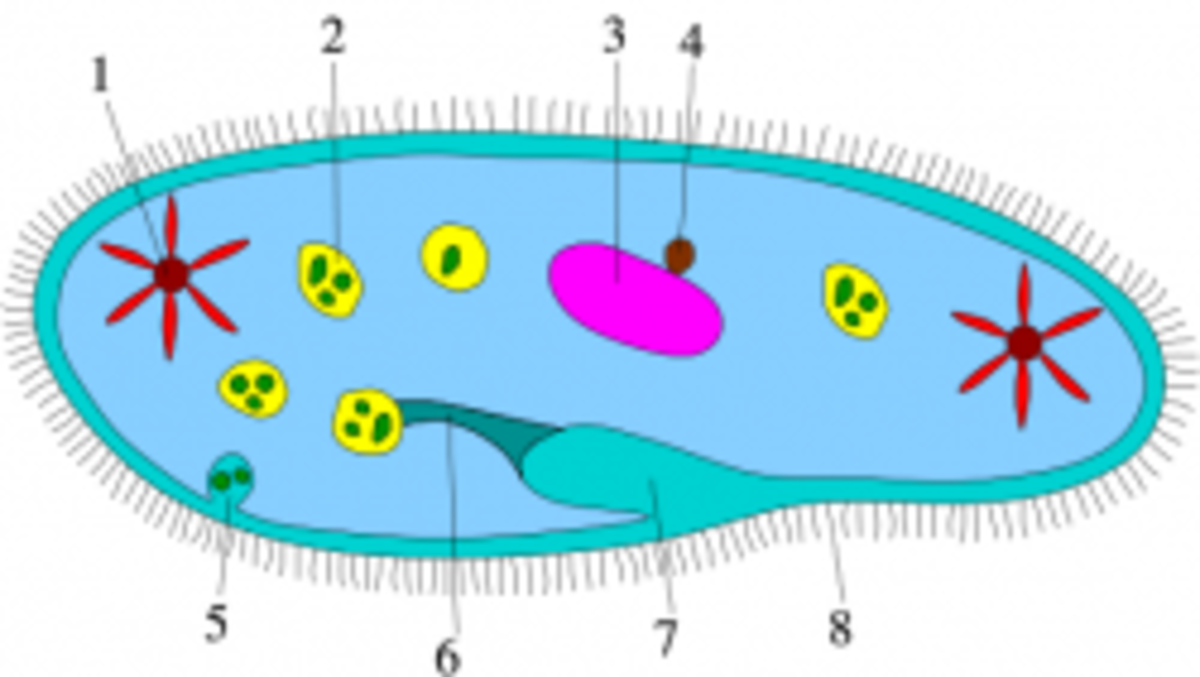
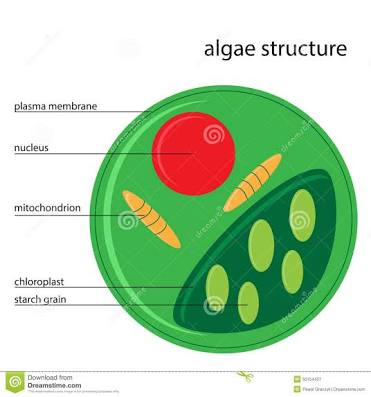
38 diagram of protist
Euglena is a motile, single-celled (unicellular) organism that is commonly found in aquatic habitats. They were among the first organisms in the kingdom Protista to be seen under the microscope, looking like a tiny particle making small movements in the water. Euglena is generally green in color due to the presence of chloroplast, the organelle ... Oct 29, 2020 · Amoeba is an aquatic, single-cell (unicellular) organism with membrane-bound (eukaryotic) organelles that has no definite shape. It is capable of movement. When seen under a microscope, the cell looks like a tiny blob of colorless jelly with a dark speck inside it.
