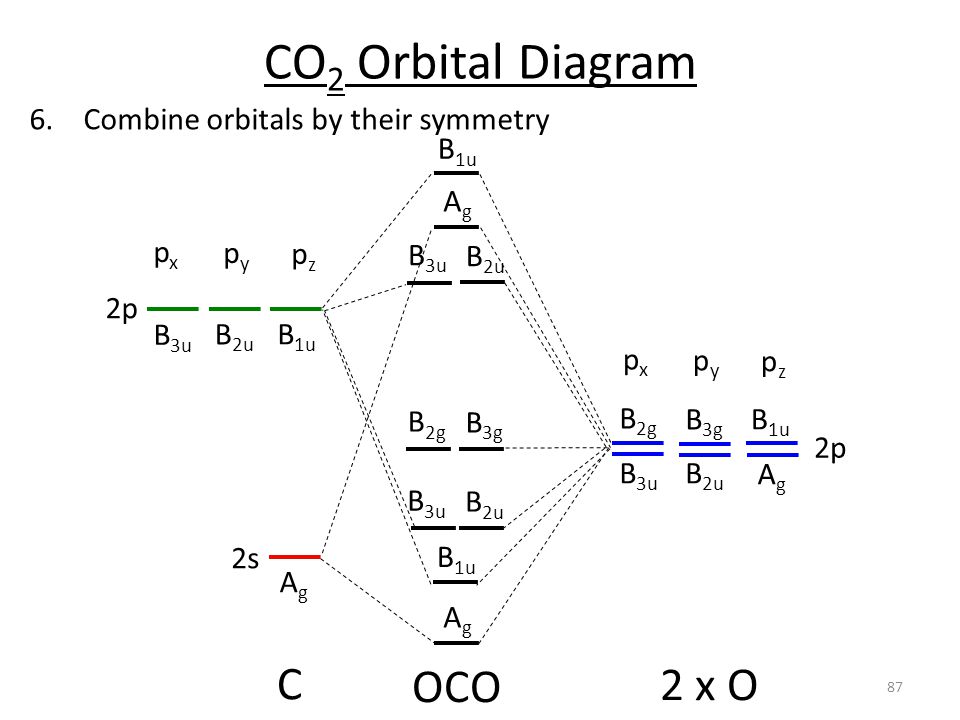
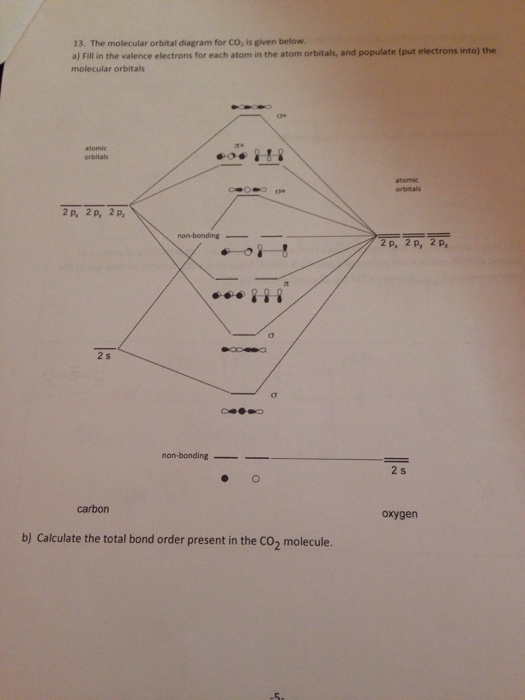
38 co2 molecular orbital diagram
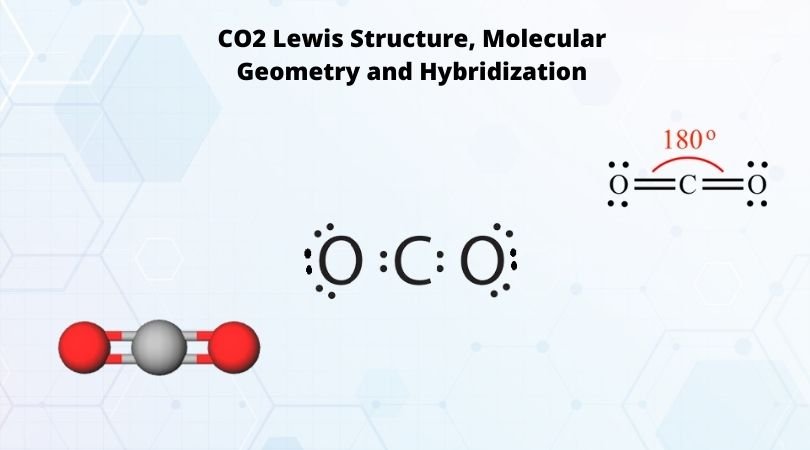
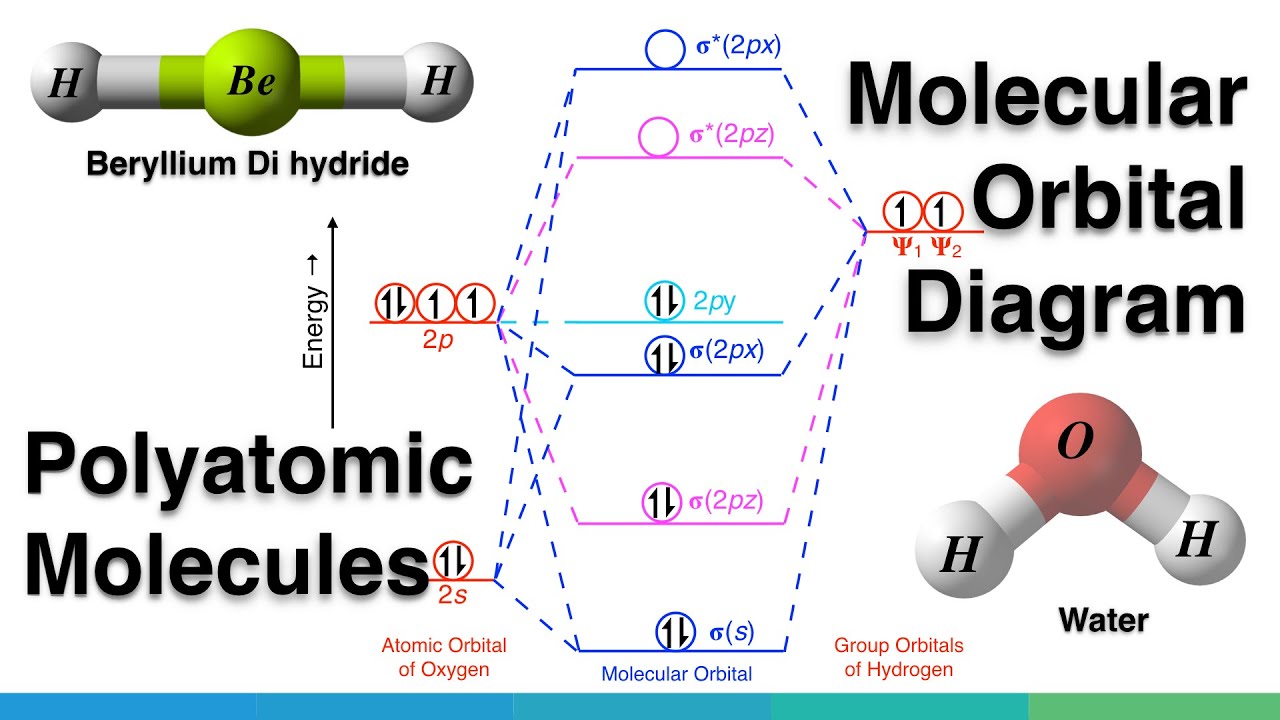
Aug 10, 2020 · Electrochemical reduction of CO2 is a promising route for sustainable production of fuels. ... Kohn–Sham molecular orbital analysis revealed that ... The Gibbs free energy diagram of the CO 2 … Carbon dioxide (CO2), molecule is triatomic and linear like Beryllium di hydride (BeH2) However, unlike hydrogen as peripheral atoms in BeH2, there are oxyge...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Co2 molecular orbital diagram
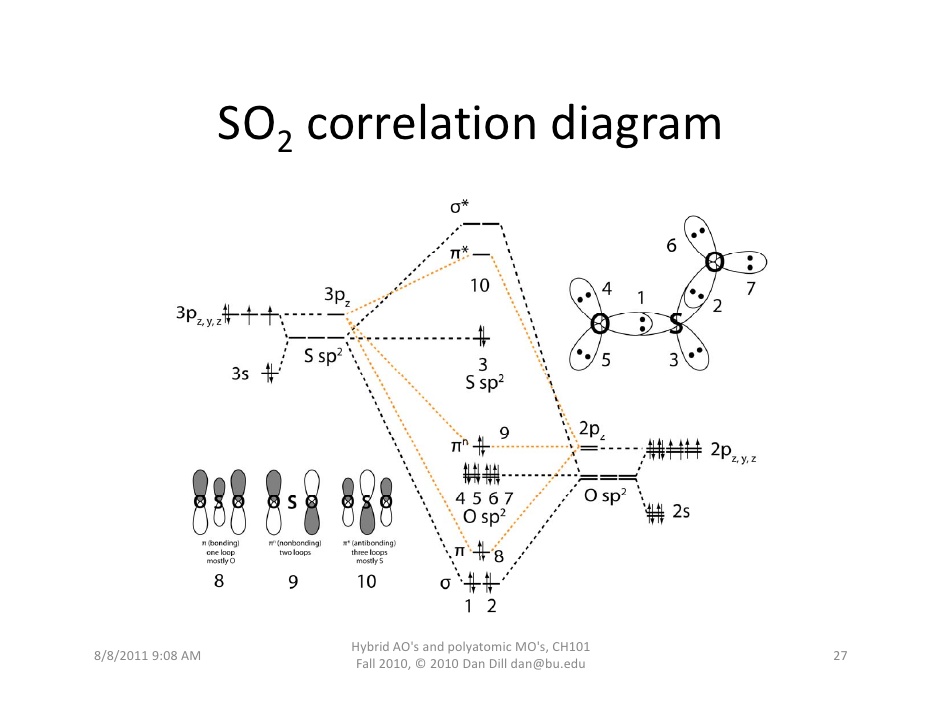
