41 ch4 molecular orbital diagram
What happens to the molecular orbital diagram when a metal-ligand complex is oxidized? Oxidation removes an electron, e.g. you go from d8 metal to d7 metal. As consequence the antibonding orbital has an unpaired electron making the complex less stable (weaker M-L bond, since less pi-backdonation), but how does it change the gap between the metal MO and LUMO of ligand, as well as the gap between the metal MO and HOMO of the ligand? hey! I have a question: how do i draw a molecular orbital diagram for SO2? i only found examples for diatomic diagrams and im not sure how to do it if i have more then two atoms in the molecule.
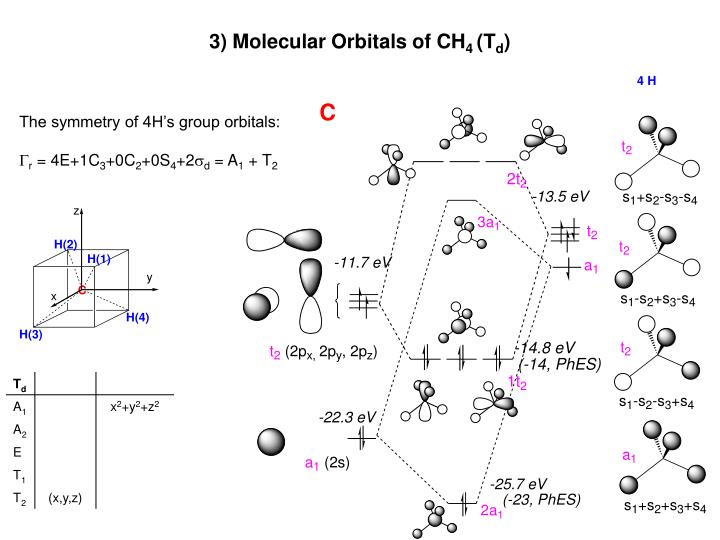
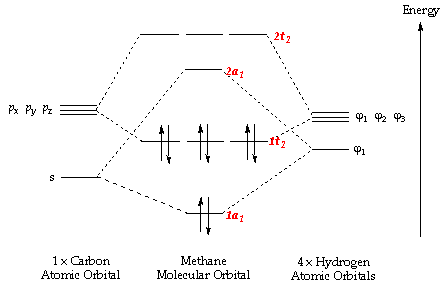
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Methane. Sigma and pi covalent bond models have proven to be valuable tools for describing the structure Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4.
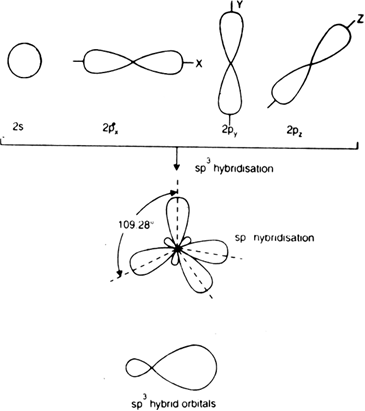
Ch4 molecular orbital diagram
Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. However, with more atoms, computers are required to calculate how the atomic orbitals combine. See three-dimensional drawings of the... The molecular orbital treatment of Hz @ can be applied to organic molecules such a s CH4 o r CH2=CH2in two different ways: F i r st, molecular orbitals can Our complete molecular diagram f o r butadiene i s now. Here the numbers below the carbons represent the calculated deviations from the... Say you have two 2s atomic orbitals, at different energies and the they form a bonding and an antibonding orbital. Say one has energy of -2ev and the other -3ev. How would I work out the energy of the new molecular orbitals? Do I add for the ab and subtract for the b?
Ch4 molecular orbital diagram. Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in Methane has Td symmetry, a cubic point group. The C3 axes in CH4 coincide with the C-H bonds. The energy level diagram of molecular orbitals of $\ce{CH4}$ is not clear to me. Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged molecules molecular-orbital-theory or ask your own question. Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. Shouldn’t you count the valence electrons for Be (which is 2) and subtract 1 because of the + sign? For O2, N2, NO, F2, etc, you count the number of valence electrons instead of the atomic number. Why is it that for Be, though, you look at the atomic number instead of the number of valence electrons it has? I apologize if this is a stupid question, but I appreciate any clarification on this
A molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H2+. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. https://i.imgur.com/GgRlFtK.jpg (Not homework) I am trying to improve by using past papers. Can someone explain how to solve these 3 questions?