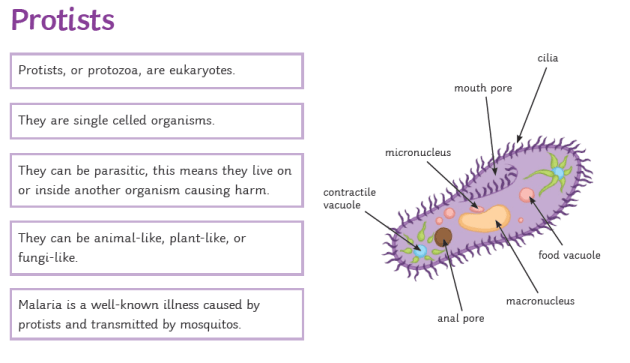
Jul 13, 2020 · A Paramecium is a free-living, motile, single-cell (unicellular) organism belonging to the kingdom Protista that are naturally found in aquatic habitats. They have a lifespan of a hundred, a thousand or even a million years. They are the most common of all ciliate organisms that are characterized by the presence of cilia all along their transparent and colorless body.

Diagram of protist
The protists called red algae support coral reefs by providing much needed nutrients for coral animals. Red algae also produces minerals corals need to form reefs. ... In the diagram of a lichen, label the alga and the fungus. Then, on the lines below, describe what benefits the fungus and alga each derive from their association in the lichen. Protist Mini Quiz #3 1. What are the three groups of protists? 2. Name two of the four types of green protists 3. What does "protozoan"mean? 4. How are animal-like protists classified? 5. List one thing that a pseudopod is used for. Protist Internal Structure. Because protists are eukaryotes, each protist cell contains a nucleus. This nucleus protects the protist's DNA, which is the blueprint or code that runs every function ...
Diagram of protist. Animal Like-Protists ( Flowchart) Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. We were unable to load the diagram. You can edit this template on Creately's Visual Workspace to get started quickly. Adapt it to suit your needs by changing text and adding ... - Protists Facts and Types - Animal Like, Plant Like, Fungus Like For most individuals, the first images seen through the lens of a microscope are protists-- unicellular organisms that don't possess enough characteristics to be defined as purely plant or animal.. The organisms within the Kingdom Protista contain a nucleus, like all Eukaryotes, and are categorized as plant-like, animal-like ... protists 4+euglena, amoeba, paramecium, volvox What is a protist?Use your Guided Notes handout with this slideshow. Protist—an organism from the Kingdom Protista May 21, 2019 · All plant, protist, fungal and animal cells are eukaryotes. Most of them are multicellular, although there are some exceptions. In contrast, prokaryotes – bacteria and archaea – are single-celled organisms, with only a few exceptions. Prokaryotes tend to have smaller cell sizes than eukaryotes.
Goal 4 - Viruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi Notes. Viruses - Pages 475-483. Viruses. Not living. Don't grow or develop. No respiration. Only reproduce within a host (can't do it alone MUST have a host) Virus multiply through the lytic cycle where the virus attacks the host, injects it nucleic acid into the host, and then spreads or ... FOSS Next Generation © The Regents of the University of California Can be duplicated for classroom or workshop use. Diversity of Life Course Investigation 3: The Cell Feb 12, 2015 - Venn diagram of the Kingdoms of Fungi, Protista, Plants. Life Cycle of Fungus-like protists. A fungus-like protist lives a part of its life as a haploid cell and the other part as a diploid cell. The haploid cell will usually join with another haploid cell to make a diploid cell. This cell will continue to grow and will have many nuclei. Once the cell gets mature enough it will form sporangium.
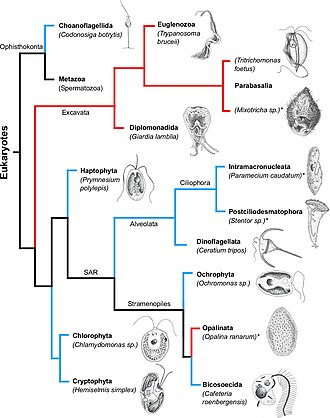
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms. ... Fungi, animals, and other heterotrophic protist-like organisms such as choanoflagellates and Mesomycetozoea are now considered part of the larger group termed opisthokonts (Cavalier-Smith, 1987) in reference to the posterior flagellum. Identify the kingdom that contains protists Draw a diagram of a protist cell Define mitochondria and Golgi bodies Find the nucleus of a protist cell; Practice Exams. Final Exam Protists are microscopic organisms. Cell structure is eukaryotic. Protists is surrounded by plasma lemma (cell membrane). There may be an outer covering of pellicle, cuticle, shell or cellulose wall. It contains organelles like mitochondria, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, 80S ribosomes, etc. They have typical 9+2 fibrils. What is the name of the structure shown in the diagram? It is also known as the "powerhouse" of the cell. answer choices . Chloroplast. Mitochondrion. Nucleus. ... Q. An Amoeba is a unicellular, animal-like protist that lives in ponds and streams. According to cell …

The Following Diagram Shows An Example Of An Animal Like Protist This Protist Does Not Contain A Brainly Com
A single cell protist that moves and eats using cilia. It is a heterotroph. capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction.