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals. Whereas molecular geometry considers only the atoms. In absence of a lone pair, both the geometries are the same for any compound. Below is the 3D view of the geometry of the SO2 molecule. SO2 Geometry. Now let’s learn the last topic of this article, the molecular orbital diagram of SO2. SO2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Nov 20, 2021 · The molecular orbital diagram of SO2 is attached below: A molecular orbital diagram gives us an idea about how the atomic orbitals of two different atoms can fuse and give rise to a new orbital. This further helps us to find out the bond order, bond length, and bond strength of any compound.
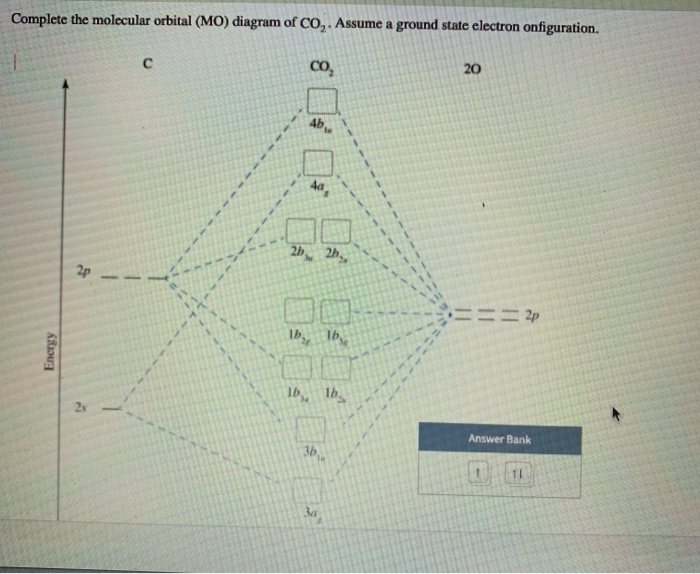
Co2 molecular orbital diagram. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above. Nov 23, 2021 · CO2 doesn’t have any lone pair, so both geometries are the same in this case. Let’s move on to the molecular orbital diagram of this compound. CO2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. #Chemistryunplugged #InorganicchemistryCarruthers Organic Chemistryhttps://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5a2l_9HUAuf7zVJKwRBlAvQuQ_s7wvDxClayden Organic Ch... Watch the video solution for the question: Draw the orbital diagram for ion Co 2+.. . can be accommodated in the metal d orbitals. • d0 ions •d7 ions – Fe1+, Ru1+, Co2+, Rh2+, Ni3+, etc. . σ-ML4 Tetrahedral MO Diagram e. Answer to Write orbital diagram for Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals.
