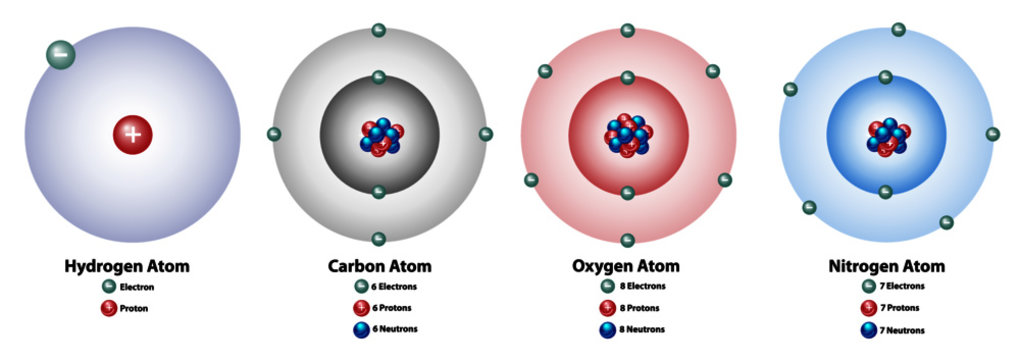
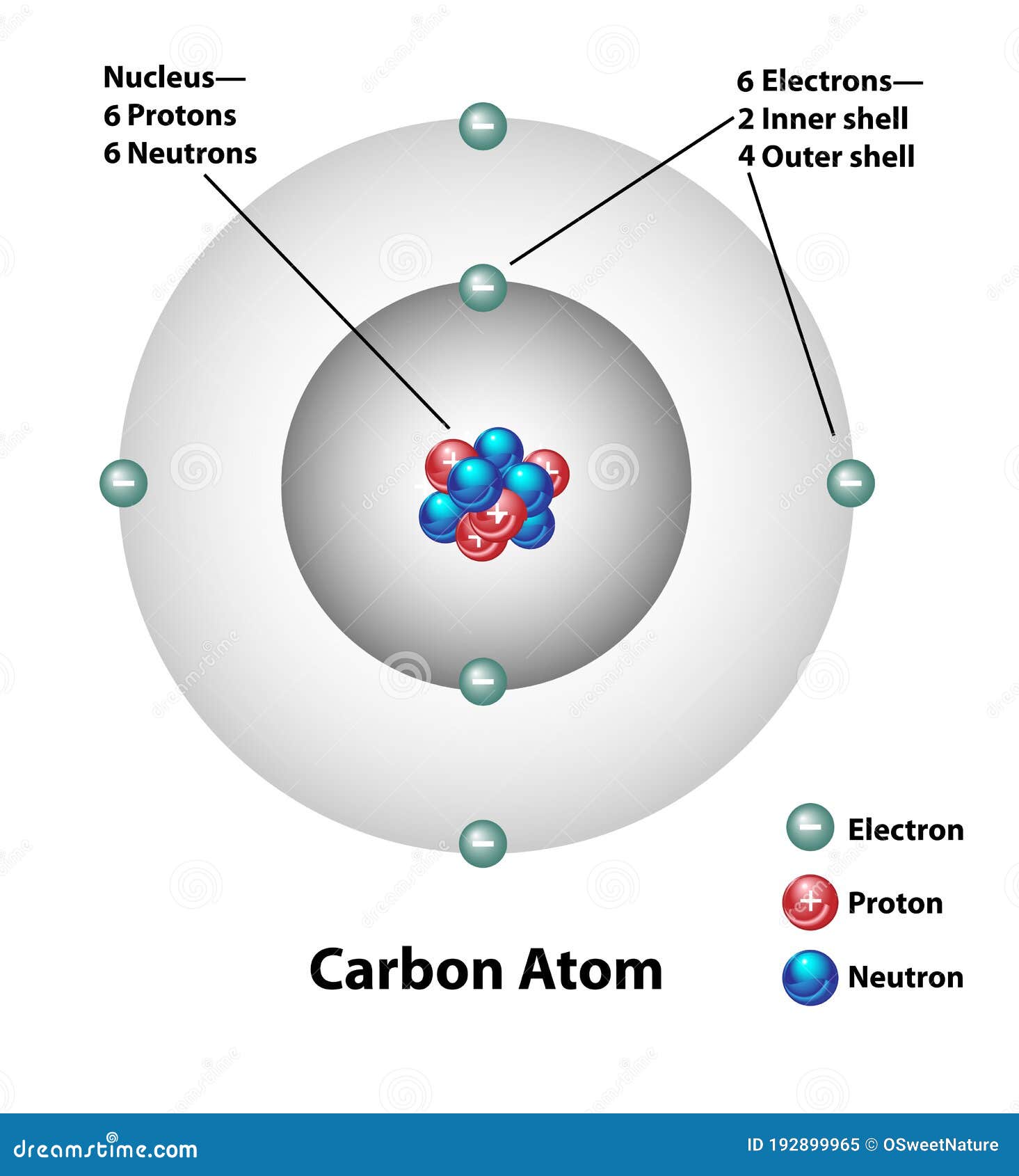