Describe representative protist organisms from each of the six presently recognized supergroups of eukaryotes; In the span of several decades, the Kingdom Protista has been disassembled because sequence analyses have revealed new genetic (and therefore evolutionary) relationships among these eukaryotes. ... This diagram shows a proposed ...
A protist is any eukaryote that cannot be classified as a plant, animal, or fungus. There are several types of protists. We will be learning about three types of protists: protozoans, algae, and decomposers. In this lab you will be observing a type of protist called a protozoan. A protozoan is a protist that is similar to an animal.
Plasmodium, commonly known as malaria parasites, may be described as a genus of intracellular parasitic protozoa. They are obligate parasites of insects (such as mosquitoes) and vertebrates and thus referred to as digenetic parasites. They require two different hosts in order to complete their life cycle. In vertebrates, they multiply within ...
Paramecium. A single cell protist that moves and eats using cilia. It is a heterotroph. Paramecium are capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction. Amoeba. A single cell protist that moves by stretching its cytoplasm into pseudopods or false feet. Surrounds and engulfs its food. It is a heterotroph.
Protista Classification The kingdom Protista (in the five kingdom system) contains mostly unicellular eukaryotes. This taxonomic grouping is polyphyletic and based only on cellular structure and life styles not on any molecular evidence. Using molecular biology and detailed comparison of cell structure, scientists
Explore the parts of an electrochemical cell, the definition of an electrochemical cell diagram, the functions of the anode and the cathode, and how to make a homemade battery. ... Protist is the ...
Feb 19, 2021 · A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. ... Functions, Labeled Diagram; Animal Cell- Definition, Organelles, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram, Worksheet; Amazing 27 things under the microscope (diagrams and descriptions)
Paramecium (also Paramoecium, / ˌ p ær ə ˈ m iː ʃ (i) ə m /, PARR-ə-MEE-sh(ee-)əm, /-s i ə m /, -see-əm) is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. Paramecia are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and are often very abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily ...
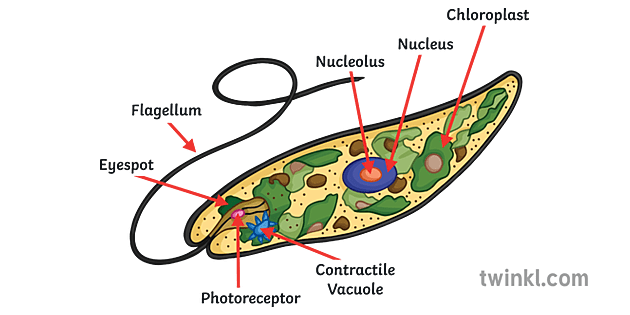