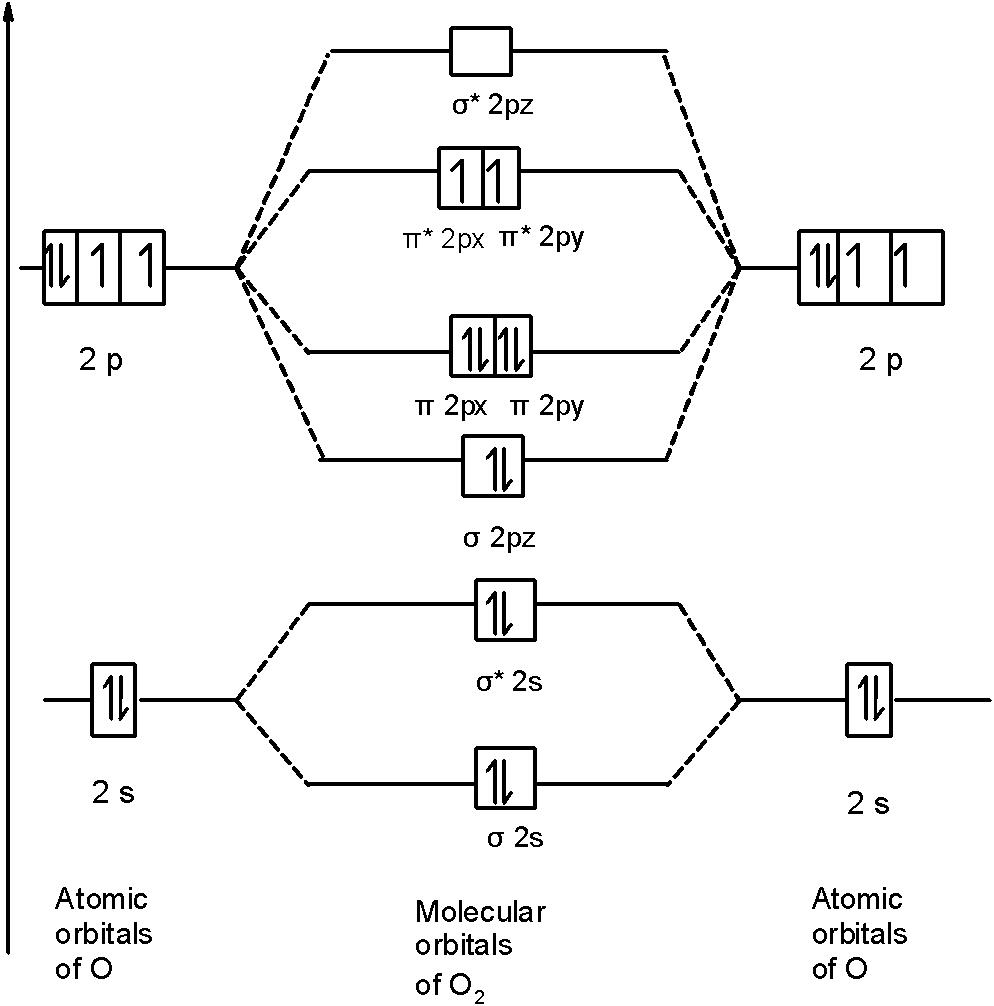
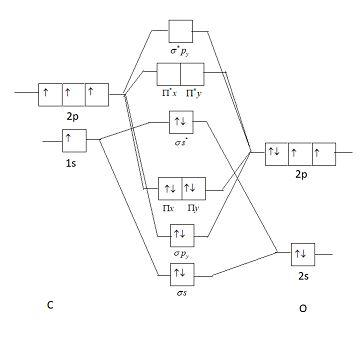
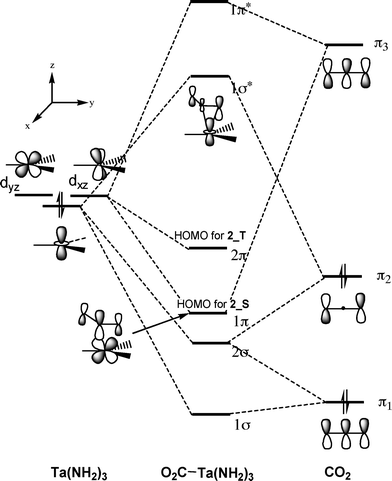
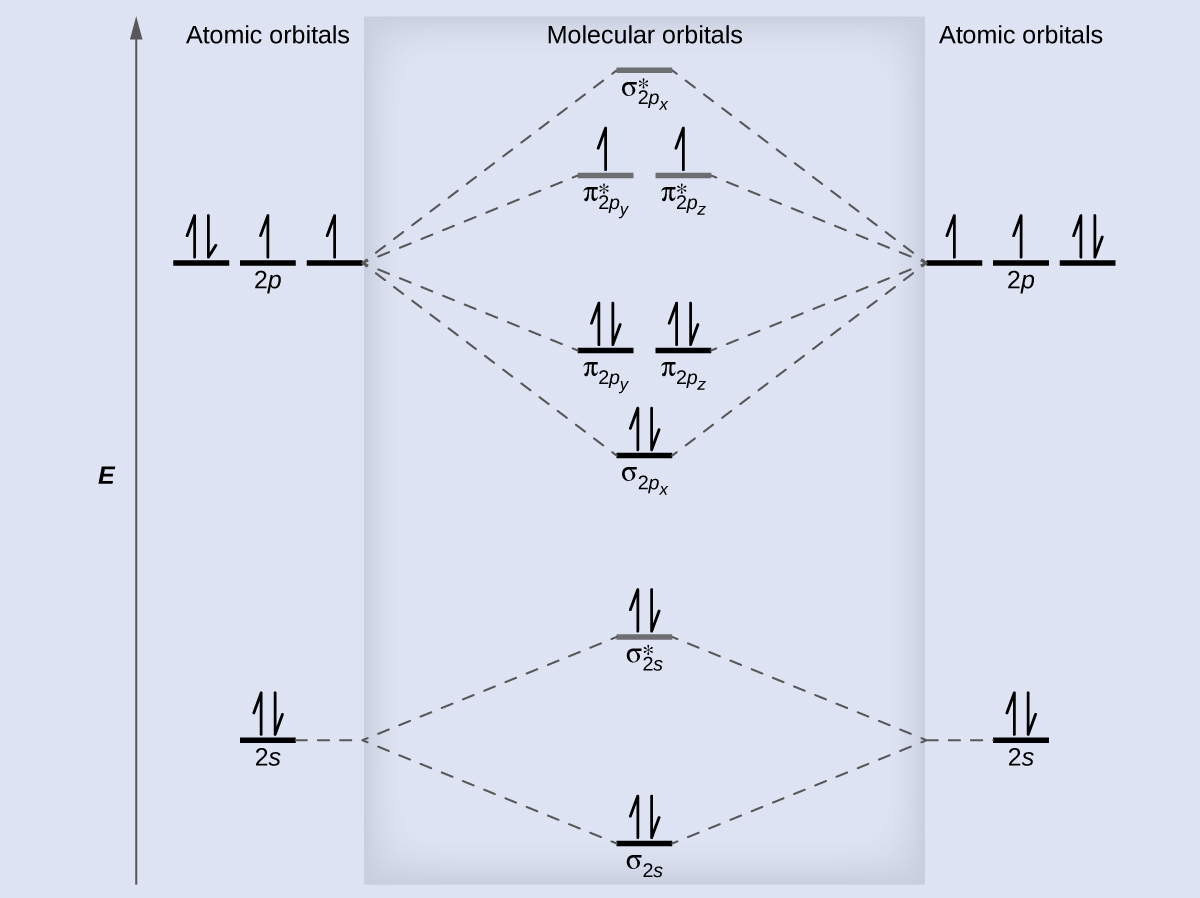
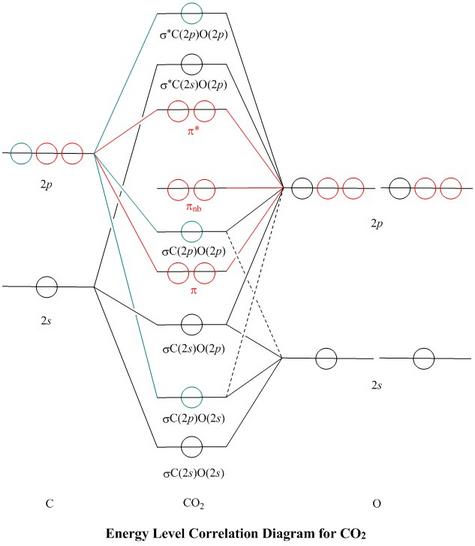
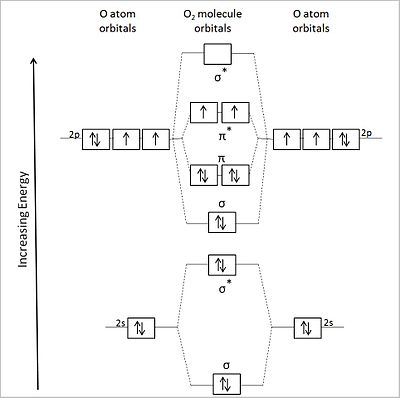
Now, these sp hybridized orbitals of the carbon atom overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to form 2 sigma bonds. As for the two remaining p electrons they will be used to form a pi bond. In carbon dioxide molecule, oxygen also hybridizes its orbitals to form three sp 2 hybrid orbitals. The p orbital in oxygen remains