I’ve been tasked with drawing rhe MO diagram for Sulfure Oxide and I’m not sure about the energies of the relatove orbitals. Since Oxygen is more electronegative I expect the 2s and 2p orbitals to have much lower energy than the 3s and 3p orbitals sulfur has. But the energy difference would be really high then. So I’m not sure what 2 orbitals combine to form the sigma 3s or sigma* 3s orbital. The difference in energy kevels confuses me as every example I’ve done has the same orbitals (2s,2p’s) c... Hi I am a PhD candidate and I need help making a frontier molecular orbital visualization diagram for the molecule pentacene. I only need 4 molecular orbital visualizations and they are HOMO, LUMO, HOMO-1, and LUMO +1. I am currently using chemissian with the imput from IQMOl but I am having difficulties getting a visual MO composition output. Can anyone help me? CH4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, and Hybridization. Methane or CH4 is a naturally occurring gas and relatively abundant on the Earth The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. Molecular Orbital Diagrams (Heteronuclear Diatomics) The molecular orbital diagram for the heteronuclear diatomic compound nitrogen monoxide, NO in virtually all molecules. The molecular orbital diagram for a slightly more complex compound, methane (CH4) is shown in Figure 9.44.
The Lowest-Energy Molecular Orbital (π1) Of The Butadiene Pi System Has Zero Nodes The Full Molecular Orbital Diagram For The Butadienyl System (n=4) The lowest energy molecular orbital will have p orbitals with phases in complete alignment with...
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
Lecture 7: ML6 molecular orbital energy diagrams incorporating p-acceptor and p-donor ligands. "Advanced Inorganic Chemistry"Ch 11, 16 "Chemistry of the Elements" Ch 19, 20-28. "A Guide to Modern Inorganic Chemistry" " Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds".
Procedure for Constructing Molecular Orbital Diagrams Based on Hybrid Orbitals. 1. Begin with the Lewis Molecular Orbital of Methane, CH4. As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4(Td), CH4(D4h) and Cyclopropane using...
Сияқты «орталық атомы» бар қарапайым полиатомдық молекулалар үшін метан (CH 4) немесе Көмір қышқыл газы (CO 2), MO диаграммасы орталық атоммен бірдей байланыстың бірін көрсетуі мүмкін. Басқа полиатомдық молекулалар үшін MO диаграммасы молекулаларға...
Molecular Orbital Theory. We know that atoms bond. That results in the diversity of matter around us. According to the Molecular Orbital Theory, individual atoms combine to form molecular orbitals. Thus the electrons of an atom are present in various atomic orbitals and are associated with several...
Ch4 Molecular Orbital Diagram ! View the latest news and breaking news today. News Post. Details: Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4 The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type.
molecular orbital theory ascribes the instability of He2 to the equal occupation of bonding and Density diagrams of the molecular orbitals for the LiH, CH, and HF molecules are illustrated in Fig. The bottom two diagrams illustrate the transformations of the 2py orbital on oxygen under the C2...
Four partial molecular orbital diagrams, showing only the molecular orbitals resulting from atomic p-orbitals, are shown below. Match each to the correct Jan 05, 2022 · Molecular Orbital Diagram of CH3Cl. The molecular orbital diagram is a pictorial representation of how chemical bonding is taking...
- Molecular orbital are formed by addition and subtraction of AO's. Æ Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO). - like hybrid AO's but the MO involves the whole details of the bonding diagram between the Lewis and MO treatments. 4. Perform the same analysis for BeH2, HF, BH3, and CH4.
A molecular orbital diagram showing both the bonding and anti-bonding. It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4(Td), CH4(D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
In molecular orbital theory, atomic orbitals on different atoms are mixed to produce bonds that can be localized between two atoms but are frequently Use the MO diagram in the figure to determine the number of bonding interactions, the number of antibonding and orbital type for each of the four MO's...