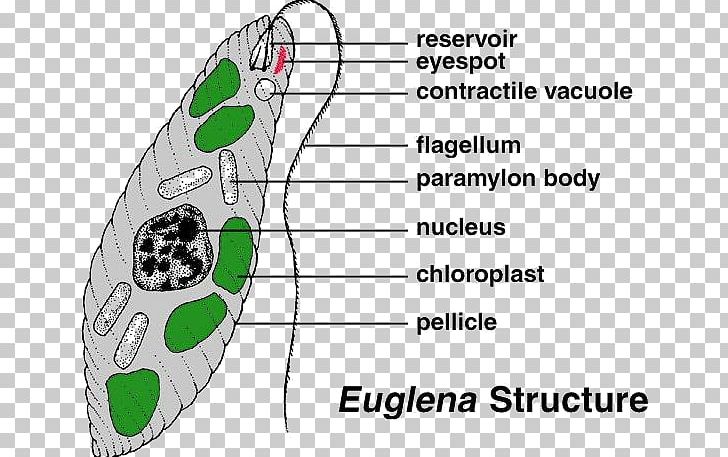
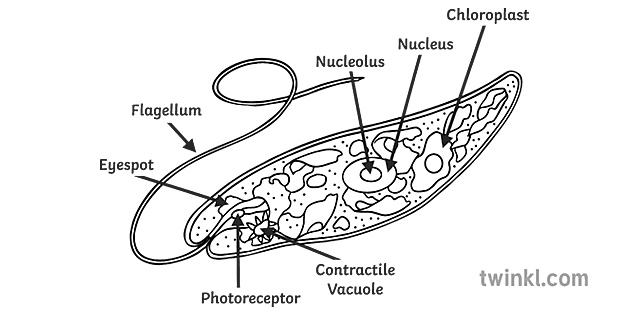
Since Euglena is a eukaryotic unicellular organism, it contains the major organelles found in more complex life. This protist is both an autotroph, meaning it can carry out photosynthesis and make its own food like plants, as well as a heteroptoph, meaning it can also capture and ingest its food.
SWIFT OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS, INC. Microscopes • Digital Imaging Products 1-800-523-5544 San Jose • San Antonio www.swiftoptical.com Pond Life: Macro & Microscopic Views Lesson Plan Page 4 Researching the Protists Next to your diagram of each protist, provide the
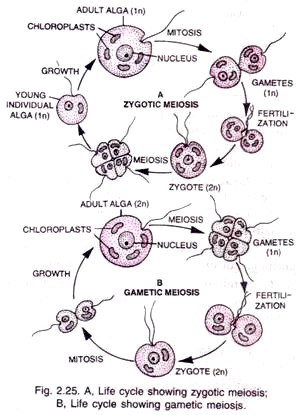
Protists exhibit a great deal of variation in their life histories (life cycles). They exhibit an alternation between diploid and haploid phases that is similar to the alternation of generations found in plants. Protist life cycles vary from diploid dominant, to haploid dominant. A generalized eukaryote life cycle is shown in Figure 1.
Protists are simple eukaryotic organisms that are neither plants nor animals or fungi. Protists are unicellular in nature but can also be found as a colony of cells. Most protists live in water, damp terrestrial environments or even as parasites. Euglena, a eukaryotic protist. The term 'Protista' is derived from the Greek word "protistos ...
Protists use cilia, pseudopods, or flagella to move. Protist Reproduction. Protists have complex life cycles. Many have both asexual and sexual reproduction. An example is a protist called Spirogyra, a type of algae, shown Figure below. It usually exists as haploid cells that reproduce by binary fission.
Diagram of the ciliate Paramecium Nuclei [ edit ] Unlike most other eukaryotes , ciliates have two different sorts of nuclei : a tiny, diploid micronucleus (the "generative nucleus," which carries the germline of the cell), and a large, ampliploid macronucleus (the "vegetative nucleus," which takes care of general cell regulation, expressing ...
Protoctists are microscopic single-celled organisms. Some protoctists, such as Amoeba, have features like an animal cell. Others, such as Chlorella, have chloroplasts and are more like plants ...
The World of Protists. For Students 9th - 12th. In this protists worksheet, students will look at 3 diagrams showing the steps of how an amoeba finds and eats its food. Students will complete 2 short answer questions based on the diagrams. Get Free Access See Review.
ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the two important methods of reproduction in protists. The methods are: 1. Asexual Reproduction 2. Sexual Reproduction. Method # 1. Asexual Reproduction: It involves only one parent. All the young ones produced asexually have the same genetic constitution as that of the parent and are called clones. ADVERTISEMENTS: Asexual reproduction […]
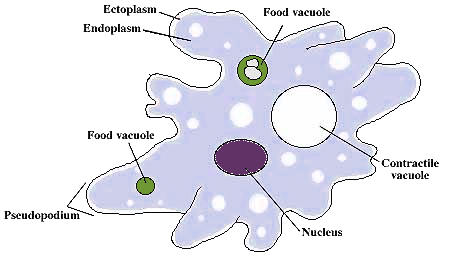
Friday, April 9th 2021. | Diagram. Cell Membrane Protist. All protist cells are surrounded by a cell membrane, which is a fluid, protective layer that helps to separate the protist cell from its external environment, keeping everything inside safe and. Single protist cells range in size from less than a micrometer to thousands of square meters ...
A protist (/ ˈ p r oʊ t ɪ s t /) is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus.While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely ...
Volvox is a polyphyletic genus in the volvocine green algae clade. Each mature Volvox colony is composed of up to thousands of cells from two differentiated cell types: numerous flagellate somatic cells and a smaller number of germ cells lacking in soma that are embedded in the surface of a hollow sphere or coenobium containing an extracellular matrix made of glycoproteins.
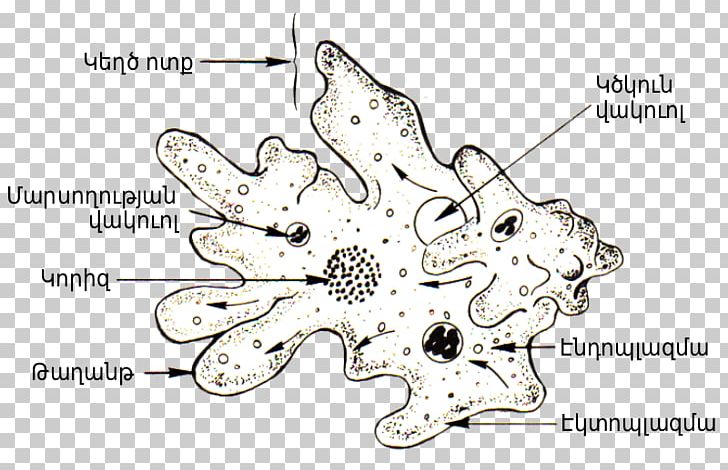
Amoeba Proteus Diagram Cell Protist Png Clipart Algae Amoeba Amoeba Proteus Area Biology Free Png Download
The Kingdom Protista consists of eukaryotic protists. Members of this very diverse kingdom are typically unicelluar and less complex in structure than other eukaryotes.In a superficial sense, these organisms are often described based on their similarities to the other groups of eukaryotes: animals, plants, and fungi. Protists do not share many similarities, but are grouped together because ...

Venn Diagram Hack 1 Pdf Protists Bacteria Protists And Bacteria Are Both Classified As Living Bacteria Have Complex Cell Walls Composed Primarily Of Course Hero
Draw and label a detailed picture of each protist (DO NOT RUSH THROUGH THIS ASSIGNMENT). Each drawing needs to be ¾-1 page in size. Place a title at the top of each page/picture. On the bottom of each picture, place the following information about each protist: method of movement. how they obtain/get food. how they reproduce. any unusual ...
Protist Internal Structure. Because protists are eukaryotes, each protist cell contains a nucleus. This nucleus protects the protist's DNA, which is the blueprint or code that runs every function ...
Protist Mini Quiz #3 1. What are the three groups of protists? 2. Name two of the four types of green protists 3. What does "protozoan"mean? 4. How are animal-like protists classified? 5. List one thing that a pseudopod is used for.
The protists called red algae support coral reefs by providing much needed nutrients for coral animals. Red algae also produces minerals corals need to form reefs. ... In the diagram of a lichen, label the alga and the fungus. Then, on the lines below, describe what benefits the fungus and alga each derive from their association in the lichen.

Euglena Cross Section Diagram Representative Protists Euglenoid Plant Like And Animal Like Microscopic Creature All Cell Part Nucleus Flagellum Eyespot Basal Body Pellicle Mitochondrion Chloroplast Poster Id 169914974





.jpg)













Comments
Post a Comment