unchanged and is ... These orbitals were calculated at a low ab initio level (rhf/3–21g*) which can, however, show bond polarisation and fully delocalised molecular orbitals At the much higher level df/6-311g(2df) the calculated molecular orbital models look very similar, but the weakly antibonding MO σC(2 p )O(2 p ) appears below the bonding π MOs in the ... Apr 30, 2017 · In order to determine this, we should reference an MO diagram. We can see that the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) is fully occupied, but the next-highest MOs are the #pi^"*"# antibonding lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMOs). Keep this in mind. Mar 18, 2018 · "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is …
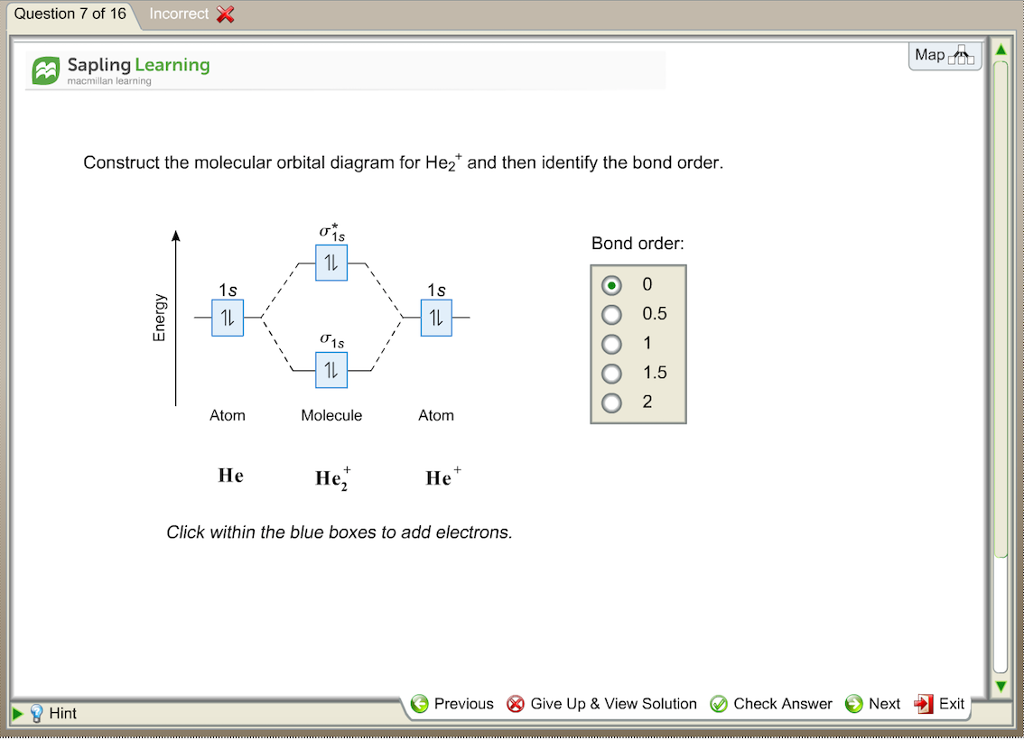
Nov 17, 2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet Oct 24, 2018 · H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. diagram for CO2 in Figure can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher ... A) The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular ... A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy than the original atomic orbitals.