I know it’s like another theory as opposed to the localized electron model but I don’t really understand the whole bonding and antibonding principles and YouTube videos aren’t helping lol
I need to construct the molecular orbital diagram for the hypothetical species Li4, which has the following geometrical arrangement: https://preview.redd.it/npsjre5pch571.png?width=197&format=png&auto=webp&s=c2a7948c2efa04a975bee1db722838fae7482456 The first step is to identify the point symmetry group. In this particular case, we consider that there is only one axis of rotation of order four (actually, other symmetry elements can be observed, but this is a previous consi...
Basics of Frontier Molecular Orbital Theory. We can compare the placement of HOMO and LUMO levels relative to placement of C-H bonds. Hierarchy of Donor & Acceptor States Following trends are made on the basis of comparing the bonding and antibonding states for the molecule CH3-X where X...
Figure 19.14 Molecular orbital diagram for an octahedral complex of a first series transition metal (only a interactions are considered in Figure B A qualitative molecular orbital diagram for ferrocene. The subscripts g and u refer to the parity of the orbitals g (German gerade, even) indicates that the...
Molecular orbital theory is more powerful than valence-bond theory because the orbitals reflect the The bonding molecular orbital concentrates electrons in the region directly between the two nuclei. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms.
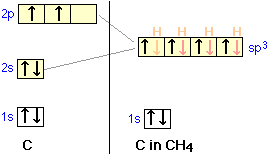
I’m a little confused on the connection between a molecules molecular orbital diagram and it’s individual atomic hybridization. Can anyone help me? Thank you
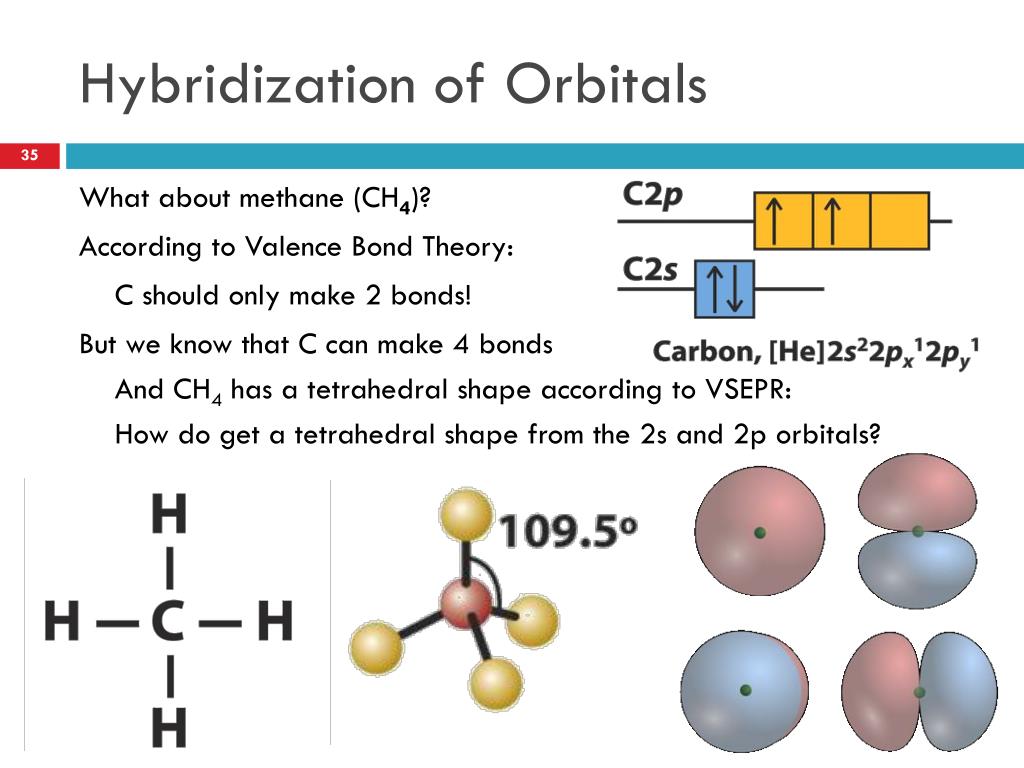
Methane is a pentatomic, tetrahedral molecule. It is formed by combination of one carbon atom with 4 hydrogen atoms. In the molecule of methane, the carbon...