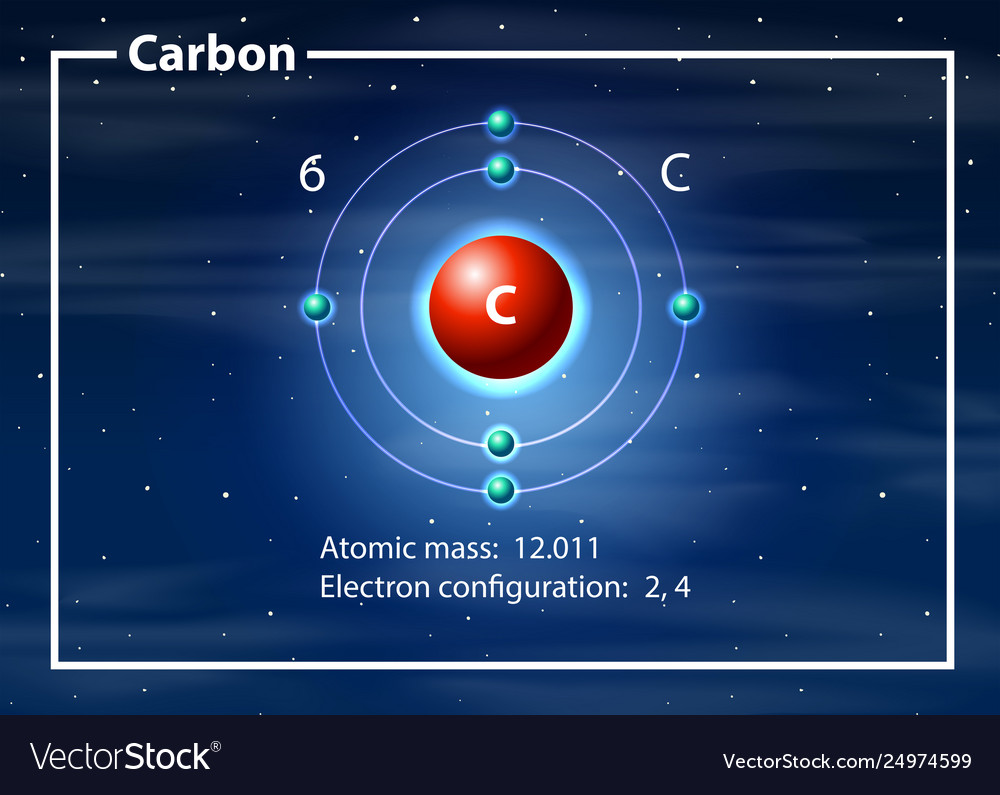








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/carbonatom-58b602855f9b5860464c8bf6.jpg)



Comments
Post a Comment