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Nov 20, 2021 · The molecular orbital diagram of SO2 is attached below: A molecular orbital diagram gives us an idea about how the atomic orbitals of two different atoms can fuse and give rise to a new orbital. This further helps us to find out the bond order, bond length, and bond strength of any compound.
Whereas molecular geometry considers only the atoms. In absence of a lone pair, both the geometries are the same for any compound. Below is the 3D view of the geometry of the SO2 molecule. SO2 Geometry. Now let’s learn the last topic of this article, the molecular orbital diagram of SO2. SO2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.

Draw The Orbital Diagram For Carbon In Co 2 Showing How Many Carbon Atom Electrons Are In Each Orbital Study Com

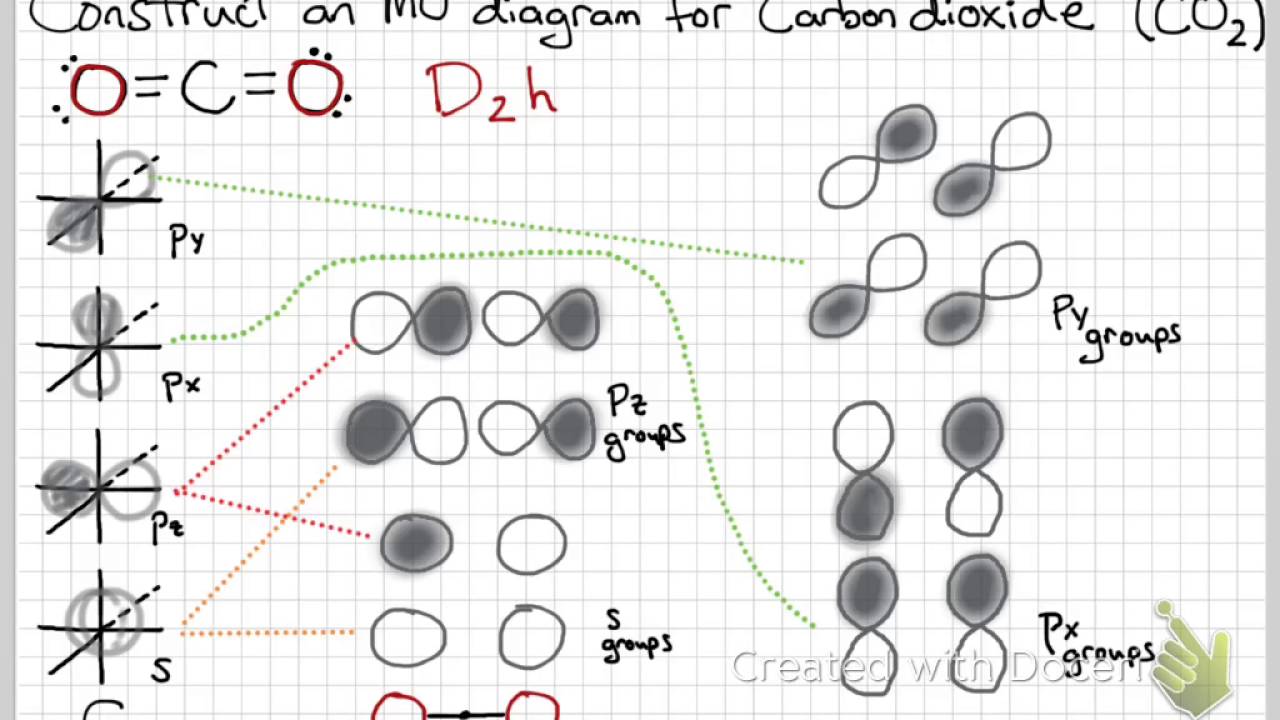
Molecular Orbital Diagram For Polyatomic Molecules Beh2 H2o Co2 Nh3 Sf6 Molecules Molecular Chemistry












Comments
Post a Comment