DNA Genotyping and Sequencing. A technician at the Cancer Genomics Research Laboratory, part of the National Cancer Institute's Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics (DCEG), washes arrays used in genome-wide association studies (GWAS). These studies search the genome for small variations, called single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs, that occur more frequently in people with a particular disease than in people without the disease.
Molecular Orbital Model. A model that regards a molecule as a collection of nuclei and electrons, where the electrons are assumed to occupy orbitals much as they do in atoms, but having the orbitals extend over the entire molecule. In this model, the electrons are assumed to be delocalized rather...
I've been getting the hang of creating MO diagrams and I understand the very basics. My problem is in the 2p orbital's bonding section where sometimes the pi 2p section is lower energy than the sigma 2p section (i.e MO diagram for B2 diatomic molecule). I understand that the lower energy must be filled in first and so my question is, how do I know if the pi 2p is lower energy than sigma 2p?
Say you have two 2s atomic orbitals, at different energies and the they form a bonding and an antibonding orbital. Say one has energy of -2ev and the other -3ev. How would I work out the energy of the new molecular orbitals? Do I add for the ab and subtract for the b?
The molecular orbital treatment of Hz @ can be applied to organic molecules such a s CH4 o r CH2=CH2in two different ways: F i r st, molecular orbitals can Our complete molecular diagram f o r butadiene i s now. Here the numbers below the carbons represent the calculated deviations from the...
Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. However, with more atoms, computers are required to calculate how the atomic orbitals combine. See three-dimensional drawings of the...

Enteric Diseases Laboratory Branch (EDLB) Public Health scientist, who was using a whole genome DNA sequencer, in order to determine the “DNA fingerprint†of a specific bacterium. Photographer James Gathany

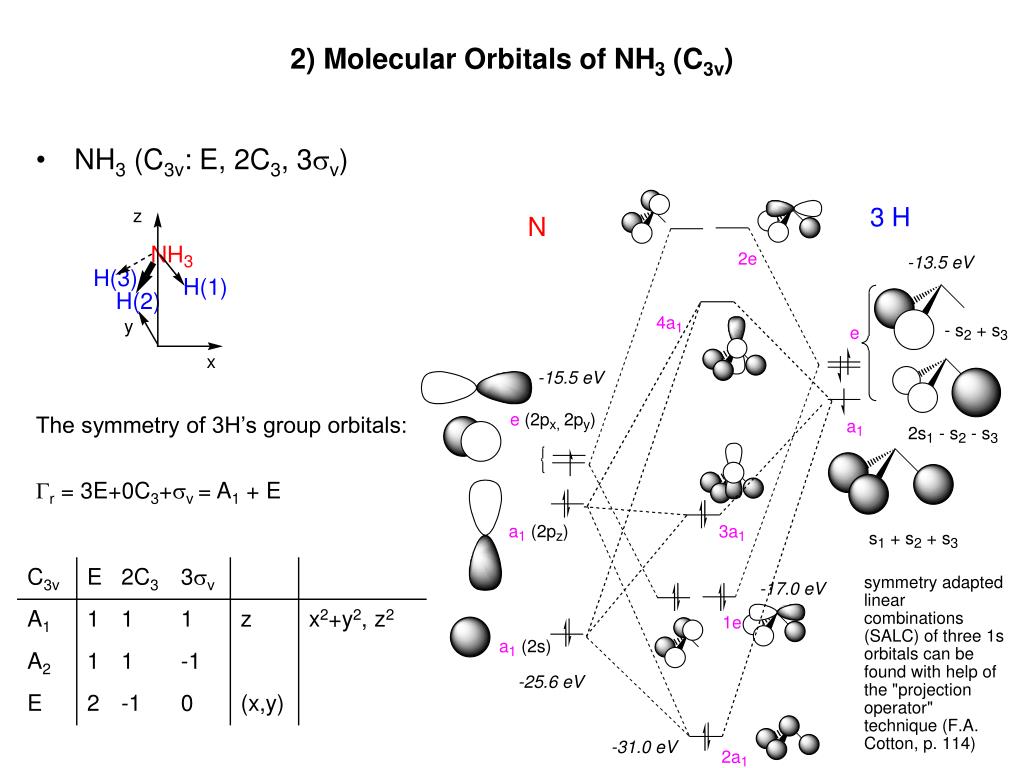



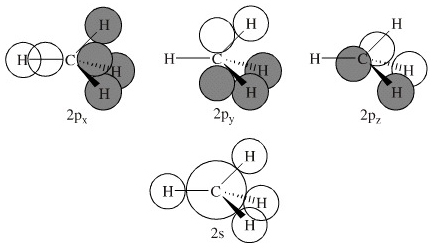
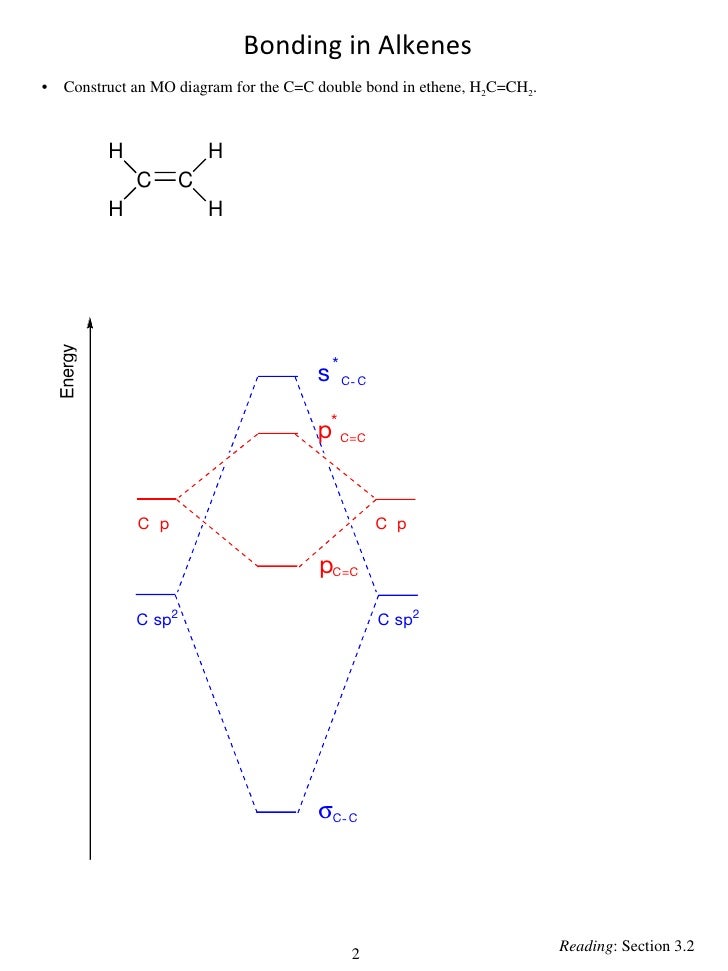




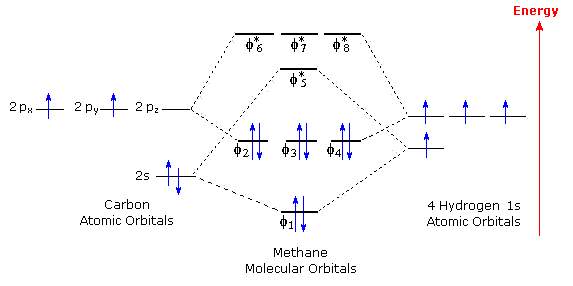




![[DIAGRAM] 6 Use The D2h Point Group To Construct The ...](https://image1.slideserve.com/2481541/the-mo-diagram-of-methane-n.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment